
How do you find the inverse of \[f\left( x \right) = \dfrac{{x - 3}}{{x + 2}}\] and graph \[f\] both and \[{f^{ - 1}}\] ?
Answer
541.8k+ views
Hint: Here in this question, we have to find the inverse of the given function y or \[f(x)\] . The inverse of a function is denoted by \[{f^{ - 1}}(x)\] . Here first we have to write the function in terms of x and then we have to solve for y using mathematics operations and simplification. We get the required solution and we have to draw a graph for both \[f\] and \[{f^{ - 1}}\] .
Complete step-by-step answer:
An inverse function or an anti-function is defined as a function, which can reverse into another function. In simple words, if any function “ \[f\] ” takes \[x\] to \[y\] then, the inverse of “ \[f\] ” will take \[y\] to \[x\] . If the function is denoted by ‘ \[f\] ’ or ‘ \[F\] ’, then the inverse function is denoted by \[{f^{ - 1}}\] or \[{F^{ - 1}}\] .
i.e., If \[f\] and \[g\] are inverse functions, then \[f\left( x \right) = y\] if and only if \[g\left( y \right) = x\] .
Consider the given function
\[f\left( x \right) = \dfrac{{x - 3}}{{x + 2}}\]
or
\[y = \dfrac{{x - 3}}{{x + 2}}\] --------(1)
switch the \[x\] 's and the \[y\] 's means replace \[x\] as \[y\] and \[y\] as \[x\] . i.e., \[f(x)\] is a substitute for " \[y\] ".
Equation (1) can be written as function of \[x\] i.e.,
\[ \Rightarrow x = \dfrac{{y - 3}}{{y + 2}}\] ------(2)
Now, to find the inverse we have to solve the equation (2) for \[y\] .
Multiply both side by \[\left( {y + 2} \right)\] , then
\[ \Rightarrow x\left( {y + 2} \right) = y - 3\]
Multiply \[x\] into the parenthesis in LHS
\[ \Rightarrow xy + 2x = y - 3\]
On rearranging
\[ \Rightarrow y - xy = 2x + 3\]
Take \[y\] as common in LHS, then
\[ \Rightarrow y\left( {1 - x} \right) = 2x + 3\]
Divide both side by \[\left( {1 - x} \right)\]
\[ \Rightarrow y = \dfrac{{2x + 3}}{{1 - x}}\]
Or
\[ \Rightarrow {f^{ - 1}}\left( x \right) = \dfrac{{2x + 3}}{{1 - x}}\]
Hence, the inverse of a function \[f\left( x \right) = \dfrac{{x - 3}}{{x + 2}}\] is \[{f^{ - 1}}\left( x \right) = \dfrac{{2x + 3}}{{1 - x}}\] .
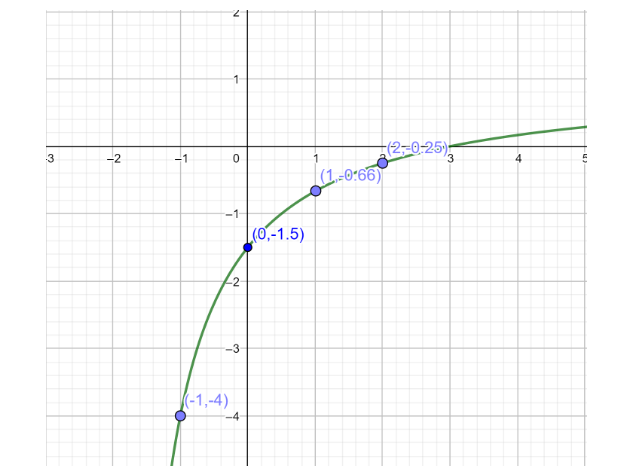
To plot graph of function \[f\left( x \right) = \dfrac{{x - 3}}{{x + 2}}\] by giving the \[x\] values as 0, 1, 2… simultaneously we get the value of \[f\left( x \right)\] follow the below table
Here is the graph of \[f\left( x \right) = \dfrac{{x - 3}}{{x + 2}}\] .
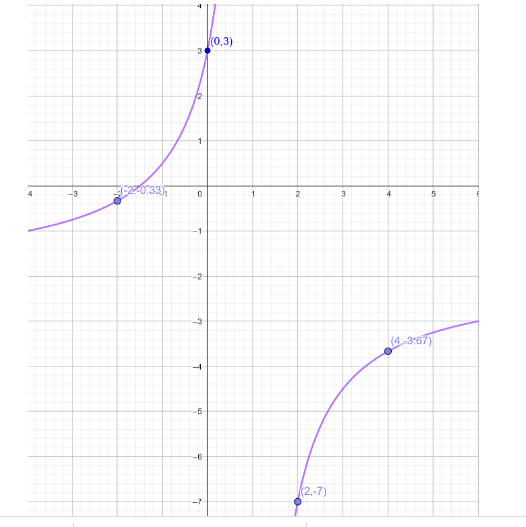
To plot graph of inverse function \[{f^{ - 1}}\left( x \right) = \dfrac{{2x + 3}}{{1 - x}}\] by giving the \[x\] values as 0, 1, 2… simultaneously we get the value of \[{f^{ - 1}}\left( x \right)\] follow the below table
Here is the graph of the inverse function \[{f^{ - 1}}\left( x \right) = g(x) = \dfrac{{2x + 3}}{{1 - x}}\] .
Note: We must know about the simple arithmetic operations. To find the inverse we swap the y variable into x and simplify the equation and determine the value for y. Since the given question contains a fraction of simplification we obtain the result. While shifting the terms we must take care of signs.
Complete step-by-step answer:
An inverse function or an anti-function is defined as a function, which can reverse into another function. In simple words, if any function “ \[f\] ” takes \[x\] to \[y\] then, the inverse of “ \[f\] ” will take \[y\] to \[x\] . If the function is denoted by ‘ \[f\] ’ or ‘ \[F\] ’, then the inverse function is denoted by \[{f^{ - 1}}\] or \[{F^{ - 1}}\] .
i.e., If \[f\] and \[g\] are inverse functions, then \[f\left( x \right) = y\] if and only if \[g\left( y \right) = x\] .
Consider the given function
\[f\left( x \right) = \dfrac{{x - 3}}{{x + 2}}\]
or
\[y = \dfrac{{x - 3}}{{x + 2}}\] --------(1)
switch the \[x\] 's and the \[y\] 's means replace \[x\] as \[y\] and \[y\] as \[x\] . i.e., \[f(x)\] is a substitute for " \[y\] ".
Equation (1) can be written as function of \[x\] i.e.,
\[ \Rightarrow x = \dfrac{{y - 3}}{{y + 2}}\] ------(2)
Now, to find the inverse we have to solve the equation (2) for \[y\] .
Multiply both side by \[\left( {y + 2} \right)\] , then
\[ \Rightarrow x\left( {y + 2} \right) = y - 3\]
Multiply \[x\] into the parenthesis in LHS
\[ \Rightarrow xy + 2x = y - 3\]
On rearranging
\[ \Rightarrow y - xy = 2x + 3\]
Take \[y\] as common in LHS, then
\[ \Rightarrow y\left( {1 - x} \right) = 2x + 3\]
Divide both side by \[\left( {1 - x} \right)\]
\[ \Rightarrow y = \dfrac{{2x + 3}}{{1 - x}}\]
Or
\[ \Rightarrow {f^{ - 1}}\left( x \right) = \dfrac{{2x + 3}}{{1 - x}}\]
Hence, the inverse of a function \[f\left( x \right) = \dfrac{{x - 3}}{{x + 2}}\] is \[{f^{ - 1}}\left( x \right) = \dfrac{{2x + 3}}{{1 - x}}\] .
To plot graph of function \[f\left( x \right) = \dfrac{{x - 3}}{{x + 2}}\] by giving the \[x\] values as 0, 1, 2… simultaneously we get the value of \[f\left( x \right)\] follow the below table
| \[x\] | \[ - 1\] | \[0\] | \[1\] | \[2\] |
| \[f\left( x \right)\] | \[ - 4\] | \[ - \dfrac{3}{2}\] | \[ - \dfrac{2}{3}\] | \[ - \dfrac{1}{4}\] |
Here is the graph of \[f\left( x \right) = \dfrac{{x - 3}}{{x + 2}}\] .

