
Find the eccentricity of the ellipse $\dfrac{{{x^2}}}{{{a^2}}} + \dfrac{{{y^2}}}{{{b^2}}} = 1$ where B is an end point of a minor axis, S and S’ are foci such that $\vartriangle BSS'$ is an equilateral triangle.
Answer
585.3k+ views
Hint: Ellipse of the form $\dfrac{{{x^2}}}{{{a^2}}} + \dfrac{{{y^2}}}{{{b^2}}} = 1$ is the one with semi major axis of length a parallel to x axis and semi minor with length b parallel to y axis. Eccentricity of an ellipse is the ratio of the distance between the centre and each focus of the ellipse to the semi major axis of the ellipse. That is $e = \dfrac{c}{a}$ . Or we have another formula to find the eccentricity e, ${e^2} = 1 - \dfrac{{{b^2}}}{{{a^2}}}$
Complete step-by-step answer:
Step 1: Let us represent the given data as a picture:
Step 2: Given that S and S’ are foci and B is the end point of the minor axis such that BSS’ forms an equilateral triangle. Thus our image will be,
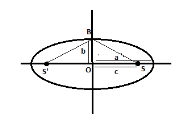
For an ellipse $\dfrac{{{x^2}}}{{{a^2}}} + \dfrac{{{y^2}}}{{{b^2}}} = 1$, with semi minor axis length a and eccentricity e, the focus S=(ae,0) and S’=(-ae,0) and B=(0,b). As the triangle is equilateral, all three sides will be equal. Thus,
SS’=S’B implies ${(SS')^2} = {(S'B)^2}$ … Formula1
where SS’ is the distance between the foci which is ae+ae=2ae and applying Pythagoras theorem in the triangle OBS’, square of hypotenuse = sum of squares of base and altitude implies,
$
{(S'B)^2} = {(OS')^2} + {(OB)^2} \\
= {(ae)^2} + {b^2} \\
$
Thus formula1 will be reframed as, ${(2ae)^2} = {(ae)^2} + {b^2}$
Step 3: Simplifying the above we get,
$
4{(ae)^2} - {(ae)^2} = {b^2} \\
3{a^2}{e^2} = {b^2} \\
$
As we need the eccentricity e, we solve with respect to e.
$3{e^2} = \dfrac{{{b^2}}}{{{a^2}}}$ … Formula2
Step 4: Recalling the formula for eccentricity of an ellipse $\dfrac{{{x^2}}}{{{a^2}}} + \dfrac{{{y^2}}}{{{b^2}}} = 1$,
${e^2} = 1 - \dfrac{{{b^2}}}{{{a^2}}}$… Formula 3
Substituting Formula 2 in Formula 3 we get, ${e^2} = 1 - 3{e^2}$
Implies
$
4{e^2} = 1 \\
e = \sqrt {\dfrac{1}{4}} \\
$
$e = \dfrac{1}{2}$
Final Answer: Eccentricity , $e = \dfrac{1}{2}$
Note: Other form of ellipse is $\dfrac{{{x^2}}}{{{b^2}}} + \dfrac{{{y^2}}}{{{a^2}}} = 1$with the major axis along y axis and minor along x axis. Its foci will be (0, ae) and (0, -ae). Thus in general, the ellipse centred at (h, k) can be represented by the formula$\dfrac{{{{(x - h)}^2}}}{{{a^2}}} + \dfrac{{{{(y - k)}^2}}}{{{b^2}}} = 1$ or vise versa according to the axis where the ellipse is oriented.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Step 1: Let us represent the given data as a picture:

Step 2: Given that S and S’ are foci and B is the end point of the minor axis such that BSS’ forms an equilateral triangle. Thus our image will be,

For an ellipse $\dfrac{{{x^2}}}{{{a^2}}} + \dfrac{{{y^2}}}{{{b^2}}} = 1$, with semi minor axis length a and eccentricity e, the focus S=(ae,0) and S’=(-ae,0) and B=(0,b). As the triangle is equilateral, all three sides will be equal. Thus,
SS’=S’B implies ${(SS')^2} = {(S'B)^2}$ … Formula1
where SS’ is the distance between the foci which is ae+ae=2ae and applying Pythagoras theorem in the triangle OBS’, square of hypotenuse = sum of squares of base and altitude implies,
$
{(S'B)^2} = {(OS')^2} + {(OB)^2} \\
= {(ae)^2} + {b^2} \\
$
Thus formula1 will be reframed as, ${(2ae)^2} = {(ae)^2} + {b^2}$
Step 3: Simplifying the above we get,
$
4{(ae)^2} - {(ae)^2} = {b^2} \\
3{a^2}{e^2} = {b^2} \\
$
As we need the eccentricity e, we solve with respect to e.
$3{e^2} = \dfrac{{{b^2}}}{{{a^2}}}$ … Formula2
Step 4: Recalling the formula for eccentricity of an ellipse $\dfrac{{{x^2}}}{{{a^2}}} + \dfrac{{{y^2}}}{{{b^2}}} = 1$,
${e^2} = 1 - \dfrac{{{b^2}}}{{{a^2}}}$… Formula 3
Substituting Formula 2 in Formula 3 we get, ${e^2} = 1 - 3{e^2}$
Implies
$
4{e^2} = 1 \\
e = \sqrt {\dfrac{1}{4}} \\
$
$e = \dfrac{1}{2}$
Final Answer: Eccentricity , $e = \dfrac{1}{2}$
Note: Other form of ellipse is $\dfrac{{{x^2}}}{{{b^2}}} + \dfrac{{{y^2}}}{{{a^2}}} = 1$with the major axis along y axis and minor along x axis. Its foci will be (0, ae) and (0, -ae). Thus in general, the ellipse centred at (h, k) can be represented by the formula$\dfrac{{{{(x - h)}^2}}}{{{a^2}}} + \dfrac{{{{(y - k)}^2}}}{{{b^2}}} = 1$ or vise versa according to the axis where the ellipse is oriented.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Accountancy: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

10 examples of friction in our daily life




