
How do you find the inflection point of a logarithmic function?
Answer
567.3k+ views
Hint: For a function, an inflection point is a point where the curve changes its shape from concave up to concave down. We can find an inflection point by checking whether its slope at a point has the highest value than any other point. That point is called an inflection point.
Complete step by step answer:
As per the given question, we have to find the inflection points of the logarithmic function.
Let the logarithmic function be \[\ln x\].
For finding the inflection point of a logarithmic function, we need to take the derivative of the logarithmic function.
We know that the derivative of \[\ln x\] is \[\dfrac{1}{x}\].
Let \[y=\ln x\].
So, the first derivative which is denoted as \[{y}'\] will be\[{y}'=\dfrac{1}{x}\].
we can decide the inflection points based on the second derivative of the function which is given by \[{y}''=\dfrac{d}{dx}({y}')\].
Here, we only require the power rule \[\dfrac{d}{dx}(a{{x}^{n}})=(na){{x}^{n-1}}\].
So, the second derivative which is denoted as \[{y}''\] is \[{y}''=\dfrac{-1}{{{x}^{2}}}\].
If \[{y}''=0\] then it is the inflection point. Here, \[{y}''=0\] for \[x=\pm \infty \]. This implies \[\ln x\] do not have any inflection point.
This implies that \[\ln x\] is a strictly increasing function.
The graph of \[y=\ln x\] is as shown below:
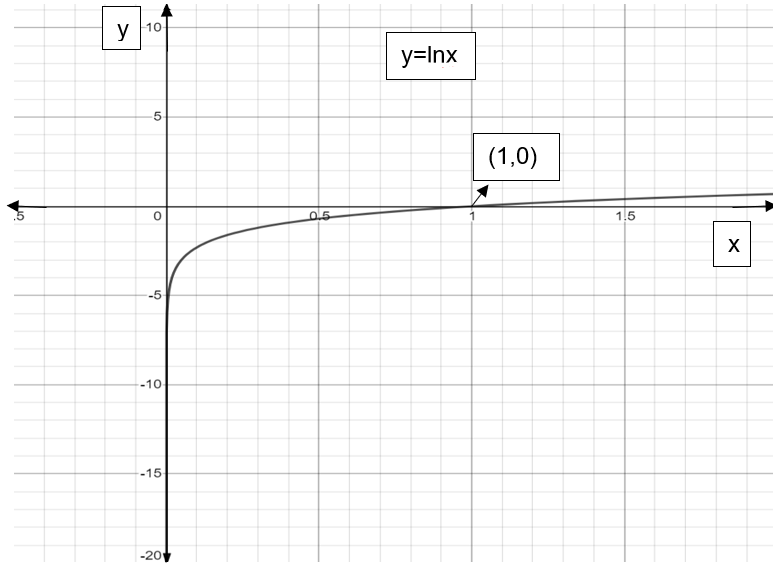
Therefore, in this way, we can find the inflection point of any logarithmic function.
Note:
In order to solve these types of problems, we must have enough knowledge about inflection points. We need to know the derivation methods to find the derivative of a function. We should avoid calculation mistakes to get the correct solution. While drawing graphs plot the points wisely to avoid any confusion.
Complete step by step answer:
As per the given question, we have to find the inflection points of the logarithmic function.
Let the logarithmic function be \[\ln x\].
For finding the inflection point of a logarithmic function, we need to take the derivative of the logarithmic function.
We know that the derivative of \[\ln x\] is \[\dfrac{1}{x}\].
Let \[y=\ln x\].
So, the first derivative which is denoted as \[{y}'\] will be\[{y}'=\dfrac{1}{x}\].
we can decide the inflection points based on the second derivative of the function which is given by \[{y}''=\dfrac{d}{dx}({y}')\].
Here, we only require the power rule \[\dfrac{d}{dx}(a{{x}^{n}})=(na){{x}^{n-1}}\].
So, the second derivative which is denoted as \[{y}''\] is \[{y}''=\dfrac{-1}{{{x}^{2}}}\].
If \[{y}''=0\] then it is the inflection point. Here, \[{y}''=0\] for \[x=\pm \infty \]. This implies \[\ln x\] do not have any inflection point.
This implies that \[\ln x\] is a strictly increasing function.
The graph of \[y=\ln x\] is as shown below:

Therefore, in this way, we can find the inflection point of any logarithmic function.
Note:
In order to solve these types of problems, we must have enough knowledge about inflection points. We need to know the derivation methods to find the derivative of a function. We should avoid calculation mistakes to get the correct solution. While drawing graphs plot the points wisely to avoid any confusion.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 10 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
A boat goes 24 km upstream and 28 km downstream in class 10 maths CBSE

State and explain Ohms law class 10 physics CBSE

Write a letter to the editor of a newspaper explaining class 10 english CBSE

Distinguish between soap and detergent class 10 chemistry CBSE

a Why did Mendel choose pea plants for his experiments class 10 biology CBSE

What is a "free hit" awarded for in limited-overs cricket?




