
How do you find the critical numbers for \[g\left( t \right) = \left| {3t - 4} \right|\] to determine the maximum and minimum?
Answer
481.5k+ views
Hint: In the above question, we are given a function of \[t\] as \[g\left( t \right) = \left| {3t - 4} \right|\] . We have to find the critical numbers to determine the maximum and minimum of the given function. Critical points of a function are those points for which the value of the derivative of the function is either zero or undefined. First we have to find the derivative of \[g\left( t \right)\] that is \[g'\left( t \right)\] and then put \[g\left( t \right) = 0\] to find the critical point \[{t_0}\] .
Complete step-by-step answer:
Given function is
\[ \Rightarrow g\left( t \right) = \left| {3t - 4} \right|\]
We have to find its critical points to determine the maximum and minimum.
Since, \[g\left( t \right) = \left| {3t - 4} \right|\] , hence we can also write it in the form
\[ \Rightarrow g\left( t \right) = \left| {3t - 4} \right|\]
Or,
\[ \Rightarrow g\left( t \right) = \left\{ \begin{gathered}
3t - 4,{\text{if }}t \geqslant \dfrac{4}{3} \\
4 - 3t,{\text{if }}t < \dfrac{4}{3} \\
\end{gathered} \right.\]
Now, differentiating the function \[g\left( t \right)\] once with respect to \[t\] , we get
\[ \Rightarrow g'\left( t \right) = \left\{ \begin{gathered}
3,{\text{if }}t > \dfrac{4}{3} \\
- 3,{\text{if }}t < \dfrac{4}{3} \\
\end{gathered} \right.\]
Now, note that the derivative \[g'\left( t \right)\] is either \[3\] or \[ - 3\] for the values \[t > \dfrac{4}{3}\] and \[t < \dfrac{4}{3}\] but it is not defined for the value \[t = \dfrac{4}{3}\] .
Hence, \[g'\left( t \right)\] is never equal to zero and also \[g'\left( t \right)\] is not differentiable at \[t = \dfrac{4}{3}\] .
Hence, here \[t = \dfrac{4}{3}\] is the only critical point for the function \[g\left( t \right) = \left| {3t - 4} \right|\] .
That means the function \[g\left( t \right)\] has either minima or maxima on the point \[t = \dfrac{4}{3}\] .
Also the function is a modulus function, hence it is always non-negative.
Therefore, it will be minimum only when \[g\left( t \right) = 0\] at \[t = \dfrac{4}{3}\] .
We can observe that the function \[g\left( t \right)\] is decreasing on the left of \[t = \dfrac{4}{3}\] and increasing on the right of \[t = \dfrac{4}{3}\] .
Therefore, \[g\left( t \right)\] has local minima at \[t = \dfrac{4}{3}\] .
The minimum value is given by \[g\left( {\dfrac{4}{3}} \right)\] that is \[0\] .
Hence, \[g\left( {\dfrac{4}{3}} \right) = 0\] is the local minima of \[g\left( t \right) = \left| {3t - 4} \right|\] at the critical point \[t = \dfrac{4}{3}\] .
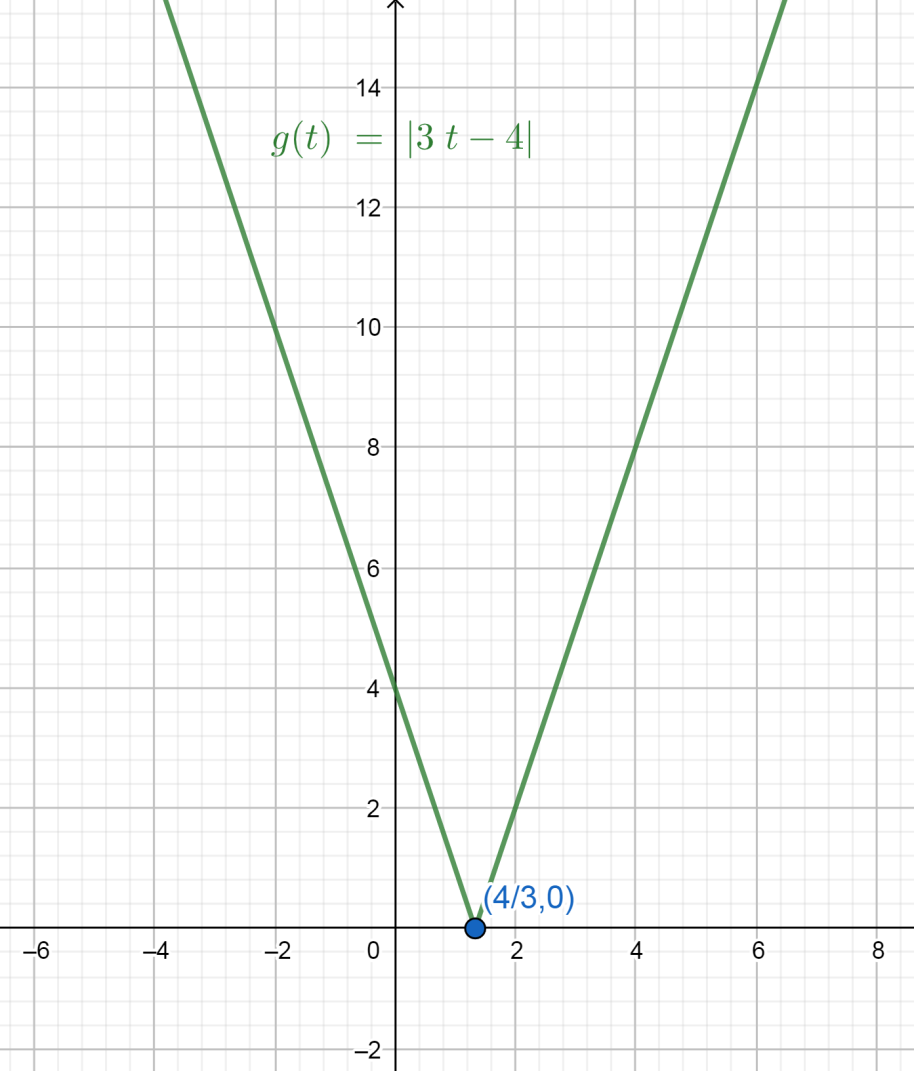
Note: We can also draw the graph for the function \[g\left( t \right) = \left| {3t - 4} \right|\] to see the increasing and decreasing nature of the function. Here, we can note that the function has the minimum value at \[t = \dfrac{4}{3}\] .
