
How do you find the equation of an ellipse with foci $\left( { \pm 2,0} \right)$ and major axis of length $8$ ?
Answer
491.1k+ views
Hint: In this problem, we are asked to find the equation of the ellipse, where the point of foci and the length of the major axis are given. Through the given major axis, we can find the value of a and from the foci point we can find the value of b and the centre point, which is the origin here. Substituting these values, we can get the equation of the ellipse.
Complete solution:
We know that the standard cartesian form of the equation of the ellipse is
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{{{\left( {x - h} \right)}^2}}}{{{a^2}}} + \dfrac{{{{\left( {y - k} \right)}^2}}}{{{b^2}}} = 1\,\,a > b - - - - \left( 1 \right)\]
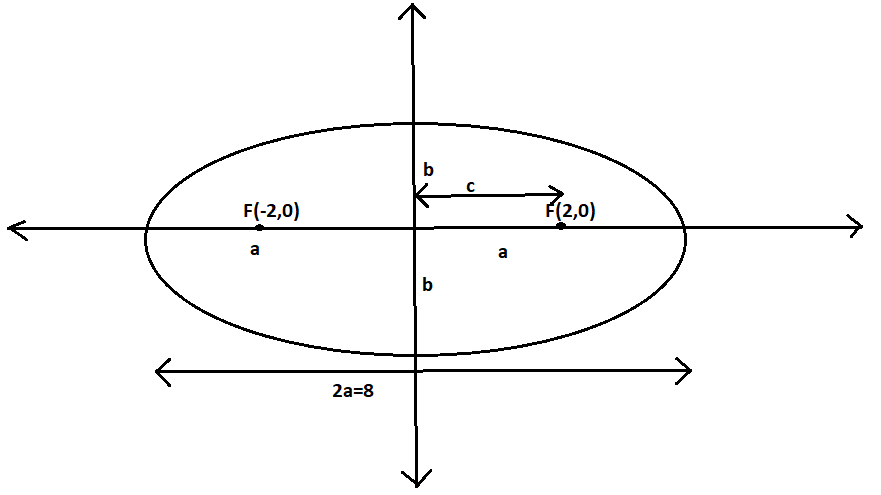
Here h and k are the centre and a is half length of the major axis and b is half length of the minor axis. We know that the given point of foci is \[\left( { \pm 2,0} \right)\]
which is of the general form\[\]\[( \pm c,0)\] for horizontal ellipses.
\[ \Rightarrow c = 2 - - - \left( 2 \right)\]
From the given point of foci, we came to know that the centre point is \[\left( {0,0} \right)\]
Now we can write the equation \[\left( 1 \right)\] as
\[\dfrac{{{{(x - 0)}^2}}}{{{a^2}}} + \dfrac{{{{(y - 0)}^2}}}{{{b^2}}} = 1\]
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{{{\left( x \right)}^2}}}{{{a^2}}} + \dfrac{{{{\left( y \right)}^2}}}{{{b^2}}} = 1......(3)\]
Now we have to find the value of a and b, to get the equation of ellipse.
We know that the length of the major axis is \[2a\].
We also know that the given length of the major axis \[ = {\text{ 8}}\].
Now we can substitute the length of the major axis to the given length, we get
\[ \Rightarrow 2a = 8\]
\[ \Rightarrow a = \dfrac{8}{2}\]
\[ \Rightarrow a = 4\]
Now we have to find the value of b.
We know that the formula to find focus is
\[{c^2} = {a^2} - {b^2}\]
We already know the value of c from \[\left( 2 \right)\]
As we know the focus point and the value of a, we can find the value of b
\[{2^2} = {4^2} - {b^2}\]
\[ \Rightarrow {b^2} = {4^2} - {2^2}\]
\[ \Rightarrow b = \sqrt {{4^2} - {2^2}} \]
\[ \Rightarrow b = \sqrt {16 - 4} \]
\[ \Rightarrow b = \sqrt {12} \]
Now we got the value of a and b, we can substitute it in the equation (3), we get
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{{{(x)}^2}}}{{{{\left( 4 \right)}^2}}} + \dfrac{{{{(y)}^2}}}{{{{\left( {\sqrt {12} } \right)}^2}}} = 1\]
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{{{(x)}^2}}}{{16}} + \dfrac{{{{(y)}^2}}}{{12}} = 1\]
Therefore, the equation of the ellipse is\[\dfrac{{{{(x)}^2}}}{{16}} + \dfrac{{{{(y)}^2}}}{{12}} = 1\]
Note:
In these types of problems, it is necessary to check for the centre point, in this problem it is the origin, if the centre point is not the origin, we will get a different solution. Students make mistakes by takes major axis as 2b instead of 2a.

Complete solution:
We know that the standard cartesian form of the equation of the ellipse is
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{{{\left( {x - h} \right)}^2}}}{{{a^2}}} + \dfrac{{{{\left( {y - k} \right)}^2}}}{{{b^2}}} = 1\,\,a > b - - - - \left( 1 \right)\]
Here h and k are the centre and a is half length of the major axis and b is half length of the minor axis. We know that the given point of foci is \[\left( { \pm 2,0} \right)\]
which is of the general form\[\]\[( \pm c,0)\] for horizontal ellipses.
\[ \Rightarrow c = 2 - - - \left( 2 \right)\]
From the given point of foci, we came to know that the centre point is \[\left( {0,0} \right)\]
Now we can write the equation \[\left( 1 \right)\] as
\[\dfrac{{{{(x - 0)}^2}}}{{{a^2}}} + \dfrac{{{{(y - 0)}^2}}}{{{b^2}}} = 1\]
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{{{\left( x \right)}^2}}}{{{a^2}}} + \dfrac{{{{\left( y \right)}^2}}}{{{b^2}}} = 1......(3)\]
Now we have to find the value of a and b, to get the equation of ellipse.
We know that the length of the major axis is \[2a\].
We also know that the given length of the major axis \[ = {\text{ 8}}\].
Now we can substitute the length of the major axis to the given length, we get
\[ \Rightarrow 2a = 8\]
\[ \Rightarrow a = \dfrac{8}{2}\]
\[ \Rightarrow a = 4\]
Now we have to find the value of b.
We know that the formula to find focus is
\[{c^2} = {a^2} - {b^2}\]
We already know the value of c from \[\left( 2 \right)\]
As we know the focus point and the value of a, we can find the value of b
\[{2^2} = {4^2} - {b^2}\]
\[ \Rightarrow {b^2} = {4^2} - {2^2}\]
\[ \Rightarrow b = \sqrt {{4^2} - {2^2}} \]
\[ \Rightarrow b = \sqrt {16 - 4} \]
\[ \Rightarrow b = \sqrt {12} \]
Now we got the value of a and b, we can substitute it in the equation (3), we get
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{{{(x)}^2}}}{{{{\left( 4 \right)}^2}}} + \dfrac{{{{(y)}^2}}}{{{{\left( {\sqrt {12} } \right)}^2}}} = 1\]
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{{{(x)}^2}}}{{16}} + \dfrac{{{{(y)}^2}}}{{12}} = 1\]
Therefore, the equation of the ellipse is\[\dfrac{{{{(x)}^2}}}{{16}} + \dfrac{{{{(y)}^2}}}{{12}} = 1\]
Note:
In these types of problems, it is necessary to check for the centre point, in this problem it is the origin, if the centre point is not the origin, we will get a different solution. Students make mistakes by takes major axis as 2b instead of 2a.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




