
How do you find the critical numbers for \[f\left( x \right) = 3{x^4} + 4{x^3} - 12{x^2} + 5\] to determine the maximum and minimum?
Answer
536.1k+ views
Hint: In the given function we need to find the critical numbers such that we need to find the derivative of the given function and then factor out the term, to get the critical numbers and then substitute the numbers in the function to determine the maximum and minimum value of the function.
Complete step by step solution:
Given,
\[f\left( x \right) = 3{x^4} + 4{x^3} - 12{x^2} + 5\]
And the first derivative of the given function is:
\[f'\left( x \right) = 12{x^3} + 12{x^2} - 24x\]
which can be factored as:
\[ = \left( {12} \right)\left( x \right)\left( {{x^2} + 1x - 2} \right)\]
We can consider that the obtained equation is of the form \[a{x^2} + bx + c\], by which we can easily find the factors of the equation using the AC method.
\[ = \left( {12} \right)\left( x \right)\left( {{x^2} + 2x - 1x - 2} \right)\]
The pair of integers we need to find for the product is c and whose sum is b, in which here the product is -2 and sum is 1.
\[ = \left( {12} \right)\left( x \right)\left( {x + 2} \right)\left( {x - 1} \right)\]
Which implies the critical points (when \[f'\left( x \right) = 0\]) occur when \[x = 0\] and the factors,
\[\left( {x + 2} \right) = 0\]
\[\left( {x - 1} \right) = 0\]
Now let us solve for the first factor i.e.,
\[\left( {x + 2} \right) = 0\]
Therefore, we get
\[x = - 2\]
Now let us solve for the second factor i.e.,
\[\left( {x - 1} \right) = 0\]
Therefore, we get
\[x = + 1\]
Therefore, the critical points occur at -2, 0 and +1 i.e., \[x \in \left\{ { - 2,0,1} \right\}\].
You need to determine if each of these critical points is a minimum or maximum by evaluating the second derivative of the function at each critical value.
\[f''\left( x \right) = 36{x^2} + 24x - 24\]
Hence, now put the values of x at \[x \in \left\{ { - 2,0,1} \right\}\], in the obtained function \[f''\left( x \right) = 36{x^2} + 24x - 24\]
At \[x = - 2\]
\[ \Rightarrow f''\left( { - 2} \right) = 36{\left( { - 2} \right)^2} + 24\left( { - 2} \right) - 24\]
Evaluate the terms, we get:
\[ \Rightarrow f''\left( { - 2} \right) = 144 - 48 - 24\]
\[ \Rightarrow f''\left( { - 2} \right) = + 72\]
As, the function at \[x = - 2\] we get \[f''\left( x \right) > 0\], hence it’s a minimum.
At \[x = 0\]
\[ \Rightarrow f''\left( 0 \right) = 36{\left( 0 \right)^2} + 24\left( 0 \right) - 24\]
Evaluate the terms, we get:
\[ \Rightarrow f''\left( 0 \right) = 0 + 0 - 24\]
\[ \Rightarrow f''\left( 0 \right) = - 24\]
As, the function at \[x = 0\] we get \[f''\left( x \right) < 0\], hence it’s a maximum.
At \[x = + 1\]
\[ \Rightarrow f''\left( 1 \right) = 36{\left( 1 \right)^2} + 24\left( 1 \right) - 24\]
Evaluate the terms, we get:
\[ \Rightarrow f''\left( 1 \right) = 36 + 24 - 24\]
\[ \Rightarrow f''\left( 1 \right) = 36\]
As, the function at \[x = + 1\] we get \[f''\left( x \right) > 0\], hence it’s a minimum.
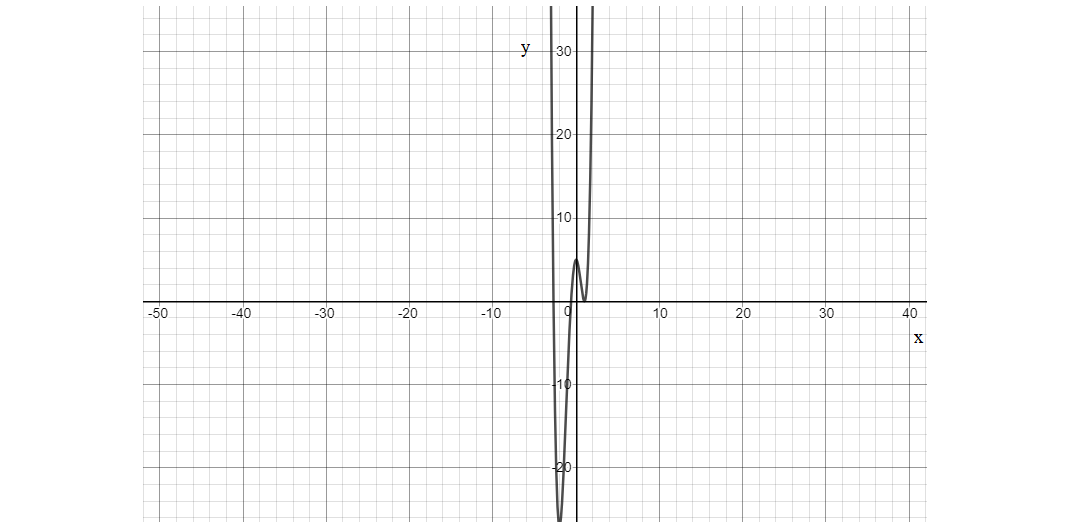
Hence, the graph is shown as:
Note: The key point to note is that the critical point occurs where the derivative of the function is equal to zero and if the function value is greater than zero indicate a local minimum; if function value less than zero indicate a local maximum and if function value equal to zero indicate an inflection point i.e., \[f''\left( x \right) > 0\], it’s a minimum, \[f''\left( x \right) < 0\], it’s a maximum and \[f''\left( x \right) = 0\], it is an inflection point.
