
Find the centroid of a triangle whose vertices are \[\left( {3,4} \right),\left( { - 7, - 2} \right){\text{ and }}\left( {10, - 5} \right)\].
Answer
491.7k+ views
Hint:Median is a line that joins the midpoint of a side and the opposite vertex of the triangle. The point of intersection of all the three medians of a triangle is called a centroid. It is denoted by \[G\]. From the question we have all the three vertices of the triangle. So, we will use the formula for calculating the centroid of a triangle.
Formula used:
Centroid of a triangle with vertices \[\left( {{x_1},{y_1}} \right),\left( {{x_2},{y_2}} \right){\text{ and }}\left( {{x_3},{y_3}} \right)\] is;
\[G = \left[ {\dfrac{{{x_1} + {x_2} + {x_3}}}{3},\dfrac{{{y_1} + {y_2} + {y_3}}}{3}} \right]\]
Complete step by step answer:
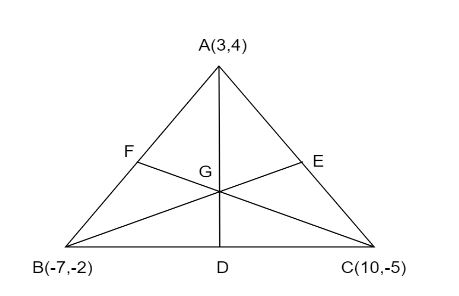
Let \[ABC\] be a triangle with the vertices given in the questions.Let \[AD,BE,CF\] are the medians on the triangle \[ABC\]. We can see from the figure that the medians intersect at point \[G\]. So, \[G\] is the centroid of the triangle \[ABC\].Now we will find the coordinates of \[G\] using the formula.We have;
\[G = \left[ {\dfrac{{{x_1} + {x_2} + {x_3}}}{3},\dfrac{{{y_1} + {y_2} + {y_3}}}{3}} \right]\]
Now we will put the value of \[{x_1},{x_2},{x_3}\] and \[{y_1},{y_2},{y_3}\] from the coordinates of the given vertices. So, we get;
\[ \Rightarrow G = \left[ {\dfrac{{3 - 7 + 10}}{3},\dfrac{{4 - 2 - 5}}{3}} \right]\]
On solving we get;
\[ \Rightarrow G = \left[ {\dfrac{6}{3},\dfrac{{ - 3}}{3}} \right]\]
On dividing we get;
\[ \Rightarrow G = \left[ {2, - 1} \right]\]
Hence the centroid of the triangle is \[\left( {2, - 1} \right)\].
Note:One thing to note here is that the centroid of a triangle cannot lie outside of the triangle. It always lies inside the triangle. Also, in an equilateral triangle the centroid, the circumcentre, the incentre and the orthocentre coincides.The centroid theorem states that the centroid of a triangle is at \[\dfrac{2}{3}\] of the distance from the vertex to the midpoint of the sides. In a square, the point of intersection of the diagonals is the centroid of the square.
Formula used:
Centroid of a triangle with vertices \[\left( {{x_1},{y_1}} \right),\left( {{x_2},{y_2}} \right){\text{ and }}\left( {{x_3},{y_3}} \right)\] is;
\[G = \left[ {\dfrac{{{x_1} + {x_2} + {x_3}}}{3},\dfrac{{{y_1} + {y_2} + {y_3}}}{3}} \right]\]
Complete step by step answer:

Let \[ABC\] be a triangle with the vertices given in the questions.Let \[AD,BE,CF\] are the medians on the triangle \[ABC\]. We can see from the figure that the medians intersect at point \[G\]. So, \[G\] is the centroid of the triangle \[ABC\].Now we will find the coordinates of \[G\] using the formula.We have;
\[G = \left[ {\dfrac{{{x_1} + {x_2} + {x_3}}}{3},\dfrac{{{y_1} + {y_2} + {y_3}}}{3}} \right]\]
Now we will put the value of \[{x_1},{x_2},{x_3}\] and \[{y_1},{y_2},{y_3}\] from the coordinates of the given vertices. So, we get;
\[ \Rightarrow G = \left[ {\dfrac{{3 - 7 + 10}}{3},\dfrac{{4 - 2 - 5}}{3}} \right]\]
On solving we get;
\[ \Rightarrow G = \left[ {\dfrac{6}{3},\dfrac{{ - 3}}{3}} \right]\]
On dividing we get;
\[ \Rightarrow G = \left[ {2, - 1} \right]\]
Hence the centroid of the triangle is \[\left( {2, - 1} \right)\].
Note:One thing to note here is that the centroid of a triangle cannot lie outside of the triangle. It always lies inside the triangle. Also, in an equilateral triangle the centroid, the circumcentre, the incentre and the orthocentre coincides.The centroid theorem states that the centroid of a triangle is at \[\dfrac{2}{3}\] of the distance from the vertex to the midpoint of the sides. In a square, the point of intersection of the diagonals is the centroid of the square.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Accountancy: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 11 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

10 examples of friction in our daily life




