
Find the domain and range of the following real functions: $f\left( x \right)=\left| x \right|$.
Answer
569.4k+ views
Hint: We first need to define the modulus function and explain how that function works. We draw the function on a graph and observe the domain and range of that function. We also expand the function in its simplest form. We also confirm the range and domain using mathematical expressions.
Complete step by step answer:
The given function $f\left( x \right)=\left| x \right|$ defines the modulus function which gives the positive value back as the result of any number that belongs in the real number domain.
$f\left( x \right)=\left| x \right|$ is a continuous function and we can take any number within real number range to apply the function.
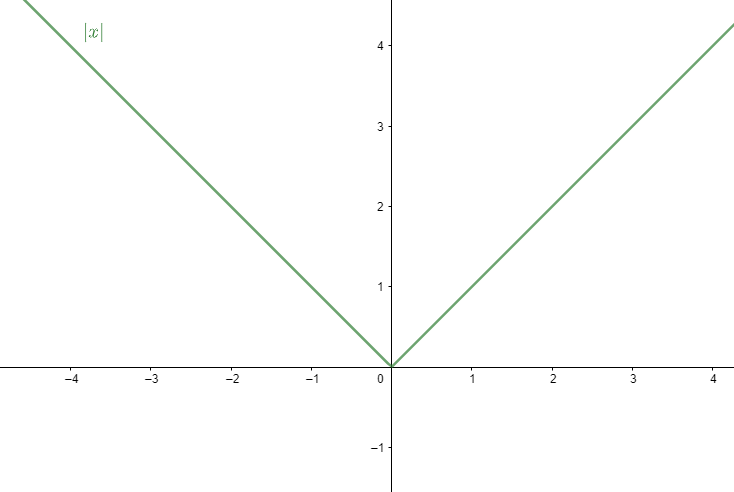
So, the domain of the function $f\left( x \right)=\left| x \right|$ is $\mathbb{R}$.
Now we expand the function in its simplest form.
$f\left( x \right)=\left| x \right|=\left\{ \begin{align}
& -x\left( x<0 \right) \\
& x\left( x\ge 0 \right) \\
\end{align} \right.$
So, for all value of $x<0$, $f\left( x \right)=\left| x \right|>0$ and for all value of $x\ge 0$, $f\left( x \right)=\left| x \right|\ge 0$.
The graph also shows that value of y is always $y=f\left( x \right)=\left| x \right|\ge 0$.
Therefore, $\forall x\in \mathbb{R}$, the range of $f\left( x \right)=\left| x \right|\ge 0$ which means $f\left( x \right)=\left| x \right|\in \left[ 0,\infty \right)$.
Let’s take an example to get a clear idea about $f\left( x \right)=\left| x \right|$.
We take values of x as $x=-1,-34,0,5,10$. For the values of x, we find
$f\left( -1 \right)=\left| -1 \right|=1$, $f\left( -34 \right)=\left| -34 \right|=34$, $f\left( 0 \right)=\left| 0 \right|=0$, $f\left( 5 \right)=\left| 5 \right|=5$, $f\left( 10 \right)=\left| 10 \right|=10$.
For all given values we took the number without any sign. For negative values, we eliminated the negative sign and for positive values, we took the number itself.
Note:
Although the graph is continuous at all points in $\mathbb{R}$, it’s not differentiable at all points. At point $x=0$, function $f\left( x \right)=\left| x \right|$ is not differentiable. The modulus function brings out the positive part of any value. So, $f\left( x \right)=\left| x \right|$ can never be negative.
Complete step by step answer:
The given function $f\left( x \right)=\left| x \right|$ defines the modulus function which gives the positive value back as the result of any number that belongs in the real number domain.
$f\left( x \right)=\left| x \right|$ is a continuous function and we can take any number within real number range to apply the function.

So, the domain of the function $f\left( x \right)=\left| x \right|$ is $\mathbb{R}$.
Now we expand the function in its simplest form.
$f\left( x \right)=\left| x \right|=\left\{ \begin{align}
& -x\left( x<0 \right) \\
& x\left( x\ge 0 \right) \\
\end{align} \right.$
So, for all value of $x<0$, $f\left( x \right)=\left| x \right|>0$ and for all value of $x\ge 0$, $f\left( x \right)=\left| x \right|\ge 0$.
The graph also shows that value of y is always $y=f\left( x \right)=\left| x \right|\ge 0$.
Therefore, $\forall x\in \mathbb{R}$, the range of $f\left( x \right)=\left| x \right|\ge 0$ which means $f\left( x \right)=\left| x \right|\in \left[ 0,\infty \right)$.
Let’s take an example to get a clear idea about $f\left( x \right)=\left| x \right|$.
We take values of x as $x=-1,-34,0,5,10$. For the values of x, we find
$f\left( -1 \right)=\left| -1 \right|=1$, $f\left( -34 \right)=\left| -34 \right|=34$, $f\left( 0 \right)=\left| 0 \right|=0$, $f\left( 5 \right)=\left| 5 \right|=5$, $f\left( 10 \right)=\left| 10 \right|=10$.
For all given values we took the number without any sign. For negative values, we eliminated the negative sign and for positive values, we took the number itself.
Note:
Although the graph is continuous at all points in $\mathbb{R}$, it’s not differentiable at all points. At point $x=0$, function $f\left( x \right)=\left| x \right|$ is not differentiable. The modulus function brings out the positive part of any value. So, $f\left( x \right)=\left| x \right|$ can never be negative.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

A moving boat is observed from the top of a 150 m high class 10 maths CBSE




