
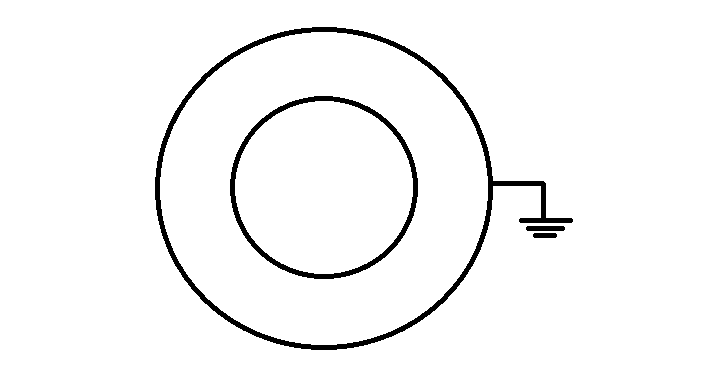
Find the capacitance of this concentric shell.

Answer
589.5k+ views
Hint: If we give + q charged to the inner shell the charge on the outer shell can be determined as the potential of the outer shell is zero due to earthing. We can find the potential of the concentric shells as it is equal to the sum of potential of the inner shell and the outer shell. Potential of a shell is given as$\dfrac{{kq}}{r}$,where k is relative permittivity of dielectric material, q is the charge, r is the radius of the shell.
Step by step answer:Let the radius of inner shell be ‘a’ and that of outer shell be ‘b’ .Let us assume that a charge + q is given to the inner shell. Due to this charge another charge (let q') appears on the outer shell. We know that due to earthing the potential of the outer shell should be equal to zero.
$\begin{gathered}
{V_b} = \dfrac{{kq}}{b} + \dfrac{{kq'}}{b} = 0 \\
q' = - q \\
\end{gathered} $
Therefore the charge q on the outer shell (q’) is equal to –q.
The net potential of the system can be written as the sum of potential of the inner shell and the outer shell.
We know that the potential of the outer shell is equal to zero therefore potential of the system is equal to the potential of the inner shell,$V = {V_a}$.
V$ = \dfrac{{kq}}{a} + \dfrac{{k( - q)}}{b}$
$\Rightarrow kq\left( {\dfrac{1}{a} - \dfrac{1}{b}} \right) = \dfrac{{kq(b - a)}}{{ab}}$
Capacitance is the ratio of charge to potential, $C = \dfrac{q}{V}$.
Therefore the capacitance of the system can be written as$C = \dfrac{q}{{\dfrac{{kq(b - a)}}{{ab}}}} = \dfrac{{ab}}{{k(b - a)}}$
We can write k$ = \dfrac{1}{{4\pi { \in _0}}}$.
Therefore capacitance of this concentric shell can also be written as $C = \dfrac{{4\pi { \in _0}ab}}{{b - a}}$.
Note: When a charged object is grounded, the excess charge is balanced by the transfer of electrons between the charged object and a ground and therefore the potential of the object becomes equal to zero.
Step by step answer:Let the radius of inner shell be ‘a’ and that of outer shell be ‘b’ .Let us assume that a charge + q is given to the inner shell. Due to this charge another charge (let q') appears on the outer shell. We know that due to earthing the potential of the outer shell should be equal to zero.
$\begin{gathered}
{V_b} = \dfrac{{kq}}{b} + \dfrac{{kq'}}{b} = 0 \\
q' = - q \\
\end{gathered} $
Therefore the charge q on the outer shell (q’) is equal to –q.
The net potential of the system can be written as the sum of potential of the inner shell and the outer shell.
We know that the potential of the outer shell is equal to zero therefore potential of the system is equal to the potential of the inner shell,$V = {V_a}$.
V$ = \dfrac{{kq}}{a} + \dfrac{{k( - q)}}{b}$
$\Rightarrow kq\left( {\dfrac{1}{a} - \dfrac{1}{b}} \right) = \dfrac{{kq(b - a)}}{{ab}}$
Capacitance is the ratio of charge to potential, $C = \dfrac{q}{V}$.
Therefore the capacitance of the system can be written as$C = \dfrac{q}{{\dfrac{{kq(b - a)}}{{ab}}}} = \dfrac{{ab}}{{k(b - a)}}$
We can write k$ = \dfrac{1}{{4\pi { \in _0}}}$.
Therefore capacitance of this concentric shell can also be written as $C = \dfrac{{4\pi { \in _0}ab}}{{b - a}}$.
Note: When a charged object is grounded, the excess charge is balanced by the transfer of electrons between the charged object and a ground and therefore the potential of the object becomes equal to zero.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Give 10 examples of unisexual and bisexual flowers

Coming together federation is practiced in A India class 12 social science CBSE

Write the formula to find the shortest distance between class 12 maths CBSE




