
How can you find the critical angle of water? Explain your steps briefly.
Answer
593.7k+ views
Hint: The critical angle of water is the angle of incidence of a light ray traveling from the denser medium to rarer medium such that the angle of refraction of the light ray is equal to 90\[^\circ \]. Using Snell’s law of refraction, we can find the critical angle for water.
Formula used:
Snell’s law of refraction defines the refractive index of a medium in the following way:
$\mu = \dfrac{{\sin i}}{{\sin r}}$
Here $\mu $ is used to represent the refractive index of a medium, ‘i’ represents the angle of incidence while r represents the angle of refraction.
Complete step-by-step solution:
The critical angle of a medium can be defined as the angle of incidence of a light ray in the denser medium which is such that the angle of refraction obtained is equal to 90$^\circ $. This can be represented as shown in the figure.
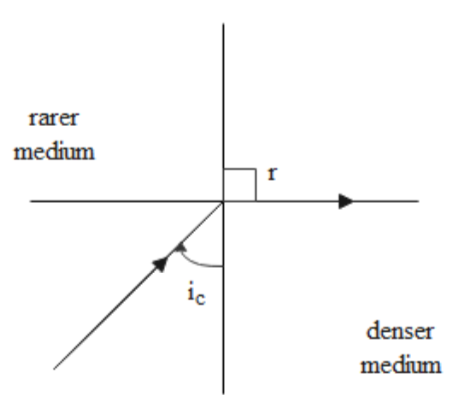
We can find the critical angle of water by using Snell's law. For the critical angle, the angle of refraction is equal to 90$^\circ $. The refractive index of water with respect to air is given as
$\mu = \dfrac{3}{4}$
Using this in Snell law and substituting i by ${i_C}$, we get
$ \mu = \dfrac{{\sin i}}{{\sin r}} \\
\dfrac{3}{4} = \dfrac{{\sin {i_C}}}{{\sin 90^\circ }} = \dfrac{{\sin {i_C}}}{1} \\
\Rightarrow \sin {i_C} = \dfrac{3}{4} = 0.7518 \\
{i_C} = {\sin ^{ - 1}}\left( {0.7518} \right) \\
{i_C} = 48.7^\circ $
This is the required value of the critical angle of water.
Note: If the angle of incidence of the light ray in the denser medium is equal to the critical angle of that medium then the light rays travel along the surface of the interface between two media. But if the angle is greater than the critical angle then total internal reflection takes place while if it’s less than the critical angle the normal refraction of light takes place.
Formula used:
Snell’s law of refraction defines the refractive index of a medium in the following way:
$\mu = \dfrac{{\sin i}}{{\sin r}}$
Here $\mu $ is used to represent the refractive index of a medium, ‘i’ represents the angle of incidence while r represents the angle of refraction.
Complete step-by-step solution:
The critical angle of a medium can be defined as the angle of incidence of a light ray in the denser medium which is such that the angle of refraction obtained is equal to 90$^\circ $. This can be represented as shown in the figure.

We can find the critical angle of water by using Snell's law. For the critical angle, the angle of refraction is equal to 90$^\circ $. The refractive index of water with respect to air is given as
$\mu = \dfrac{3}{4}$
Using this in Snell law and substituting i by ${i_C}$, we get
$ \mu = \dfrac{{\sin i}}{{\sin r}} \\
\dfrac{3}{4} = \dfrac{{\sin {i_C}}}{{\sin 90^\circ }} = \dfrac{{\sin {i_C}}}{1} \\
\Rightarrow \sin {i_C} = \dfrac{3}{4} = 0.7518 \\
{i_C} = {\sin ^{ - 1}}\left( {0.7518} \right) \\
{i_C} = 48.7^\circ $
This is the required value of the critical angle of water.
Note: If the angle of incidence of the light ray in the denser medium is equal to the critical angle of that medium then the light rays travel along the surface of the interface between two media. But if the angle is greater than the critical angle then total internal reflection takes place while if it’s less than the critical angle the normal refraction of light takes place.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

A moving boat is observed from the top of a 150 m high class 10 maths CBSE




