
How do you find the exact value of \[\cos \dfrac{{33\pi }}{4}\]?
Answer
558.6k+ views
Hint: Given the expression in trigonometric form. First, write the measure of an angle as a sum of two angles. Now, we will use the Pythagorean Theorem to calculate the third side of the triangle with unit distance. Then, apply the cosine formula to substitute the value of the measure of angle into the expression.
Formula used:
The cosine formula for cos theta is given as:
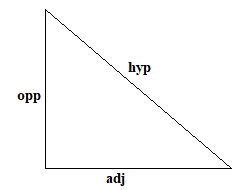
\[\cos \theta = \dfrac{{adj}}{{hyp}}\]
The Pythagorean Theorem states that the sum of squares of two smaller sides of the right triangle is equal to the square of the third side called hypotenuse.
Complete step-by-step answer:
We are given the measure of the angle. Now, we will write the angle \[\dfrac{{33\pi }}{4}\] as a sum of two angles.
\[ \Rightarrow \cos \dfrac{{33\pi }}{4} = \cos \left( {\dfrac{{32\pi }}{4} + \dfrac{\pi }{4}} \right)\]
Again we will rewrite the term \[\dfrac{{32\pi }}{4}\] as product of constant and \[2\pi \], we get:
\[ \Rightarrow \cos \dfrac{{33\pi }}{4} = \cos \left( {4 \times 2\pi + \dfrac{\pi }{4}} \right)\]
Since \[2\pi \] shows the complete circle which means \[2\pi = 0\]. Therefore, substitute the value of \[2\pi \].
\[ \Rightarrow \cos \dfrac{{33\pi }}{4} = \cos \left( {4 \times 0 + \dfrac{\pi }{4}} \right)\]
\[ \Rightarrow \cos \dfrac{{33\pi }}{4} = \cos \left( {\dfrac{\pi }{4}} \right)\]
Now, compute the value of hypotenuse in the triangle if the value of adjacent and opposite sides represents the unit circle using the Pythagorean Theorem.
\[hy{p^2} = op{p^2} + ad{j^2}\]
Now substitute the values into the formula.
\[hy{p^2} = {1^2} + {1^2}\]
On simplifying the expression, we get:
\[ \Rightarrow hy{p^2} = 2\]
We will take square root at both sides, we get:
\[ \Rightarrow hyp = \sqrt 2 \]
Now, we will apply the cosine formula to compute the value of \[\cos \left( {\dfrac{\pi }{4}} \right)\].
$ \Rightarrow \cos \left( {\dfrac{\pi }{4}} \right) = \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 2 }}$
Hence the exact value of \[\cos \dfrac{{33\pi }}{4}\] is $\dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 2 }}$
Note:
In such types of questions the students mainly don't get an approach on how to solve it. In such types of questions students mainly make mistakes while applying the formula for finding the value of the trigonometric angle. In such types of questions, students mainly get confused to represent the angle as a sum of two angles.
Formula used:
The cosine formula for cos theta is given as:

\[\cos \theta = \dfrac{{adj}}{{hyp}}\]
The Pythagorean Theorem states that the sum of squares of two smaller sides of the right triangle is equal to the square of the third side called hypotenuse.
Complete step-by-step answer:
We are given the measure of the angle. Now, we will write the angle \[\dfrac{{33\pi }}{4}\] as a sum of two angles.
\[ \Rightarrow \cos \dfrac{{33\pi }}{4} = \cos \left( {\dfrac{{32\pi }}{4} + \dfrac{\pi }{4}} \right)\]
Again we will rewrite the term \[\dfrac{{32\pi }}{4}\] as product of constant and \[2\pi \], we get:
\[ \Rightarrow \cos \dfrac{{33\pi }}{4} = \cos \left( {4 \times 2\pi + \dfrac{\pi }{4}} \right)\]
Since \[2\pi \] shows the complete circle which means \[2\pi = 0\]. Therefore, substitute the value of \[2\pi \].
\[ \Rightarrow \cos \dfrac{{33\pi }}{4} = \cos \left( {4 \times 0 + \dfrac{\pi }{4}} \right)\]
\[ \Rightarrow \cos \dfrac{{33\pi }}{4} = \cos \left( {\dfrac{\pi }{4}} \right)\]
Now, compute the value of hypotenuse in the triangle if the value of adjacent and opposite sides represents the unit circle using the Pythagorean Theorem.
\[hy{p^2} = op{p^2} + ad{j^2}\]
Now substitute the values into the formula.
\[hy{p^2} = {1^2} + {1^2}\]
On simplifying the expression, we get:
\[ \Rightarrow hy{p^2} = 2\]
We will take square root at both sides, we get:
\[ \Rightarrow hyp = \sqrt 2 \]
Now, we will apply the cosine formula to compute the value of \[\cos \left( {\dfrac{\pi }{4}} \right)\].
$ \Rightarrow \cos \left( {\dfrac{\pi }{4}} \right) = \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 2 }}$
Hence the exact value of \[\cos \dfrac{{33\pi }}{4}\] is $\dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 2 }}$
Note:
In such types of questions the students mainly don't get an approach on how to solve it. In such types of questions students mainly make mistakes while applying the formula for finding the value of the trigonometric angle. In such types of questions, students mainly get confused to represent the angle as a sum of two angles.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




