
How do you find the derivative of ${(\tan x)^{ - 1}}?$
Answer
558.9k+ views
Hint:
First look at the function they have given which is ${(\tan x)^{ - 1}}$, now we need to rewrite the function in order to find the derivative of the function. So ${(\tan x)^{ - 1}}$ can be written as $\dfrac{1}{{\tan x}}$ , now by using trigonometric ratios try to find what is $\dfrac{1}{{\tan x}}$ and find the derivative of that function.
Complete step by step solution:
First look at the function they have given which is ${(\tan x)^{ - 1}}$ , now we need to rewrite the function in order to find the derivative of the function. So ${(\tan x)^{ - 1}}$ can be written as $\dfrac{1}{{\tan x}}$.
Now by using trigonometric ratios try to find what is $\dfrac{1}{{\tan x}}$ to find the derivative of the function.
So consider the below triangle $ABC$ as shown,
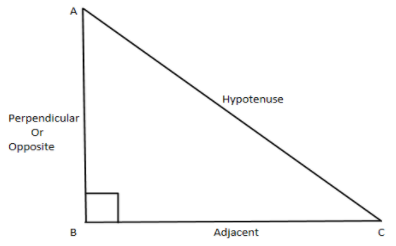
From the above diagram we have $AC = hypotenuse$ , $BC = Adjacent$ and $AB = Opposite$
So, now we can write the trigonometric ratios of functions as follows:
1: Sine function is given by: $\dfrac{{opposite}}{{hypotenuse}}$ .
2: Cosine function is given by: $\dfrac{{adjacent}}{{hypotenuse}}$.
3: Tangent function is given by: $\dfrac{{opposite}}{{adjacent}}$ .
4: Cosecant function is given by: $\dfrac{{hypotenuse}}{{opposite}}$ which is the inverse of sine function, so we can write it in terms of sine function as $\dfrac{1}{{\sin x}}$ .
5: Secant function is given by: $\dfrac{{hypotenuse}}{{adjacent}}$ which is the inverse of cosine function, so we can write it in terms of cosine function as $\dfrac{1}{{\cos x}}$ .
6: Cotangent function is given by: $\dfrac{{adjacent}}{{opposite}}$ which is the inverse of tangent function, so we can write it in terms of tangent function as $\dfrac{1}{{\tan x}}$.
By the above discussion of trigonometric ratios $\dfrac{1}{{\tan x}} = \cot x$
Now differentiate the function $\cot x$ ,
That is $\dfrac{d}{{dx}}\cot x$
We know that the derivative of $\cot x$ is $ - {\csc ^2}x$.
Therefore the answer for the given question is $ - {\csc ^2}x$
Note:
When finding the derivative of $\cot x$ , if you don’t know the derivative of that then try to rewrite the function as $\cot x = \dfrac{{\cos x}}{{\sin x}}$ and now apply quotient rule to simplify and find the derivative of the same function, you will get the same as above.
First look at the function they have given which is ${(\tan x)^{ - 1}}$, now we need to rewrite the function in order to find the derivative of the function. So ${(\tan x)^{ - 1}}$ can be written as $\dfrac{1}{{\tan x}}$ , now by using trigonometric ratios try to find what is $\dfrac{1}{{\tan x}}$ and find the derivative of that function.
Complete step by step solution:
First look at the function they have given which is ${(\tan x)^{ - 1}}$ , now we need to rewrite the function in order to find the derivative of the function. So ${(\tan x)^{ - 1}}$ can be written as $\dfrac{1}{{\tan x}}$.
Now by using trigonometric ratios try to find what is $\dfrac{1}{{\tan x}}$ to find the derivative of the function.
So consider the below triangle $ABC$ as shown,

From the above diagram we have $AC = hypotenuse$ , $BC = Adjacent$ and $AB = Opposite$
So, now we can write the trigonometric ratios of functions as follows:
1: Sine function is given by: $\dfrac{{opposite}}{{hypotenuse}}$ .
2: Cosine function is given by: $\dfrac{{adjacent}}{{hypotenuse}}$.
3: Tangent function is given by: $\dfrac{{opposite}}{{adjacent}}$ .
4: Cosecant function is given by: $\dfrac{{hypotenuse}}{{opposite}}$ which is the inverse of sine function, so we can write it in terms of sine function as $\dfrac{1}{{\sin x}}$ .
5: Secant function is given by: $\dfrac{{hypotenuse}}{{adjacent}}$ which is the inverse of cosine function, so we can write it in terms of cosine function as $\dfrac{1}{{\cos x}}$ .
6: Cotangent function is given by: $\dfrac{{adjacent}}{{opposite}}$ which is the inverse of tangent function, so we can write it in terms of tangent function as $\dfrac{1}{{\tan x}}$.
By the above discussion of trigonometric ratios $\dfrac{1}{{\tan x}} = \cot x$
Now differentiate the function $\cot x$ ,
That is $\dfrac{d}{{dx}}\cot x$
We know that the derivative of $\cot x$ is $ - {\csc ^2}x$.
Therefore the answer for the given question is $ - {\csc ^2}x$
Note:
When finding the derivative of $\cot x$ , if you don’t know the derivative of that then try to rewrite the function as $\cot x = \dfrac{{\cos x}}{{\sin x}}$ and now apply quotient rule to simplify and find the derivative of the same function, you will get the same as above.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




