
Find the correct order of $ {\text{p}}{{\text{K}}_{\text{a}}} $ for the following acids:
Acid $ p{K_a} $ Oxalic acid $ {\text{p}}{{\text{K}}_1} $ Malonic acid $ {\text{p}}{{\text{K}}_2} $ Heptanedioic acid $ {\text{p}}{{\text{K}}_3} $
where $ {\text{p}}{{\text{K}}_1} $ , $ {\text{p}}{{\text{K}}_2} $ and $ {\text{p}}{{\text{K}}_3} $ are first ionization constants.
(A) $ {\text{p}}{{\text{K}}_{\text{1}}}{\text{ > p}}{{\text{K}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{ > p}}{{\text{K}}_{\text{3}}} $
(B) $ {\text{p}}{{\text{K}}_{\text{1}}}{\text{ < p}}{{\text{K}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{ < p}}{{\text{K}}_{\text{3}}} $
(C) $ {\text{p}}{{\text{K}}_3}{\text{ > p}}{{\text{K}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{ > p}}{{\text{K}}_1} $
(D) $ {\text{p}}{{\text{K}}_2}{\text{ > p}}{{\text{K}}_1}{\text{ > p}}{{\text{K}}_{\text{3}}} $
| Acid | $ p{K_a} $ |
| Oxalic acid | $ {\text{p}}{{\text{K}}_1} $ |
| Malonic acid | $ {\text{p}}{{\text{K}}_2} $ |
| Heptanedioic acid | $ {\text{p}}{{\text{K}}_3} $ |
Answer
537.6k+ views
Hint : (1) In chemistry, $ {{\text{K}}_{\text{a}}} $ means the acid dissociation constant which is a quantitative measure to determine the strength of an acid.
(2) The negative log of the acid dissociation constant $ {{\text{K}}_{\text{a}}} $ is termed as $ {\text{p}}{{\text{K}}_{\text{a}}} $ and its value is also used to indicate the strength of an acid.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
The $ {\text{p}}{{\text{K}}_{\text{a}}} $ value of an acid is indirectly proportional to its acid strength. This means lower the $ {\text{p}}{{\text{K}}_{\text{a}}} $ value of an acid, higher is its acid strength.
The given three acids are oxalic acid, malonic acid and heptanedioic acid and their $ {\text{p}}{{\text{K}}_{\text{a}}} $ values are $ {\text{p}}{{\text{K}}_1} $ , $ {\text{p}}{{\text{K}}_2} $ and $ {\text{p}}{{\text{K}}_3} $ respectively. We need to find out the order in which the $ {\text{p}}{{\text{K}}_{\text{a}}} $ values of the three given acids are related.
Let us first draw the structures of the three acids.
Oxalic acid is ethanedioic acid and malonic acid is propanedioic acid.
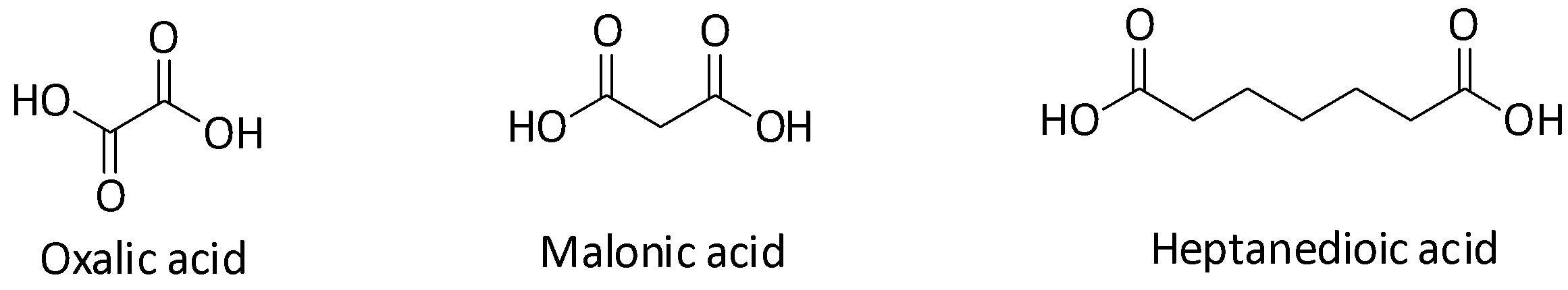
Now, let us first compare the acid strengths of oxalic acid and malonic acid. They have very similar skeletal structures but the difference in their acid strengths is very significant. The inductive effect of the carboxylate ion plays an important role in determining acidity. Groups which exhibit –I effect on a molecule reduce its electron density, making it more electron deficient and hence more acidic. Carboxylate ion group is an electron withdrawing –I group and so it will make the molecule more acidic.
Inductive effect decreases with the increase in the number of atoms between the inductive group and the group on which the inductive effect is being checked on. In other words, inductive effect decreases or gets weaker with increasing distance. In case of oxalic acid or ethanedioic acid, there is only one bond which separates the two carboxylic groups and so they can exert a very strong inductive effect. But in case of malonic acid or propanedioic acid, the two carboxylic groups are separated by one $ {\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}} $ group (two bonds) making the inductive effect weaker in comparison to that of oxalic acid. Thus, oxalic acid is more acidic than malonic acid.
