
Find the equation of the tangent line to the curve $y={{x}^{2}}-2x+7$ which is
(i) parallel to $2x-y+9=0$
(ii) Perpendicular to $5y-15x=13$
Answer
574.8k+ views
Hint: We have given a curve and we need to find the tangent to the curve, so here we can calculate the value of the slope of the required tangent by differentiating the given curve with respect to $y$. From the given condition that the tangent is to be parallel with the given line $2x-y+9=0$. We will calculate the slope of the line $2x-y+9=0$ by converting it into the slope intersecting form i.e. $y=mx+c$. From the value of the slope of the line $2x-y+9=0$ and given condition, we will equate the slopes of the line and required tangent, then we will get the coordinates of the point where we have to find the equation of the tangent. From the coordinates and slope of the tangent, we can write the equation of the tangent as $\left( y-{{y}_{1}} \right)=m\left( x-{{x}_{1}} \right)$. To find the equation of tangent perpendicular to $5y-15x=13$. We will calculate the slope of the line $5y-15x=13$ by converting it into the slope intersecting form i.e. $y=mx+c$. From the value of the slope of the line $5y-15x=13$ and given condition, we will equate the slopes of the line and required tangent, then we will get the coordinates of the point where we have to find the equation of the tangent. From the coordinates and slope of the tangent, we can write the equation of the tangent as $\left( y-{{y}_{1}} \right)=m\left( x-{{x}_{1}} \right)$.
Complete step by step solution:
Given that, the equation of the curve is $y={{x}^{2}}-2x+7$.
Differentiating the above equation with respect to $y$, then we will have
$\dfrac{dy}{dx}=\dfrac{d}{dx}\left( {{x}^{2}}-2x+7 \right)$
Applying derivatives individually, then we will get
$\dfrac{dy}{dx}=\dfrac{d}{dx}\left( {{x}^{2}} \right)-2\dfrac{d}{dx}\left( x \right)+\dfrac{d}{dx}\left( 7 \right)$
We know that $\dfrac{d}{dx}\left( {{x}^{n}} \right)=n{{x}^{n-1}}$, derivative of constant value will give zero, then
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{dy}{dx}=2{{x}^{2-1}}-1{{x}^{1-1}}+0 \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{dy}{dx}=2x-2 \\
\end{align}$
Given that, the required tangent is parallel to the line $2x-y+9=0$.
Converting the line $2x-y+9=0$ in the form of slope intercept form i.e. $y=mx+c$, then
$y=2x+9$
And the value of slope of the line $2x-y+9=0$ is $m=2$.
If the line $2x-y+9=0$ is parallel to the required tangent, then the slopes of both the lines should be equal. So, we are going to equate the both the slopes of the lines as
$\begin{align}
& \dfrac{dy}{dx}=2 \\
& \Rightarrow 2x-2=2 \\
& \Rightarrow 2x=4 \\
& \Rightarrow x=2 \\
\end{align}$
Hence, the $x$ coordinate of the point is $2$. Now the value of $y$ at $x=2$ will be calculated by substituting the value of $x$ in the curve $y={{x}^{2}}-2x+7$, then
$\begin{align}
& y={{2}^{2}}-2\times 2+7 \\
& \Rightarrow y=4-4+7 \\
& \Rightarrow y=7 \\
\end{align}$
Hence, the tangent point is $\left( 2,7 \right)$. Now the equation of the tangent to the curve $y={{x}^{2}}-2x+7$ at $\left( 2,7 \right)$ with slope $m=2$ is given by
$\begin{align}
& \left( y-{{y}_{1}} \right)=m\left( x-{{x}_{1}} \right) \\
& \Rightarrow \left( y-7 \right)=2\left( x-2 \right) \\
& \Rightarrow y-7=2x-4 \\
& \Rightarrow 2x-y+3=0 \\
\end{align}$
Hence, the equation of the required tangent is $2x-y+3=0$.
(ii) Given that, the required tangent is perpendicular to the line $5y-15x=13$.
Converting the given line $5y-15x=13$ into slope intercept form i.e. $y=mx+c$, then
$\begin{align}
& 5y=15x+13 \\
& \Rightarrow y=\dfrac{15}{5}x+\dfrac{13}{5} \\
& \Rightarrow y=3x+\dfrac{13}{5} \\
\end{align}$
The slope of the line $5y-15x=13$ is given by $m=3$.