Complete step by step solution:
Given,
\[f\left( x \right) = 3{x^4} + 4{x^3} - 12{x^2} + 5\]
And the first derivative of the given function is:
\[f'\left( x \right) = 12{x^3} + 12{x^2} - 24x\]
which can be factored as:
\[ = \left( {12} \right)\left( x \right)\left( {{x^2} + 1x - 2} \right)\]
We can consider that the obtained equation is of the form \[a{x^2} + bx + c\], by which we can easily find the factors of the equation using the AC method.
\[ = \left( {12} \right)\left( x \right)\left( {{x^2} + 2x - 1x - 2} \right)\]
The pair of integers we need to find for the product is c and whose sum is b, in which here the product is -2 and sum is 1.
\[ = \left( {12} \right)\left( x \right)\left( {x + 2} \right)\left( {x - 1} \right)\]
Which implies the critical points (when \[f'\left( x \right) = 0\]) occur when \[x = 0\] and the factors,
\[\left( {x + 2} \right) = 0\]
\[\left( {x - 1} \right) = 0\]
Now let us solve for the first factor i.e.,
\[\left( {x + 2} \right) = 0\]
Therefore, we get
\[x = - 2\]
Now let us solve for the second factor i.e.,
\[\left( {x - 1} \right) = 0\]
Therefore, we get
\[x = + 1\]
Therefore, the critical points occur at -2, 0 and +1 i.e., \[x \in \left\{ { - 2,0,1} \right\}\].
You need to determine if each of these critical points is a minimum or maximum by evaluating the second derivative of the function at each critical value.
\[f''\left( x \right) = 36{x^2} + 24x - 24\]
Hence, now put the values of x at \[x \in \left\{ { - 2,0,1} \right\}\], in the obtained function \[f''\left( x \right) = 36{x^2} + 24x - 24\]
At \[x = - 2\]
\[ \Rightarrow f''\left( { - 2} \right) = 36{\left( { - 2} \right)^2} + 24\left( { - 2} \right) - 24\]
Evaluate the terms, we get:
\[ \Rightarrow f''\left( { - 2} \right) = 144 - 48 - 24\]
\[ \Rightarrow f''\left( { - 2} \right) = + 72\]
As, the function at \[x = - 2\] we get \[f''\left( x \right) > 0\], hence it’s a minimum.
At \[x = 0\]
\[ \Rightarrow f''\left( 0 \right) = 36{\left( 0 \right)^2} + 24\left( 0 \right) - 24\]
Evaluate the terms, we get:
\[ \Rightarrow f''\left( 0 \right) = 0 + 0 - 24\]
\[ \Rightarrow f''\left( 0 \right) = - 24\]
As, the function at \[x = 0\] we get \[f''\left( x \right) < 0\], hence it’s a maximum.
At \[x = + 1\]
\[ \Rightarrow f''\left( 1 \right) = 36{\left( 1 \right)^2} + 24\left( 1 \right) - 24\]
Evaluate the terms, we get:
\[ \Rightarrow f''\left( 1 \right) = 36 + 24 - 24\]
\[ \Rightarrow f''\left( 1 \right) = 36\]
As, the function at \[x = + 1\] we get \[f''\left( x \right) > 0\], hence it’s a minimum.
Hence, the graph is shown as:

Note: The key point to note is that the critical point occurs where the derivative of the function is equal to zero and if the function value is greater than zero indicate a local minimum; if function value less than zero indicate a local maximum and if function value equal to zero indicate an inflection point i.e., \[f''\left( x \right) > 0\], it’s a minimum, \[f''\left( x \right) < 0\], it’s a maximum and \[f''\left( x \right) = 0\], it is an inflection point.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Chemistry: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 12 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Complete reduction of benzene diazonium chloride with class 12 chemistry CBSE

How can you identify optical isomers class 12 chemistry CBSE

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between homogeneous and heterogeneous class 12 chemistry CBSE