Similarly, if we compare malonic acid and heptanedioic acid, we will see that in heptanedioic acid the inductive effect is further reduced because of the separation by five $ {\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}} $ groups. So, malonic acid is more acidic than heptanedioic acid. Therefore, the acidic strength of the three acids decrease in the order: oxalic acid>malonic acid>heptanedioic acid. Since higher the acid strength, lower the $ {\text{p}}{{\text{K}}_{\text{a}}} $ value, therefore $ {\text{p}}{{\text{K}}_{\text{1}}}{\text{ < p}}{{\text{K}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{ < p}}{{\text{K}}_{\text{3}}} $ .
So, the correct option is (B).
Note :
If we are to find the order of the $ {\text{p}}{{\text{K}}_{\text{a}}} $ values of acids, we must compare their acidic strengths at first because lower the $ {\text{p}}{{\text{K}}_{\text{a}}} $ value, stronger will be the acid. Similarly, the negative logarithm of the dissociation constant of a base is termed as $ {\text{p}}{{\text{K}}_{\text{b}}} $ . The sum of $ {\text{p}}{{\text{K}}_{\text{a}}} $ and $ {\text{p}}{{\text{K}}_{\text{b}}} $ values gives $ {\text{p}}{{\text{K}}_{\text{w}}} $ , where $ {{\text{K}}_{\text{w}}} $ is the ionic product of water.
$ {\text{p}}{{\text{K}}_{\text{a}}} + {\text{p}}{{\text{K}}_{\text{b}}} = {\text{p}}{{\text{K}}_{\text{w}}} $
(2) The negative log of the acid dissociation constant $ {{\text{K}}_{\text{a}}} $ is termed as $ {\text{p}}{{\text{K}}_{\text{a}}} $ and its value is also used to indicate the strength of an acid.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
The $ {\text{p}}{{\text{K}}_{\text{a}}} $ value of an acid is indirectly proportional to its acid strength. This means lower the $ {\text{p}}{{\text{K}}_{\text{a}}} $ value of an acid, higher is its acid strength.
The given three acids are oxalic acid, malonic acid and heptanedioic acid and their $ {\text{p}}{{\text{K}}_{\text{a}}} $ values are $ {\text{p}}{{\text{K}}_1} $ , $ {\text{p}}{{\text{K}}_2} $ and $ {\text{p}}{{\text{K}}_3} $ respectively. We need to find out the order in which the $ {\text{p}}{{\text{K}}_{\text{a}}} $ values of the three given acids are related.
Let us first draw the structures of the three acids.
Oxalic acid is ethanedioic acid and malonic acid is propanedioic acid.

Now, let us first compare the acid strengths of oxalic acid and malonic acid. They have very similar skeletal structures but the difference in their acid strengths is very significant. The inductive effect of the carboxylate ion plays an important role in determining acidity. Groups which exhibit –I effect on a molecule reduce its electron density, making it more electron deficient and hence more acidic. Carboxylate ion group is an electron withdrawing –I group and so it will make the molecule more acidic.
Inductive effect decreases with the increase in the number of atoms between the inductive group and the group on which the inductive effect is being checked on. In other words, inductive effect decreases or gets weaker with increasing distance. In case of oxalic acid or ethanedioic acid, there is only one bond which separates the two carboxylic groups and so they can exert a very strong inductive effect. But in case of malonic acid or propanedioic acid, the two carboxylic groups are separated by one $ {\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}} $ group (two bonds) making the inductive effect weaker in comparison to that of oxalic acid. Thus, oxalic acid is more acidic than malonic acid.
Similarly, if we compare malonic acid and heptanedioic acid, we will see that in heptanedioic acid the inductive effect is further reduced because of the separation by five $ {\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}} $ groups. So, malonic acid is more acidic than heptanedioic acid. Therefore, the acidic strength of the three acids decrease in the order: oxalic acid>malonic acid>heptanedioic acid. Since higher the acid strength, lower the $ {\text{p}}{{\text{K}}_{\text{a}}} $ value, therefore $ {\text{p}}{{\text{K}}_{\text{1}}}{\text{ < p}}{{\text{K}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{ < p}}{{\text{K}}_{\text{3}}} $ .
So, the correct option is (B).
Note :
If we are to find the order of the $ {\text{p}}{{\text{K}}_{\text{a}}} $ values of acids, we must compare their acidic strengths at first because lower the $ {\text{p}}{{\text{K}}_{\text{a}}} $ value, stronger will be the acid. Similarly, the negative logarithm of the dissociation constant of a base is termed as $ {\text{p}}{{\text{K}}_{\text{b}}} $ . The sum of $ {\text{p}}{{\text{K}}_{\text{a}}} $ and $ {\text{p}}{{\text{K}}_{\text{b}}} $ values gives $ {\text{p}}{{\text{K}}_{\text{w}}} $ , where $ {{\text{K}}_{\text{w}}} $ is the ionic product of water.
$ {\text{p}}{{\text{K}}_{\text{a}}} + {\text{p}}{{\text{K}}_{\text{b}}} = {\text{p}}{{\text{K}}_{\text{w}}} $
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




