
Find the equivalent resistance between any two terminals and find the total current:
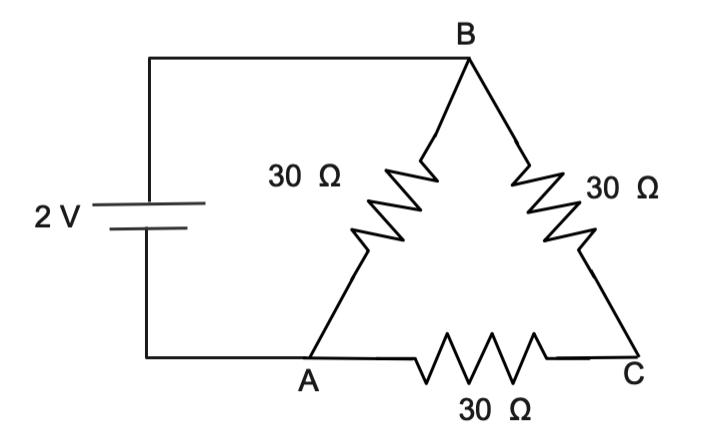

Answer
497.4k+ views
Hint: In order to solve the question, first of all we will extend the circuit in the form of simple series and parallel connection then we will first solve the series connection then we will solve the parallel connection after we find resultant resistance we will find current by using ohm’s law and in which we will substitute resultant resistance.
Formula Used:
Series connection of resistance
${R_{eq}} = {R_1} + {R_2} + {R_3} + .......{R_N}$
Parallel connection of resistance
$\dfrac{1}{{{R_{eq}}}} = \dfrac{1}{{{R_1}\,}} + \dfrac{1}{{{R_2}\,}} + \dfrac{1}{{{R_3}\,}} + .......\dfrac{1}{{{R_N}\,}}$
Ohm’s law
$I = \dfrac{V}{{{R_{eq}}}}$
I refer to current
V refers to potential difference
${R_{eq}}$ refers to equivalent resistance
Complete step by step solution: 7
In the question we are given circuit connection of resistance and battery
All the resistance in the circuit is $30{\text{ }}\Omega $
Potential difference in the circuit is 2V
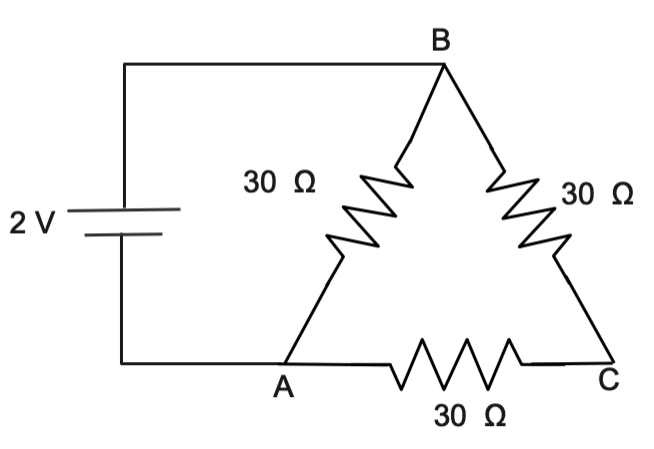
The diagram shows that circuit in question now we will solve the circuit by extended the circuit and represent in the simple form of parallel and series connection
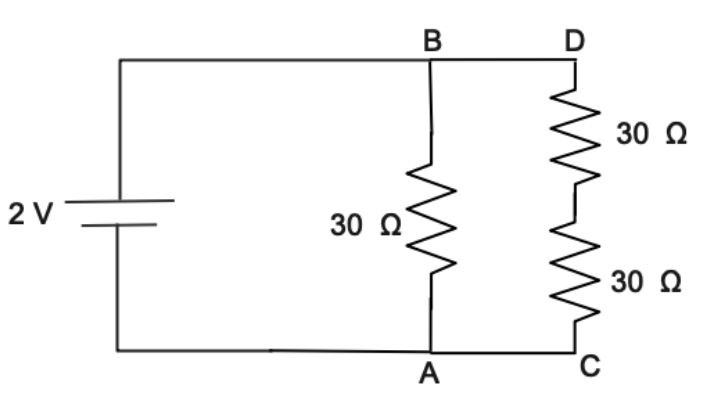
Now we will solve the resistance between the terminal D and C
The connection between terminal D and terminal C is
Series connection of resistance
${R_{eq}} = {R_1} + {R_2} + {R_3} + .......{R_N}$
Substituting the value of resistance from the diagram
${R_{eq}} = 30{\text{ }}\Omega + 30{\text{ }}\Omega $
${R_{eq}} = 60{\text{ }}\Omega $
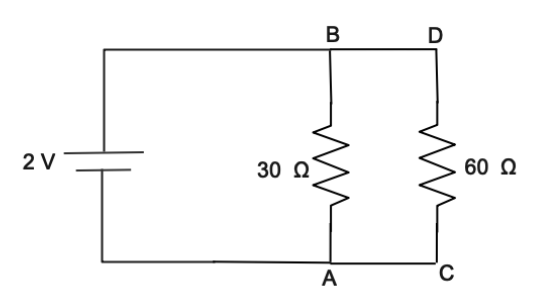
Now we will solve the resistance between A, B, C, D terminals the connection between circuit is
Parallel connection of resistance
$\dfrac{1}{{{R_{eq}}}} = \dfrac{1}{{{R_1}\,}} + \dfrac{1}{{{R_2}\,}} + \dfrac{1}{{{R_3}\,}} + .......\dfrac{1}{{{R_N}\,}}$
Substituting the value of resistance from the diagram
\[\dfrac{1}{{{R_{eq}}}} = \dfrac{1}{{60{\text{ }}\Omega \,}} + \dfrac{1}{{30{\text{ }}\Omega }}\]
\[\dfrac{1}{{{R_{eq}}}} = \dfrac{1}{{{\text{20 }}\Omega \,}}\]
Taking the reciprocal we will get
\[{R_{eq}}{\text{ = 20 }}\Omega \,\]
Hence we solved the circuit with equivalent resistance and current
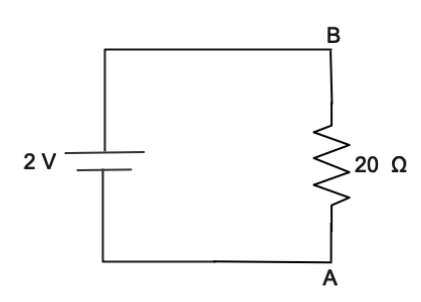
Now we will apply Ohm’s law
$I = \dfrac{V}{{{R_{eq}}}}$
Substituting the value of ${R_{eq}} = 20\Omega $ and V = 2V
$I = \dfrac{{2{\text{ V}}}}{{20\Omega }}$
$I = 0.1{\text{ A}}$
Hence, the answers are $I = 0.1{\text{ A}}$ and \[{R_{eq}}{\text{ = 20 }}\Omega \,\]
Note:
Many of the people will make mistake by not breaking the circuit and doing it directly it can be short it would not be clear as it is with step by step circuit along with the unit should be taken care and should be written at each step and should be converted into simple unit as voltage upon ohm is converted into ampere
Formula Used:
Series connection of resistance
${R_{eq}} = {R_1} + {R_2} + {R_3} + .......{R_N}$
Parallel connection of resistance
$\dfrac{1}{{{R_{eq}}}} = \dfrac{1}{{{R_1}\,}} + \dfrac{1}{{{R_2}\,}} + \dfrac{1}{{{R_3}\,}} + .......\dfrac{1}{{{R_N}\,}}$
Ohm’s law
$I = \dfrac{V}{{{R_{eq}}}}$
I refer to current
V refers to potential difference
${R_{eq}}$ refers to equivalent resistance
Complete step by step solution: 7
In the question we are given circuit connection of resistance and battery
All the resistance in the circuit is $30{\text{ }}\Omega $
Potential difference in the circuit is 2V

