
Find the exact value of $ \cos \left( -\dfrac{5\pi }{4} \right) $ .
Answer
594.9k+ views
Hint: We have to find the value of $ \cos \left( -\dfrac{5\pi }{4} \right) $ . We know that, $ \cos \left( -\theta \right)=\cos \theta $ . Now, $ \cos \left( -\dfrac{5\pi }{4} \right) $ is also in the form of $ \cos \left( -\theta \right) $ so we can use this trigonometric relation $ \cos \left( -\theta \right)=\cos \theta $ . We know that $ \dfrac{5\pi }{4} $ lies in the third quadrant in which the value of cosine is negative so whatever the value of $ \cos \left( -\dfrac{5\pi }{4} \right) $ , it comes with a negative sign. There is a trigonometric property which states that $ \cos \left( \pi +\theta \right)=-\cos \theta $ so we can write $ \cos \left( \dfrac{5\pi }{4} \right) $ as $ \cos \left( \pi +\dfrac{\pi }{4} \right) $ and then we can use this trigonometric property. Then substitute the value of $ \cos \left( \dfrac{\pi }{4} \right) $ to get the exact value.
Complete step-by-step answer:
We are asked to find the value of $ \cos \left( -\dfrac{5\pi }{4} \right) $ .
We know that,
$ \cos \left( -\theta \right)=\cos \theta $
As in the above problem, the angle at which we have to find the cosine is also negative so we can use this relation in the given $ \cos \left( -\dfrac{5\pi }{4} \right) $ .
$ \cos \left( -\dfrac{5\pi }{4} \right)=\cos \left( \dfrac{5\pi }{4} \right) $
So, we have reduced the given expression in cosine to:
$ \cos \left( \dfrac{5\pi }{4} \right) $
Now, the angle given above is $ \dfrac{5\pi }{4} $ and we can also write this angle as:
$ \dfrac{5\pi }{4}=\pi +\dfrac{\pi }{4} $
Substituting the above angle in $ \cos \left( \dfrac{5\pi }{4} \right) $ we get,
$ \cos \left( \dfrac{5\pi }{4} \right)=\cos \left( \pi +\dfrac{\pi }{4} \right) $
As the above angle lies in the third quadrant so the value of cosine in the third quadrant is negative.
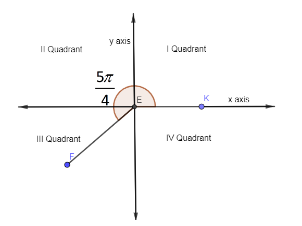
In the below figure, we have shown the four quadrants and have also shown the angle $ \dfrac{5\pi }{4} $ lies in the III Quadrant from the positive x axis.
We know that,
$ \cos \left( \pi +\theta \right)=-\cos \theta $
Using the above relation in $ \cos \left( \pi +\dfrac{\pi }{4} \right) $ we get,
$ \cos \left( \pi +\dfrac{\pi }{4} \right)=-\cos \left( \dfrac{\pi }{4} \right) $ …………. Eq. (1)
From the trigonometric ratios we know that,
$ \cos \left( \dfrac{\pi }{4} \right)=\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{2}} $
Substituting the above value in eq. (1) we get,
$ \cos \left( \pi +\dfrac{\pi }{4} \right)=-\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{2}} $
From the above calculations, we have got the value of $ \cos \left( -\dfrac{5\pi }{4} \right) $ as $ -\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{2}} $ .
Note: The plausible problem that could happen is that instead of writing $ \cos \left( \dfrac{5\pi }{4} \right) $ as $ \cos \left( \pi +\dfrac{\pi }{4} \right) $ you might make a mistake of perceiving the angle $ \dfrac{5\pi }{4} $ as $ \dfrac{3\pi }{4} $ and write $ \cos \left( \dfrac{5\pi }{4} \right) $ as $ \cos \left( \pi -\dfrac{\pi }{4} \right) $ .
You might think that how it will click in the mind that we can write $ \dfrac{5\pi }{4} $ as $ \pi +\dfrac{\pi }{4} $ . The answer is it is clearly visible on the prima facie that $ \dfrac{5\pi }{4} $ is greater than $ \pi $ and we know the value of $ \cos \dfrac{\pi }{4} $ so in the following line of logic you can write $ \dfrac{5\pi }{4} $ as $ \pi +\dfrac{\pi }{4} $ .
Complete step-by-step answer:
We are asked to find the value of $ \cos \left( -\dfrac{5\pi }{4} \right) $ .
We know that,
$ \cos \left( -\theta \right)=\cos \theta $
As in the above problem, the angle at which we have to find the cosine is also negative so we can use this relation in the given $ \cos \left( -\dfrac{5\pi }{4} \right) $ .
$ \cos \left( -\dfrac{5\pi }{4} \right)=\cos \left( \dfrac{5\pi }{4} \right) $
So, we have reduced the given expression in cosine to:
$ \cos \left( \dfrac{5\pi }{4} \right) $
Now, the angle given above is $ \dfrac{5\pi }{4} $ and we can also write this angle as:
$ \dfrac{5\pi }{4}=\pi +\dfrac{\pi }{4} $
Substituting the above angle in $ \cos \left( \dfrac{5\pi }{4} \right) $ we get,
$ \cos \left( \dfrac{5\pi }{4} \right)=\cos \left( \pi +\dfrac{\pi }{4} \right) $
As the above angle lies in the third quadrant so the value of cosine in the third quadrant is negative.
In the below figure, we have shown the four quadrants and have also shown the angle $ \dfrac{5\pi }{4} $ lies in the III Quadrant from the positive x axis.

We know that,
$ \cos \left( \pi +\theta \right)=-\cos \theta $
Using the above relation in $ \cos \left( \pi +\dfrac{\pi }{4} \right) $ we get,
$ \cos \left( \pi +\dfrac{\pi }{4} \right)=-\cos \left( \dfrac{\pi }{4} \right) $ …………. Eq. (1)
From the trigonometric ratios we know that,
$ \cos \left( \dfrac{\pi }{4} \right)=\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{2}} $
Substituting the above value in eq. (1) we get,
$ \cos \left( \pi +\dfrac{\pi }{4} \right)=-\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{2}} $
From the above calculations, we have got the value of $ \cos \left( -\dfrac{5\pi }{4} \right) $ as $ -\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{2}} $ .
Note: The plausible problem that could happen is that instead of writing $ \cos \left( \dfrac{5\pi }{4} \right) $ as $ \cos \left( \pi +\dfrac{\pi }{4} \right) $ you might make a mistake of perceiving the angle $ \dfrac{5\pi }{4} $ as $ \dfrac{3\pi }{4} $ and write $ \cos \left( \dfrac{5\pi }{4} \right) $ as $ \cos \left( \pi -\dfrac{\pi }{4} \right) $ .
You might think that how it will click in the mind that we can write $ \dfrac{5\pi }{4} $ as $ \pi +\dfrac{\pi }{4} $ . The answer is it is clearly visible on the prima facie that $ \dfrac{5\pi }{4} $ is greater than $ \pi $ and we know the value of $ \cos \dfrac{\pi }{4} $ so in the following line of logic you can write $ \dfrac{5\pi }{4} $ as $ \pi +\dfrac{\pi }{4} $ .
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




