
How do you find the base of a right triangle when given the hypotenuse is 14 ft. The angle formed between the hypotenuse and base is 41 degrees?
Answer
555.9k+ views
Hint: First assume the angle formed between the hypotenuse and base as ‘$\alpha $’. Then put the values of angle ‘$\alpha $’ and hypotenuse ‘h’ in the formula $\cos \alpha =\dfrac{b}{h}$. Do the necessary calculation to get the value of ‘b’ which is the required solution.
Complete step by step solution:
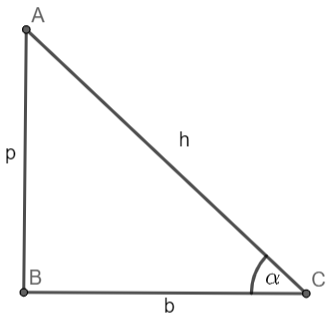
ABC is a right angle triangle with base ‘b’, perpendicular ‘p’ and hypotenuse ‘h’.
Given, the hypotenuse is 14 ft. and the angle formed between the hypotenuse and base is 41 degrees.
Let the angle formed between the hypotenuse and base is ‘$\alpha $’.
So, h=14 ft. and $\alpha ={{41}^{\circ }}$
We know, in right angle triangle ABC $\cos \alpha =\dfrac{BC}{AC}=\dfrac{b}{h}$
Putting the values of angle ‘$\alpha $’ and hypotenuse ‘h’ in $\cos \alpha =\dfrac{b}{h}$, we get
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow \cos 41=\dfrac{b}{14} \\
& \Rightarrow 0.7547\times 14=b \\
& \Rightarrow b=10.566 \\
\end{align}$
Hence the base is 10.566 ft.
This is the required solution of the given question.
Note: Since now we have both the values of hypotenuse and base, we can also find the perpendicular using Pythagoras' theorem. For the above triangle Pythagoras' theorem can be applied as ${{h}^{2}}={{p}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}}$.
Putting the values of ‘h’ and ‘b’ in ${{h}^{2}}={{p}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}}$, we get
\[\begin{align}
& {{14}^{2}}={{p}^{2}}+{{10.566}^{2}} \\
& \Rightarrow 196={{p}^{2}}+111.64 \\
& \Rightarrow 196-111.64={{p}^{2}} \\
& \Rightarrow p=\sqrt{84.36} \\
& \Rightarrow p=9.18 \\
\end{align}\]
Complete step by step solution:

ABC is a right angle triangle with base ‘b’, perpendicular ‘p’ and hypotenuse ‘h’.
Given, the hypotenuse is 14 ft. and the angle formed between the hypotenuse and base is 41 degrees.
Let the angle formed between the hypotenuse and base is ‘$\alpha $’.
So, h=14 ft. and $\alpha ={{41}^{\circ }}$
We know, in right angle triangle ABC $\cos \alpha =\dfrac{BC}{AC}=\dfrac{b}{h}$
Putting the values of angle ‘$\alpha $’ and hypotenuse ‘h’ in $\cos \alpha =\dfrac{b}{h}$, we get
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow \cos 41=\dfrac{b}{14} \\
& \Rightarrow 0.7547\times 14=b \\
& \Rightarrow b=10.566 \\
\end{align}$
Hence the base is 10.566 ft.
This is the required solution of the given question.
Note: Since now we have both the values of hypotenuse and base, we can also find the perpendicular using Pythagoras' theorem. For the above triangle Pythagoras' theorem can be applied as ${{h}^{2}}={{p}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}}$.
Putting the values of ‘h’ and ‘b’ in ${{h}^{2}}={{p}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}}$, we get
\[\begin{align}
& {{14}^{2}}={{p}^{2}}+{{10.566}^{2}} \\
& \Rightarrow 196={{p}^{2}}+111.64 \\
& \Rightarrow 196-111.64={{p}^{2}} \\
& \Rightarrow p=\sqrt{84.36} \\
& \Rightarrow p=9.18 \\
\end{align}\]
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Chemistry: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

Chemical formula of Bleaching powder is A Ca2OCl2 B class 11 chemistry CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

A solution of a substance X is used for white washing class 11 chemistry CBSE

Differentiate between calcination and roasting class 11 chemistry CBSE