The diagram shows that circuit in question now we will solve the circuit by extended the circuit and represent in the simple form of parallel and series connection

Now we will solve the resistance between the terminal D and C
The connection between terminal D and terminal C is
Series connection of resistance
${R_{eq}} = {R_1} + {R_2} + {R_3} + .......{R_N}$
Substituting the value of resistance from the diagram
${R_{eq}} = 30{\text{ }}\Omega + 30{\text{ }}\Omega $
${R_{eq}} = 60{\text{ }}\Omega $

Now we will solve the resistance between A, B, C, D terminals the connection between circuit is
Parallel connection of resistance
$\dfrac{1}{{{R_{eq}}}} = \dfrac{1}{{{R_1}\,}} + \dfrac{1}{{{R_2}\,}} + \dfrac{1}{{{R_3}\,}} + .......\dfrac{1}{{{R_N}\,}}$
Substituting the value of resistance from the diagram
\[\dfrac{1}{{{R_{eq}}}} = \dfrac{1}{{60{\text{ }}\Omega \,}} + \dfrac{1}{{30{\text{ }}\Omega }}\]
\[\dfrac{1}{{{R_{eq}}}} = \dfrac{1}{{{\text{20 }}\Omega \,}}\]
Taking the reciprocal we will get
\[{R_{eq}}{\text{ = 20 }}\Omega \,\]
Hence we solved the circuit with equivalent resistance and current

Now we will apply Ohm’s law
$I = \dfrac{V}{{{R_{eq}}}}$
Substituting the value of ${R_{eq}} = 20\Omega $ and V = 2V
$I = \dfrac{{2{\text{ V}}}}{{20\Omega }}$
$I = 0.1{\text{ A}}$
Hence, the answers are $I = 0.1{\text{ A}}$ and \[{R_{eq}}{\text{ = 20 }}\Omega \,\]
Note:
Many of the people will make mistake by not breaking the circuit and doing it directly it can be short it would not be clear as it is with step by step circuit along with the unit should be taken care and should be written at each step and should be converted into simple unit as voltage upon ohm is converted into ampere
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE

Give 10 examples of unisexual and bisexual flowers




