
How do you find the general solution of \[\dfrac{dy}{dx} = \dfrac{x}{y}\]?
Answer
478.2k+ views
Hint:In this question, we need to find the general solution of the given expression \[\dfrac{dy}{dx} = \dfrac{x}{y}\]. We can find the general solution of the differential equation by using separation of variable methods. First by using the separation of variables method, we can separate the derivative term and variable term. Then we need to use the reverse power rule . On further integrating, we can find the integral of the given expression.
Formula used:
Reverse power rule: Reverse power rule is used to integrate the expression which is in the form of \[x^{n}\]
\[\int x^{n}{dx} = \dfrac{x^{n + 1}}{n + 1} + c\]
Where \[c\] is the constant of integration.
This rule is not applicable when \[n = - 1\] .
Complete step by step answer:
Given , \[\dfrac{dy}{dx} = \dfrac{x}{y}\]
The degree and order of the given differential equation is one. Thus we can use the separation of variables method to find the general solution of the given equation.
In the separation of variables method, we need to separate the derivative term and variable term to another side of equality.
We have \[\dfrac{dy}{dx} = \dfrac{x}{y}\]
On cross multiplying,
We get,
\[\Rightarrow \ y\ dy = x\ dx\]
On integrating both sides,
We get,
\[\Rightarrow \ \int y\ dy = \int x\ dx\]
Now by using reverse power rule,
\[\Rightarrow \dfrac{y^{2}}{2} = \dfrac{x^{2}}{2} + \ c\]
Where \[c\] is the constant of integration .
On simplifying,
We get,
\[\Rightarrow \dfrac{y^{2}}{2} = \dfrac{x^{2} + 2c}{2}\]
Now on multiplying both sides by \[2\] ,
We get,
\[\Rightarrow \ y^{2} = x^{2} + 2c\]
On rearranging the terms,
We get,
\[\Rightarrow \ y^{2} – x^{2} = 2c\] which is can be written as \[y^{2} – x^{2} = C\] where \[C\] is the constant which is equal to \[2c\] .
Now depending on the value of \[C\] , whether it is positive , negative or zero, we get a hyperbola open to x axis, also open to y axis or a pair of straight lines through the origin. Thus the solution of the equation \[\dfrac{dy}{dx} = \dfrac{x}{y}\] are the members of the family of the cure. All the curves are hyperbole which is of the form of \[x^{2} – y^{2} = C\] . For the different values of \[C\], the equation of hyperbola may give two intersecting lines.Also if \[C = 0\] , the hyperbolic equation \[y^{2} – x^{2} = \ 0\] gives two intersecting straight lines.Now the equation is \[y^{2} – x^{2} = 0\]. On adding \[x^{2}\] on both sides,
We get,
\[\Rightarrow \ y^{2} = x^{2}\]
On taking square root on both sides,
We get,
\[\Rightarrow \ y = \pm x\]
That is \[y = x\] and \[y = - x\]
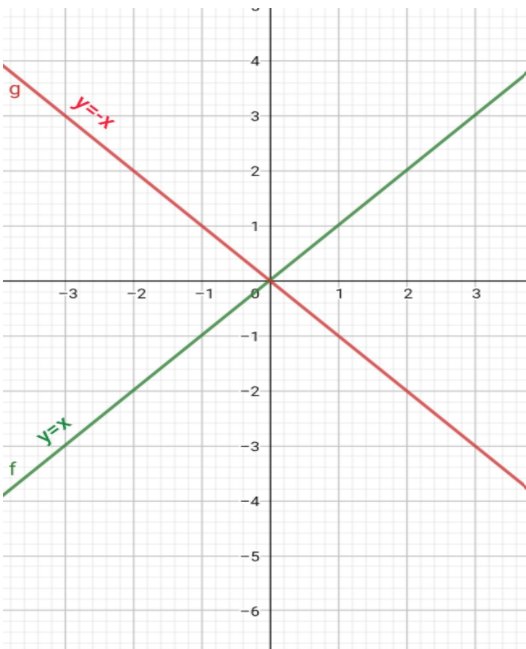
Thus we get the general solution of the \[\dfrac{dy}{dx} = \dfrac{x}{y}\] is \[y = \pm x\].
Note:The concept used in this question is integration method, that is integration by separation of variable methods and reverse power rule . Since this is an indefinite integral we have to add an arbitrary constant ‘\[c\]’. \[c\] is called the constant of integration.Mathematically , the order of the derivative can be found without actually solving the given question. The order of the equation is nothing but the number of constants in the equation. We must be careful in choosing the methods to solve the problem, Choosing the wrong method may lead to the wrong calculation.
Formula used:
Reverse power rule: Reverse power rule is used to integrate the expression which is in the form of \[x^{n}\]
\[\int x^{n}{dx} = \dfrac{x^{n + 1}}{n + 1} + c\]
Where \[c\] is the constant of integration.
This rule is not applicable when \[n = - 1\] .
Complete step by step answer:
Given , \[\dfrac{dy}{dx} = \dfrac{x}{y}\]
The degree and order of the given differential equation is one. Thus we can use the separation of variables method to find the general solution of the given equation.
In the separation of variables method, we need to separate the derivative term and variable term to another side of equality.
We have \[\dfrac{dy}{dx} = \dfrac{x}{y}\]
On cross multiplying,
We get,
\[\Rightarrow \ y\ dy = x\ dx\]
On integrating both sides,
We get,
\[\Rightarrow \ \int y\ dy = \int x\ dx\]
Now by using reverse power rule,
\[\Rightarrow \dfrac{y^{2}}{2} = \dfrac{x^{2}}{2} + \ c\]
Where \[c\] is the constant of integration .
On simplifying,
We get,
\[\Rightarrow \dfrac{y^{2}}{2} = \dfrac{x^{2} + 2c}{2}\]
Now on multiplying both sides by \[2\] ,
We get,
\[\Rightarrow \ y^{2} = x^{2} + 2c\]
On rearranging the terms,
We get,
\[\Rightarrow \ y^{2} – x^{2} = 2c\] which is can be written as \[y^{2} – x^{2} = C\] where \[C\] is the constant which is equal to \[2c\] .
Now depending on the value of \[C\] , whether it is positive , negative or zero, we get a hyperbola open to x axis, also open to y axis or a pair of straight lines through the origin. Thus the solution of the equation \[\dfrac{dy}{dx} = \dfrac{x}{y}\] are the members of the family of the cure. All the curves are hyperbole which is of the form of \[x^{2} – y^{2} = C\] . For the different values of \[C\], the equation of hyperbola may give two intersecting lines.Also if \[C = 0\] , the hyperbolic equation \[y^{2} – x^{2} = \ 0\] gives two intersecting straight lines.Now the equation is \[y^{2} – x^{2} = 0\]. On adding \[x^{2}\] on both sides,
We get,
\[\Rightarrow \ y^{2} = x^{2}\]
On taking square root on both sides,
We get,
\[\Rightarrow \ y = \pm x\]
That is \[y = x\] and \[y = - x\]

Thus we get the general solution of the \[\dfrac{dy}{dx} = \dfrac{x}{y}\] is \[y = \pm x\].
Note:The concept used in this question is integration method, that is integration by separation of variable methods and reverse power rule . Since this is an indefinite integral we have to add an arbitrary constant ‘\[c\]’. \[c\] is called the constant of integration.Mathematically , the order of the derivative can be found without actually solving the given question. The order of the equation is nothing but the number of constants in the equation. We must be careful in choosing the methods to solve the problem, Choosing the wrong method may lead to the wrong calculation.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE

RNA and DNA are chiral molecules their chirality is class 12 chemistry CBSE




