
How do you find the equations of the tangent and normal of the curve at $x={{t}^{2}}$, $y=t+3$, $t=1$?
Answer
539.1k+ views
Hint: In this question we have to find the slope and points of the tangent and the normal of the curve. We will first take the derivative of the term $x={{t}^{2}}$ with respect to $t$. Then we will take the derivative of $y=t+3$ with respect to $t$. Then divide both to get $\dfrac{dy}{dx}$ which is the slope and substitute the value of $t=1$ to get the value of the slope. We will then use point slope form to find the equation of tangent and then use the formula ${{m}_{n}}=\dfrac{-1}{m}$ to find the slope of the normal and use point slope form to get its equation.
Complete step by step solution:
We have the curve as $x={{t}^{2}}$ and $y=t+3$.
On differentiating the term $x={{t}^{2}}$, we get:
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{dx}{dt}=\dfrac{d}{dt}\left( {{t}^{2}} \right)$
On using the formula $\dfrac{d}{dx}{{x}^{n}}=n{{x}^{n-1}}$, we get:
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{dx}{dt}=2t$
On differentiating the term $y=t+3$, we get:
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{dy}{dt}=\dfrac{d}{dt}\left( t+3 \right)$
On splitting the derivative, we get:
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{dy}{dx}=\dfrac{dt}{dt}+\dfrac{d}{dt}3$
On using the formula $\dfrac{dx}{dx}=1$ and $\dfrac{d}{dx}k=0$, we get:
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{dy}{dt}=1$
We know that tangent of a curve is given by $\dfrac{dy}{dx}$ therefore, we can write:
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{\dfrac{dy}{dt}}{\dfrac{dx}{dt}}=\dfrac{1}{2t}$
On simplifying, we get:
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{dy}{dx}=\dfrac{1}{2t}$
Now at $t=1$, we have:
$\Rightarrow {{\left. \dfrac{dy}{dx} \right|}_{t=1}}=\dfrac{1}{2\left( 1 \right)}$
On simplifying, we get:
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{dy}{dx}=\dfrac{1}{2}$
Which is the required slope therefore, $m=\dfrac{1}{2}$.
Now at $t=1$, $x$ will be:
$\Rightarrow x={{\left( 1 \right)}^{2}}=1$
And at $t=1$, $y$ will be:
$\Rightarrow y=1+3=4$
So, the tangent passes through $\left( 1,4 \right)$ and has slope $\dfrac{1}{2}$, so using the point slope form which is $y-{{y}_{1}}=m\left( x-{{x}_{1}} \right)$, we get:
$\Rightarrow y-4=\dfrac{1}{2}\left( x-1 \right)$
On simplifying, we get:
$\Rightarrow y=\dfrac{1}{2}x+\dfrac{7}{2}$
And the normal passes through $\left( 1,4 \right)$ and has slope ${{m}_{n}}=\dfrac{-1}{m}=\dfrac{-1}{1/2}=-2$, so using the point slope form, we get:
$\Rightarrow y-4=-2\left( x-1 \right)$
On simplifying, we get:
$\Rightarrow y=-2x+6$
On drawing the curve, the tangent and normal on the graph, we get:
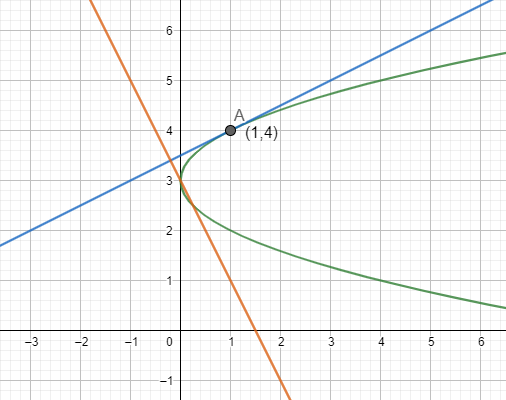
Note: This type of question belongs to the category of calculus. the addition rule of differentiation should be remembered which is $\dfrac{dy}{dx}\left( f\left( x \right)+g\left( x \right) \right)=\dfrac{d}{dx}\left( f\left( x \right) \right)+\dfrac{d}{dx}\left( g\left( x \right) \right)$. It is to be remembered that the derivative of the equation of the line gives the slope of the line and a normal is a line perpendicular to the tangent of a curve.
Complete step by step solution:
We have the curve as $x={{t}^{2}}$ and $y=t+3$.
On differentiating the term $x={{t}^{2}}$, we get:
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{dx}{dt}=\dfrac{d}{dt}\left( {{t}^{2}} \right)$
On using the formula $\dfrac{d}{dx}{{x}^{n}}=n{{x}^{n-1}}$, we get:
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{dx}{dt}=2t$
On differentiating the term $y=t+3$, we get:
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{dy}{dt}=\dfrac{d}{dt}\left( t+3 \right)$
On splitting the derivative, we get:
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{dy}{dx}=\dfrac{dt}{dt}+\dfrac{d}{dt}3$
On using the formula $\dfrac{dx}{dx}=1$ and $\dfrac{d}{dx}k=0$, we get:
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{dy}{dt}=1$
We know that tangent of a curve is given by $\dfrac{dy}{dx}$ therefore, we can write:
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{\dfrac{dy}{dt}}{\dfrac{dx}{dt}}=\dfrac{1}{2t}$
On simplifying, we get:
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{dy}{dx}=\dfrac{1}{2t}$
Now at $t=1$, we have:
$\Rightarrow {{\left. \dfrac{dy}{dx} \right|}_{t=1}}=\dfrac{1}{2\left( 1 \right)}$
On simplifying, we get:
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{dy}{dx}=\dfrac{1}{2}$
Which is the required slope therefore, $m=\dfrac{1}{2}$.
Now at $t=1$, $x$ will be:
$\Rightarrow x={{\left( 1 \right)}^{2}}=1$
And at $t=1$, $y$ will be:
$\Rightarrow y=1+3=4$
So, the tangent passes through $\left( 1,4 \right)$ and has slope $\dfrac{1}{2}$, so using the point slope form which is $y-{{y}_{1}}=m\left( x-{{x}_{1}} \right)$, we get:
$\Rightarrow y-4=\dfrac{1}{2}\left( x-1 \right)$
On simplifying, we get:
$\Rightarrow y=\dfrac{1}{2}x+\dfrac{7}{2}$
And the normal passes through $\left( 1,4 \right)$ and has slope ${{m}_{n}}=\dfrac{-1}{m}=\dfrac{-1}{1/2}=-2$, so using the point slope form, we get:
$\Rightarrow y-4=-2\left( x-1 \right)$
On simplifying, we get:
$\Rightarrow y=-2x+6$
On drawing the curve, the tangent and normal on the graph, we get:

Note: This type of question belongs to the category of calculus. the addition rule of differentiation should be remembered which is $\dfrac{dy}{dx}\left( f\left( x \right)+g\left( x \right) \right)=\dfrac{d}{dx}\left( f\left( x \right) \right)+\dfrac{d}{dx}\left( g\left( x \right) \right)$. It is to be remembered that the derivative of the equation of the line gives the slope of the line and a normal is a line perpendicular to the tangent of a curve.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




