
How do you find the inverse of an exponential function?
Answer
556.5k+ views
Hint: Here, we need to find the inverse of an exponential function. We will write the exponential function and we will assume that it is equal to \[y\]. Then, we will use the rule of logarithms to simplify the equation for the particular variable \[x\]. Then, we will interchange the variables to find the required inverse of the exponential function.
Complete step-by-step answer:
The exponential function is given by \[f\left( x \right) = a{b^x}\], where \[b\] is a positive real number, and \[b \ne 1\].
Let \[f\left( x \right)\] be equal to \[y\].
Therefore, we get
\[y = a{b^x}\]
We will use the rule of logarithms to simplify the equation for the particular variable \[x\].
First, we will isolate the exponential expression.
Dividing both sides of the equation by \[a\], we get
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac{y}{a} = {b^x}\]
If an equation is of the form \[x = {b^y}\], it can be written using logarithms as \[y = {\log _b}x\], where \[x > 0\], \[b > 0\] and \[b\] is not equal to 1.
Therefore, since \[\dfrac{y}{a} = {b^x}\], we get the equation
\[x = {\log _b}\left( {\dfrac{y}{a}} \right)\]
Now, we will interchange the variables to find the value of the inverse of the exponential function.
Interchanging the variable \[x\] and variable \[y\], we get
\[ \Rightarrow y = {\log _b}\left( {\dfrac{x}{a}} \right)\]
This is the value of the inverse of \[f\left( x \right)\].
Therefore, we get
\[ \Rightarrow {f^{ - 1}}\left( x \right) = {\log _b}\left( {\dfrac{x}{a}} \right)\]
Therefore, the inverse of an exponential function \[a{b^x}\] is given by the expression \[{\log _b}\left( {\dfrac{x}{a}} \right)\].
Note: We can verify the inverse by drawing the graph of an exponential function and its inverse.
Let the exponential function be \[y = 2 \times {3^x}\].
We will draw the graphs of \[y = 2 \times {3^x}\] and its inverse, that is \[y = {\log _3}\left( {\dfrac{x}{2}} \right)\].
If the graphs are symmetrical along the line \[x = y\], then the two functions are the inverse of each other.
Drawing the graphs, we get
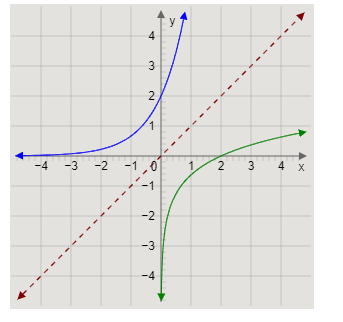
The red line is the graph of the equation \[x = y\], the blue curve is the graph of the equation \[y = 2 \times {3^x}\], and the green curve is the graph of the equation \[y = {\log _3}\left( {\dfrac{x}{2}} \right)\].
We can observe that the graphs are symmetrical along the line \[x = y\].
Therefore, we have verified that \[y = 2 \times {3^x}\] is the inverse of \[y = {\log _3}\left( {\dfrac{x}{2}} \right)\], and \[y = {\log _3}\left( {\dfrac{x}{2}} \right)\] is the inverse of \[y = 2 \times {3^x}\].
Complete step-by-step answer:
The exponential function is given by \[f\left( x \right) = a{b^x}\], where \[b\] is a positive real number, and \[b \ne 1\].
Let \[f\left( x \right)\] be equal to \[y\].
Therefore, we get
\[y = a{b^x}\]
We will use the rule of logarithms to simplify the equation for the particular variable \[x\].
First, we will isolate the exponential expression.
Dividing both sides of the equation by \[a\], we get
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac{y}{a} = {b^x}\]
If an equation is of the form \[x = {b^y}\], it can be written using logarithms as \[y = {\log _b}x\], where \[x > 0\], \[b > 0\] and \[b\] is not equal to 1.
Therefore, since \[\dfrac{y}{a} = {b^x}\], we get the equation
\[x = {\log _b}\left( {\dfrac{y}{a}} \right)\]
Now, we will interchange the variables to find the value of the inverse of the exponential function.
Interchanging the variable \[x\] and variable \[y\], we get
\[ \Rightarrow y = {\log _b}\left( {\dfrac{x}{a}} \right)\]
This is the value of the inverse of \[f\left( x \right)\].
Therefore, we get
\[ \Rightarrow {f^{ - 1}}\left( x \right) = {\log _b}\left( {\dfrac{x}{a}} \right)\]
Therefore, the inverse of an exponential function \[a{b^x}\] is given by the expression \[{\log _b}\left( {\dfrac{x}{a}} \right)\].
Note: We can verify the inverse by drawing the graph of an exponential function and its inverse.
Let the exponential function be \[y = 2 \times {3^x}\].
We will draw the graphs of \[y = 2 \times {3^x}\] and its inverse, that is \[y = {\log _3}\left( {\dfrac{x}{2}} \right)\].
If the graphs are symmetrical along the line \[x = y\], then the two functions are the inverse of each other.
Drawing the graphs, we get

The red line is the graph of the equation \[x = y\], the blue curve is the graph of the equation \[y = 2 \times {3^x}\], and the green curve is the graph of the equation \[y = {\log _3}\left( {\dfrac{x}{2}} \right)\].
We can observe that the graphs are symmetrical along the line \[x = y\].
Therefore, we have verified that \[y = 2 \times {3^x}\] is the inverse of \[y = {\log _3}\left( {\dfrac{x}{2}} \right)\], and \[y = {\log _3}\left( {\dfrac{x}{2}} \right)\] is the inverse of \[y = 2 \times {3^x}\].
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