If the line $5y-15x=13$ is perpendicular to the required tangent, then the slope of the tangent is given by
$\begin{align}
& {{m}_{t}}=\dfrac{-1}{m} \\
& \Rightarrow {{m}_{t}}=-\dfrac{1}{3} \\
\end{align}$
But we have the slope of the tangent as $\dfrac{dy}{dx}=2x-2$, so we are going to equate the both the values, then we will have
$\begin{align}
& \dfrac{dy}{dx}={{m}_{t}} \\
& \Rightarrow 2x-2=-\dfrac{1}{3} \\
& \Rightarrow 6x-6=-1 \\
& \Rightarrow 6x=5 \\
& \Rightarrow x=\dfrac{5}{6} \\
\end{align}$
Hence the $x$ coordinate of the tangent point is $\dfrac{5}{6}$ and the $y$ coordinate of the tangent point will be obtained by substituting the value of $x$ in the given curve $y={{x}^{2}}-2x+7$. Then
$\begin{align}
& y={{\left( \dfrac{5}{6} \right)}^{2}}-2\left( \dfrac{5}{6} \right)+7 \\
& \Rightarrow y=\dfrac{25}{36}-\dfrac{10}{6}+7 \\
& \Rightarrow y=\dfrac{25-60+252}{36} \\
& \Rightarrow y=\dfrac{217}{36} \\
\end{align}$
Thus, the equation of the tangent at point $\left( \dfrac{5}{6},\dfrac{217}{36} \right)$ with the slope ${{m}_{t}}=-\dfrac{1}{3}$is given by
$\begin{align}
& \left( y-{{y}_{1}} \right)={{m}_{t}}\left( x-{{x}_{1}} \right) \\
& \Rightarrow \left( y-\dfrac{217}{36} \right)=-\dfrac{1}{3}\left( x-\dfrac{5}{6} \right) \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{36y-217}{36}=-\dfrac{1}{3}\left( \dfrac{6x-5}{6} \right) \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{36y-217}{36}=\dfrac{5-6x}{18} \\
& \Rightarrow 36y-217=2\left( 5-6x \right) \\
& \Rightarrow 36y-217=10-12x \\
& \Rightarrow 12x+36y-227=0 \\
\end{align}$
Hence the equation of the tangent perpendicular to $5y-15x=13$ for the curve $y={{x}^{2}}-2x+7$ is $2x+36y-227=0$.
Note: We can also solve this problem using the geometric construction. First we will draw all the given curves and lines $y={{x}^{2}}-2x+7$, $2x-y+9=0$, $5y-15x=13$. After that according to the given conditions, we will draw a line that is parallel to $2x-y+9=0$ and touches the curve $y={{x}^{2}}-2x+7$. Now we can simply find the equation of the line in the geometry as we can see so many points on the line. Similarly, we will draw a perpendicular line to $5y-15x=13$ and touch the curve $y={{x}^{2}}-2x+7$, and then we will find the equation of that tangent also. The lines in the graph are shown below
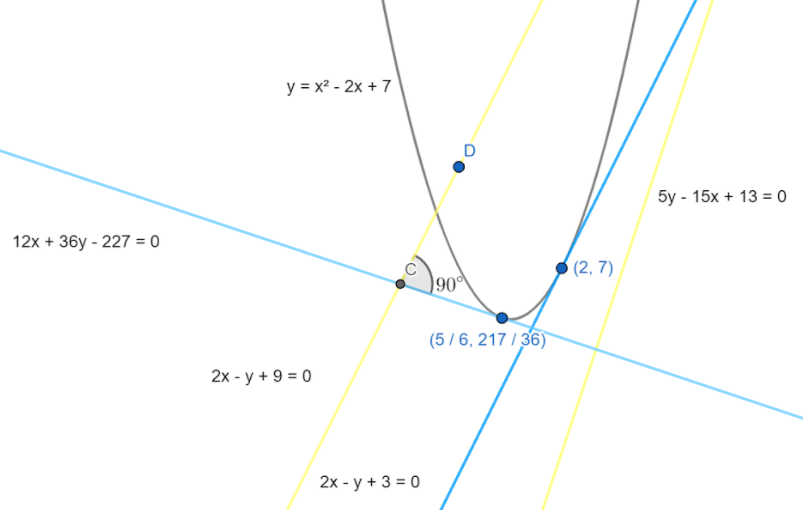
Complete step by step solution:
Given that, the equation of the curve is $y={{x}^{2}}-2x+7$.
Differentiating the above equation with respect to $y$, then we will have
$\dfrac{dy}{dx}=\dfrac{d}{dx}\left( {{x}^{2}}-2x+7 \right)$
Applying derivatives individually, then we will get
$\dfrac{dy}{dx}=\dfrac{d}{dx}\left( {{x}^{2}} \right)-2\dfrac{d}{dx}\left( x \right)+\dfrac{d}{dx}\left( 7 \right)$
We know that $\dfrac{d}{dx}\left( {{x}^{n}} \right)=n{{x}^{n-1}}$, derivative of constant value will give zero, then
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{dy}{dx}=2{{x}^{2-1}}-1{{x}^{1-1}}+0 \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{dy}{dx}=2x-2 \\
\end{align}$
Given that, the required tangent is parallel to the line $2x-y+9=0$.
Converting the line $2x-y+9=0$ in the form of slope intercept form i.e. $y=mx+c$, then
$y=2x+9$
And the value of slope of the line $2x-y+9=0$ is $m=2$.
