
How do you find the exact value of \[arctan1\text{ or }{{\tan }^{-1}}1\]?
Answer
561.3k+ views
Hint:
tan\[x\] is the ratio of \[perpendicular\] to \[base\] in a right angled triangle and if this ratio is \[1\] that means the two sides are equal and using the property of an isosceles triangle their corresponding angles are also equal and that is \[45{}^\circ \] each by applying the angle sum property.
Complete step by step solution:
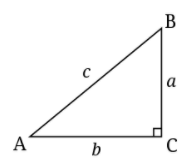
As we know that the \[tangent\] function for acute angles can be viewed as the ratio of the opposite to the adjacent side of the angle.
\[\Rightarrow \tan A=\dfrac{perpendicular}{base}=\dfrac{a}{b}\]
Let the given value \[{{\tan }^{-1}}1\] be \[x\]
\[\Rightarrow {{\tan }^{-1}}1=x\]
Now taking \[\tan \]both sides
\[\Rightarrow \tan \left( {{\tan }^{-1}}1 \right)=x\]
\[\Rightarrow 1=\tan x\]
If the ratio is 1, it means that the triangle is a right angle isosceles
Therefore, \[m\angle A=m\angle B--(1)\]
Now, using the angle sum property of the triangle
\[\Rightarrow \angle A+\angle B+\angle C=\angle 180{}^\circ --(2)\]
Since \[\angle C=90{}^\circ --(3)\]
From Equation \[(1),(2),(3)\]
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow \angle A+\angle B=90{}^\circ \\
& \Rightarrow \angle A=\angle B=45{}^\circ \\
\end{align}\]
And therefore the corresponding angle is \[45{}^\circ \] degrees of \[\dfrac{\pi }{4}rad\].
Hence, \[\arctan 1=\dfrac{\pi }{4}\]
Note:
To find the exact value we will use the basic foundations of trigonometry. Normally for \[45{}^\circ \] or \[\dfrac{\pi}{4} radian\] and in general form \[(2n+1)\dfrac{\pi }{4}\] where \[n\in Z\] the length other two sides are equal and the domain of \[arctan1\text{ or }{{\tan }^{-1}}1\] is \[\left[ -1,1 \right]\] and the range is \[\left( -\dfrac{\pi }{2},\dfrac{\pi }{2} \right)\].
tan\[x\] is the ratio of \[perpendicular\] to \[base\] in a right angled triangle and if this ratio is \[1\] that means the two sides are equal and using the property of an isosceles triangle their corresponding angles are also equal and that is \[45{}^\circ \] each by applying the angle sum property.
Complete step by step solution:

As we know that the \[tangent\] function for acute angles can be viewed as the ratio of the opposite to the adjacent side of the angle.
\[\Rightarrow \tan A=\dfrac{perpendicular}{base}=\dfrac{a}{b}\]
Let the given value \[{{\tan }^{-1}}1\] be \[x\]
\[\Rightarrow {{\tan }^{-1}}1=x\]
Now taking \[\tan \]both sides
\[\Rightarrow \tan \left( {{\tan }^{-1}}1 \right)=x\]
\[\Rightarrow 1=\tan x\]
If the ratio is 1, it means that the triangle is a right angle isosceles
Therefore, \[m\angle A=m\angle B--(1)\]
Now, using the angle sum property of the triangle
\[\Rightarrow \angle A+\angle B+\angle C=\angle 180{}^\circ --(2)\]
Since \[\angle C=90{}^\circ --(3)\]
From Equation \[(1),(2),(3)\]
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow \angle A+\angle B=90{}^\circ \\
& \Rightarrow \angle A=\angle B=45{}^\circ \\
\end{align}\]
And therefore the corresponding angle is \[45{}^\circ \] degrees of \[\dfrac{\pi }{4}rad\].
Hence, \[\arctan 1=\dfrac{\pi }{4}\]
Note:
To find the exact value we will use the basic foundations of trigonometry. Normally for \[45{}^\circ \] or \[\dfrac{\pi}{4} radian\] and in general form \[(2n+1)\dfrac{\pi }{4}\] where \[n\in Z\] the length other two sides are equal and the domain of \[arctan1\text{ or }{{\tan }^{-1}}1\] is \[\left[ -1,1 \right]\] and the range is \[\left( -\dfrac{\pi }{2},\dfrac{\pi }{2} \right)\].
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

10 examples of friction in our daily life