To plot graph of inverse function \[{f^{ - 1}}\left( x \right) = \dfrac{{2x + 3}}{{1 - x}}\] by giving the \[x\] values as 0, 1, 2… simultaneously we get the value of \[{f^{ - 1}}\left( x \right)\] follow the below table
| \[x\] | \[ - 2\] | \[0\] | \[2\] | \[4\] |
| \[{f^{ - 1}}\left( x \right) = g\left( x \right)\] | \[ - \dfrac{1}{3}\] | \[3\] | \[ - 7\] | \[ - \dfrac{{11}}{3}\] |
Here is the graph of the inverse function \[{f^{ - 1}}\left( x \right) = g(x) = \dfrac{{2x + 3}}{{1 - x}}\] .

Note: We must know about the simple arithmetic operations. To find the inverse we swap the y variable into x and simplify the equation and determine the value for y. Since the given question contains a fraction of simplification we obtain the result. While shifting the terms we must take care of signs.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 9 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 9 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Trending doubts
Difference Between Plant Cell and Animal Cell

Fill the blanks with the suitable prepositions 1 The class 9 english CBSE

Who is eligible for RTE class 9 social science CBSE

Which places in India experience sunrise first and class 9 social science CBSE

What is pollution? How many types of pollution? Define it

Name 10 Living and Non living things class 9 biology CBSE