If the line $2x-y+9=0$ is parallel to the required tangent, then the slopes of both the lines should be equal. So, we are going to equate the both the slopes of the lines as
$\begin{align}
& \dfrac{dy}{dx}=2 \\
& \Rightarrow 2x-2=2 \\
& \Rightarrow 2x=4 \\
& \Rightarrow x=2 \\
\end{align}$
Hence, the $x$ coordinate of the point is $2$. Now the value of $y$ at $x=2$ will be calculated by substituting the value of $x$ in the curve $y={{x}^{2}}-2x+7$, then
$\begin{align}
& y={{2}^{2}}-2\times 2+7 \\
& \Rightarrow y=4-4+7 \\
& \Rightarrow y=7 \\
\end{align}$
Hence, the tangent point is $\left( 2,7 \right)$. Now the equation of the tangent to the curve $y={{x}^{2}}-2x+7$ at $\left( 2,7 \right)$ with slope $m=2$ is given by
$\begin{align}
& \left( y-{{y}_{1}} \right)=m\left( x-{{x}_{1}} \right) \\
& \Rightarrow \left( y-7 \right)=2\left( x-2 \right) \\
& \Rightarrow y-7=2x-4 \\
& \Rightarrow 2x-y+3=0 \\
\end{align}$
Hence, the equation of the required tangent is $2x-y+3=0$.
(ii) Given that, the required tangent is perpendicular to the line $5y-15x=13$.
Converting the given line $5y-15x=13$ into slope intercept form i.e. $y=mx+c$, then
$\begin{align}
& 5y=15x+13 \\
& \Rightarrow y=\dfrac{15}{5}x+\dfrac{13}{5} \\
& \Rightarrow y=3x+\dfrac{13}{5} \\
\end{align}$
The slope of the line $5y-15x=13$ is given by $m=3$.
If the line $5y-15x=13$ is perpendicular to the required tangent, then the slope of the tangent is given by
$\begin{align}
& {{m}_{t}}=\dfrac{-1}{m} \\
& \Rightarrow {{m}_{t}}=-\dfrac{1}{3} \\
\end{align}$
But we have the slope of the tangent as $\dfrac{dy}{dx}=2x-2$, so we are going to equate the both the values, then we will have
$\begin{align}
& \dfrac{dy}{dx}={{m}_{t}} \\
& \Rightarrow 2x-2=-\dfrac{1}{3} \\
& \Rightarrow 6x-6=-1 \\
& \Rightarrow 6x=5 \\
& \Rightarrow x=\dfrac{5}{6} \\
\end{align}$
Hence the $x$ coordinate of the tangent point is $\dfrac{5}{6}$ and the $y$ coordinate of the tangent point will be obtained by substituting the value of $x$ in the given curve $y={{x}^{2}}-2x+7$. Then
$\begin{align}
& y={{\left( \dfrac{5}{6} \right)}^{2}}-2\left( \dfrac{5}{6} \right)+7 \\
& \Rightarrow y=\dfrac{25}{36}-\dfrac{10}{6}+7 \\
& \Rightarrow y=\dfrac{25-60+252}{36} \\
& \Rightarrow y=\dfrac{217}{36} \\
\end{align}$
Thus, the equation of the tangent at point $\left( \dfrac{5}{6},\dfrac{217}{36} \right)$ with the slope ${{m}_{t}}=-\dfrac{1}{3}$is given by
$\begin{align}
& \left( y-{{y}_{1}} \right)={{m}_{t}}\left( x-{{x}_{1}} \right) \\
& \Rightarrow \left( y-\dfrac{217}{36} \right)=-\dfrac{1}{3}\left( x-\dfrac{5}{6} \right) \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{36y-217}{36}=-\dfrac{1}{3}\left( \dfrac{6x-5}{6} \right) \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{36y-217}{36}=\dfrac{5-6x}{18} \\
& \Rightarrow 36y-217=2\left( 5-6x \right) \\
& \Rightarrow 36y-217=10-12x \\
& \Rightarrow 12x+36y-227=0 \\
\end{align}$
Hence the equation of the tangent perpendicular to $5y-15x=13$ for the curve $y={{x}^{2}}-2x+7$ is $2x+36y-227=0$.
Note: We can also solve this problem using the geometric construction. First we will draw all the given curves and lines $y={{x}^{2}}-2x+7$, $2x-y+9=0$, $5y-15x=13$. After that according to the given conditions, we will draw a line that is parallel to $2x-y+9=0$ and touches the curve $y={{x}^{2}}-2x+7$. Now we can simply find the equation of the line in the geometry as we can see so many points on the line. Similarly, we will draw a perpendicular line to $5y-15x=13$ and touch the curve $y={{x}^{2}}-2x+7$, and then we will find the equation of that tangent also. The lines in the graph are shown below

Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

RNA and DNA are chiral molecules their chirality is class 12 chemistry CBSE

RNA and DNA are chiral molecules their chirality is class 12 chemistry CBSE