The first derivative of a point is the slope of the tangent line at that point. When the slope of the tangent line is 0, the point is either a local minimum or a local maximum. Thus when the first derivative of a point is 0, the point is the location of a local minimum or maximum. The function either has local minima or local maxima at the critical point \[{x_0}\] . If then it has local maxima at \[{x_0}\] and if then the function has local minima at the critical point \[{x_0}\] .
Complete step-by-step answer:
Given function is
\[ \Rightarrow g\left( t \right) = \left| {3t - 4} \right|\]
We have to find its critical points to determine the maximum and minimum.
Since, \[g\left( t \right) = \left| {3t - 4} \right|\] , hence we can also write it in the form
\[ \Rightarrow g\left( t \right) = \left| {3t - 4} \right|\]
Or,
\[ \Rightarrow g\left( t \right) = \left\{ \begin{gathered}
3t - 4,{\text{if }}t \geqslant \dfrac{4}{3} \\
4 - 3t,{\text{if }}t < \dfrac{4}{3} \\
\end{gathered} \right.\]
Now, differentiating the function \[g\left( t \right)\] once with respect to \[t\] , we get
\[ \Rightarrow g'\left( t \right) = \left\{ \begin{gathered}
3,{\text{if }}t > \dfrac{4}{3} \\
- 3,{\text{if }}t < \dfrac{4}{3} \\
\end{gathered} \right.\]
Now, note that the derivative \[g'\left( t \right)\] is either \[3\] or \[ - 3\] for the values \[t > \dfrac{4}{3}\] and \[t < \dfrac{4}{3}\] but it is not defined for the value \[t = \dfrac{4}{3}\] .
Hence, \[g'\left( t \right)\] is never equal to zero and also \[g'\left( t \right)\] is not differentiable at \[t = \dfrac{4}{3}\] .
Hence, here \[t = \dfrac{4}{3}\] is the only critical point for the function \[g\left( t \right) = \left| {3t - 4} \right|\] .
That means the function \[g\left( t \right)\] has either minima or maxima on the point \[t = \dfrac{4}{3}\] .
Also the function is a modulus function, hence it is always non-negative.
Therefore, it will be minimum only when \[g\left( t \right) = 0\] at \[t = \dfrac{4}{3}\] .
We can observe that the function \[g\left( t \right)\] is decreasing on the left of \[t = \dfrac{4}{3}\] and increasing on the right of \[t = \dfrac{4}{3}\] .
Therefore, \[g\left( t \right)\] has local minima at \[t = \dfrac{4}{3}\] .
The minimum value is given by \[g\left( {\dfrac{4}{3}} \right)\] that is \[0\] .
Hence, \[g\left( {\dfrac{4}{3}} \right) = 0\] is the local minima of \[g\left( t \right) = \left| {3t - 4} \right|\] at the critical point \[t = \dfrac{4}{3}\] .
Note: We can also draw the graph for the function \[g\left( t \right) = \left| {3t - 4} \right|\] to see the increasing and decreasing nature of the function. Here, we can note that the function has the minimum value at \[t = \dfrac{4}{3}\] .

The first derivative of a point is the slope of the tangent line at that point. When the slope of the tangent line is 0, the point is either a local minimum or a local maximum. Thus when the first derivative of a point is 0, the point is the location of a local minimum or maximum. The function either has local minima or local maxima at the critical point \[{x_0}\] . If then it has local maxima at \[{x_0}\] and if then the function has local minima at the critical point \[{x_0}\] .
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Accountancy: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

10 examples of friction in our daily life




