
How do you find the exact value of $\cos \left( {\dfrac{{2\pi }}{3}} \right)$ ?
Answer
556.5k+ views
Hint: In order to evaluate the given trigonometric number, we recall our unit circle of angles of trigonometric identities. We find that the given number falls in the second quadrant, and since all values of cosine are negative in the second quadrant, hence our required value is also negative, then, we find the complementary acute angle and find its value to get our required answer.
Complete step by step solution:
According to thee given question, we need to find the value of $\cos \left( {\dfrac{{2\pi }}{3}} \right)$
Now, if we evaluate the angle, we find that $\dfrac{{2\pi }}{3} = {120^ \circ }$
This angle falls in the second quadrant where all the values of cosine are negative. Thus, our value will also be negative.
Now the acute angle related to this angle is: $\cos \left( {\pi - \dfrac{{2\pi }}{3}} \right) = - \cos \left( {\dfrac{\pi }{3}} \right)$
As we know that the value of $\cos \left( {\dfrac{\pi }{3}} \right) = \dfrac{1}{2}$
Therefore our required answer is: $\cos \left( {\dfrac{{2\pi }}{3}} \right) = - \cos \left( {\dfrac{\pi }{3}} \right) = - \dfrac{1}{2}$
Note: Trigonometry is a branch of mathematics which deals with triangles. There are many trigonometric formulas that establish a relation between the lengths and angles of respective triangles. In trigonometry, we use a right-angled triangle to find ratios of its different sides and angles such as sine, cosine, tan, and their respective inverse like cosec, sec, and cot.
We may even consider a complete circle and divide it into four quadrants to help us understand our trigonometric identities as so:
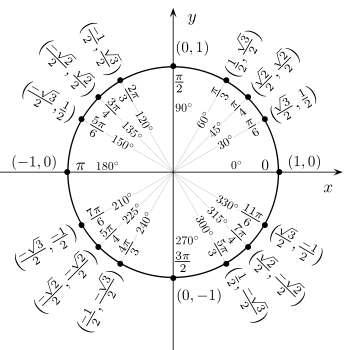
When the whole turn around the circle is equal to $2\pi $ , while a half circle is equal to$\pi $ . The different quadrants are divided into different angles. All trigonometric identities have positive signs in the first quadrant, while sine has positive values in the second quadrant. Tan has positive values in the third quadrant and cosine has positive values in the fourth quadrant.
Complete step by step solution:
According to thee given question, we need to find the value of $\cos \left( {\dfrac{{2\pi }}{3}} \right)$
Now, if we evaluate the angle, we find that $\dfrac{{2\pi }}{3} = {120^ \circ }$
This angle falls in the second quadrant where all the values of cosine are negative. Thus, our value will also be negative.
Now the acute angle related to this angle is: $\cos \left( {\pi - \dfrac{{2\pi }}{3}} \right) = - \cos \left( {\dfrac{\pi }{3}} \right)$
As we know that the value of $\cos \left( {\dfrac{\pi }{3}} \right) = \dfrac{1}{2}$
Therefore our required answer is: $\cos \left( {\dfrac{{2\pi }}{3}} \right) = - \cos \left( {\dfrac{\pi }{3}} \right) = - \dfrac{1}{2}$
Note: Trigonometry is a branch of mathematics which deals with triangles. There are many trigonometric formulas that establish a relation between the lengths and angles of respective triangles. In trigonometry, we use a right-angled triangle to find ratios of its different sides and angles such as sine, cosine, tan, and their respective inverse like cosec, sec, and cot.
We may even consider a complete circle and divide it into four quadrants to help us understand our trigonometric identities as so:

When the whole turn around the circle is equal to $2\pi $ , while a half circle is equal to$\pi $ . The different quadrants are divided into different angles. All trigonometric identities have positive signs in the first quadrant, while sine has positive values in the second quadrant. Tan has positive values in the third quadrant and cosine has positive values in the fourth quadrant.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 9 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 9 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Trending doubts
Difference Between Plant Cell and Animal Cell

Fill the blanks with the suitable prepositions 1 The class 9 english CBSE

Who is eligible for RTE class 9 social science CBSE

Which places in India experience sunrise first and class 9 social science CBSE

What is pollution? How many types of pollution? Define it

Name 10 Living and Non living things class 9 biology CBSE




