
How do you find the asymptotes for $y = \dfrac{{x + 2}}{{x + 3}}$ ?
Answer
555k+ views
Hint:First we will start by defining the asymptote, properties of asymptote and types of asymptote. Then we apply different conditions to evaluate the value of $x,y$.
Complete step by step answer:
We will first start by defining the asymptotes.
So, an asymptote is a straight line that continually approaches a given curve but does not meet it at any finite distance. There are three types of asymptotes namely: vertical asymptote, horizontal asymptote and oblique asymptote.
Vertical asymptotes occur as a denominator of a rational function tends to zero. Now, to find the equation equate the denominator to zero.
Hence, we substitute $x + 3$ equals to zero.
$
x + 3 = 0 \\
\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,x = - 3 \\
$
Also, if the degree of the numerator and denominator are equal, as in our case both the degrees are $1$. The equation can be found by taking the ratio of leading coefficients.
$
y = \dfrac{1}{1} \\
y = 1 \\
$
Now plot the graph for asymptotes.
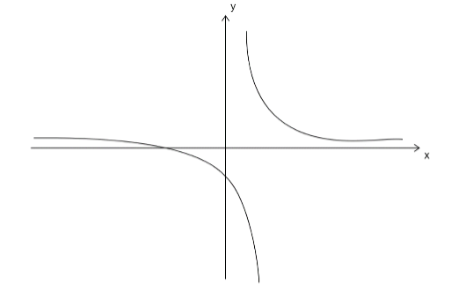
Additional Information:An asymptote is a line that a curve approaches, as it heads towards infinity.
The distance between the curve and the asymptote tends to zero as they head to infinity.
There are a total three types of asymptotes: horizontal, vertical and oblique asymptotes.
Note: Always be sure that all of the terms are of the same type while equating them to zero. While defining types of asymptotes try to define them along with their respective properties. While plotting the graph always draw the axes first and then mark points and then plot the graph.
Complete step by step answer:
We will first start by defining the asymptotes.
So, an asymptote is a straight line that continually approaches a given curve but does not meet it at any finite distance. There are three types of asymptotes namely: vertical asymptote, horizontal asymptote and oblique asymptote.
Vertical asymptotes occur as a denominator of a rational function tends to zero. Now, to find the equation equate the denominator to zero.
Hence, we substitute $x + 3$ equals to zero.
$
x + 3 = 0 \\
\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,x = - 3 \\
$
Also, if the degree of the numerator and denominator are equal, as in our case both the degrees are $1$. The equation can be found by taking the ratio of leading coefficients.
$
y = \dfrac{1}{1} \\
y = 1 \\
$
Now plot the graph for asymptotes.

Additional Information:An asymptote is a line that a curve approaches, as it heads towards infinity.
The distance between the curve and the asymptote tends to zero as they head to infinity.
There are a total three types of asymptotes: horizontal, vertical and oblique asymptotes.
Note: Always be sure that all of the terms are of the same type while equating them to zero. While defining types of asymptotes try to define them along with their respective properties. While plotting the graph always draw the axes first and then mark points and then plot the graph.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

10 examples of friction in our daily life




