
How to find the hybridization of chlorine in chlorate ions?
Answer
493.2k+ views
Hint: When two atomic orbitals combine to form hybrid orbital in a molecule then redistribution of the energy of orbitals of individual atoms produces orbitals of equivalent energy and the new orbital formed are known as hybrid orbitals and the phenomenon is known as hybridization.
Complete answer:
According to valence bond theory the metal atom or ion in presence of ligands can use its outer orbitals for hybridization which yield a set of equivalent orbitals of definite geometry like octahedral, tetrahedral, square planar and so on. These hybrid orbitals are allowed to overlap with ligand orbitals which can easily donate electron pairs for bonding.
Chlorate ion is represented by the chemical formula \[Cl{{O}_{3}}^{-}\] in which three oxygen atoms will have 1 unpaired orbital in which chlorine have unoccupied d orbitals which will be used for bonding. Here the chlorine form two double bonds with oxygen and one single bond with ${{O}^{-}}$and one lone pair is present on chlorines which show some distortion in the arrangement.
Structure of chlorate ion is given below:
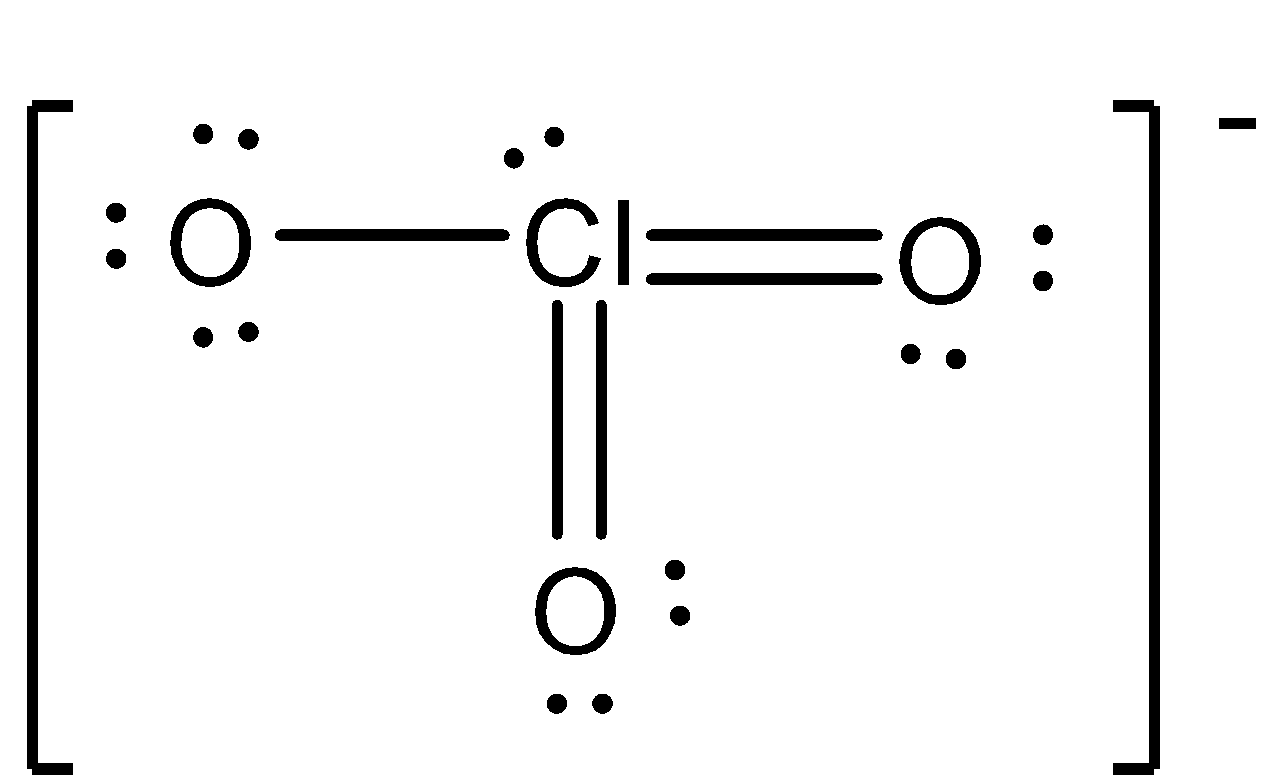
Hence from this we can conclude that the hybridization of the atom can be calculated by the formula:
½ (Number of valence electron in central atom + monovalent atom attached to central metal atom + anionic charge-cationic charge)
On solving this we get the value as 4 and for 4 the hybridization is $s{{p}^{3}}$.
Hybridization of chlorine in chlorate ions will be $s{{p}^{3}}$.
Note:
The shape and the hybridization of any compound can be concluded with the help of a theory given by the German Physicists called valence bond theory. This theory explains the electronic structure of the molecule formed by the overlapping of atomic orbitals.
Complete answer:
According to valence bond theory the metal atom or ion in presence of ligands can use its outer orbitals for hybridization which yield a set of equivalent orbitals of definite geometry like octahedral, tetrahedral, square planar and so on. These hybrid orbitals are allowed to overlap with ligand orbitals which can easily donate electron pairs for bonding.
Chlorate ion is represented by the chemical formula \[Cl{{O}_{3}}^{-}\] in which three oxygen atoms will have 1 unpaired orbital in which chlorine have unoccupied d orbitals which will be used for bonding. Here the chlorine form two double bonds with oxygen and one single bond with ${{O}^{-}}$and one lone pair is present on chlorines which show some distortion in the arrangement.
Structure of chlorate ion is given below:

Hence from this we can conclude that the hybridization of the atom can be calculated by the formula:
½ (Number of valence electron in central atom + monovalent atom attached to central metal atom + anionic charge-cationic charge)
On solving this we get the value as 4 and for 4 the hybridization is $s{{p}^{3}}$.
Hybridization of chlorine in chlorate ions will be $s{{p}^{3}}$.
Note:
The shape and the hybridization of any compound can be concluded with the help of a theory given by the German Physicists called valence bond theory. This theory explains the electronic structure of the molecule formed by the overlapping of atomic orbitals.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




