
How do you find the asymptote for $y=\csc \left( 4x+\pi \right)$?
Answer
549k+ views
Hint: Now we know that $\csc \left( x \right)=\dfrac{1}{\sin x}$ hence using this we will write the given function in sin. Now we know that asymptote will exit when the denominator is equal to zero. Hence we will find the values of x form which the denominator of the obtained function is 0.
Complete step by step solution:
Now let us first understand the concept of asymptote.
The asymptote is a line to which the curve gets very close to but does not touch.
Hence if the line represents value 3 then the curve approaches 3 bet never reaches the value.
Now to find asymptote and check the values on which the function is not defined and the end points behavior on function.
Hence we can get the asymptote x = a and y = $\underset{x\to \infty }{\mathop{\lim }}\,f\left( x \right)$
Now let us understand this with an example.
Consider the expression $\dfrac{1}{x-1}$
Here we know that the function is not defined on x = 1 and the $\underset{x\to \infty }{\mathop{\lim }}\,f\left( x \right)\to 0$
Hence x = 1 and y = 0 are asymptote of the equation.
Now if we draw the graph of expression we get,
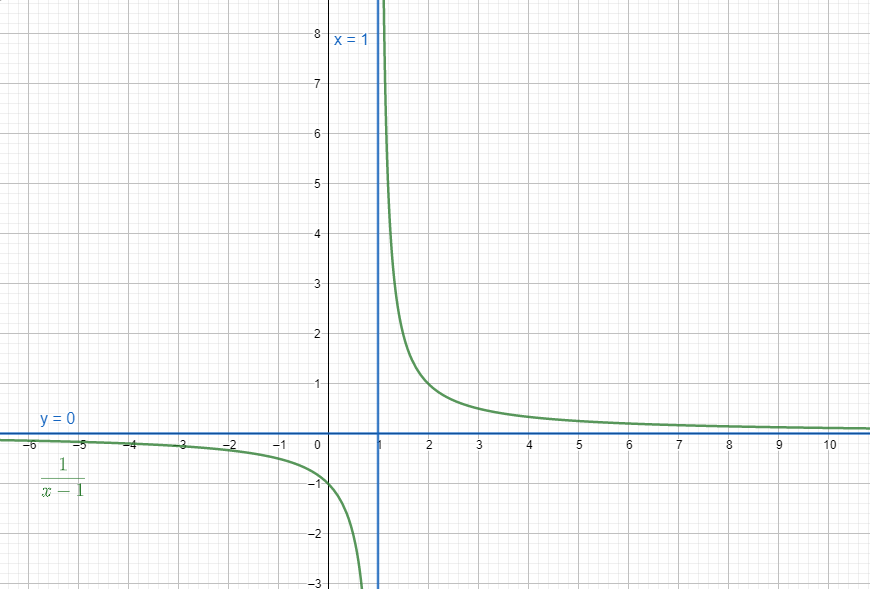
Hence we get an asymptote on y = 0 and x = 1
Now let us consider the given equation $y=\csc \left( 4x+\pi \right)$
Now we know that $\csc \theta =\dfrac{1}{\sin \theta }$ .
Hence we can write the equation as $y=\dfrac{1}{\sin \left( 4x+\pi \right)}$
Now the function is not defined when the value of $\sin \left( 4x+\pi \right)$ is 0.
Now we know that $\sin x=0$ for $x=n\pi $
Hence $\sin \left( 4x+\pi \right)=0$ when $4x+\pi =n\pi $
Now rearranging the terms we get, $4x=\left( 3n-1 \right)\pi $
Hence we have the denominator is 0 form $x=\dfrac{\left( 3n-1 \right)\pi }{4}$
Hence we have a asymptote $x=\dfrac{2\pi }{4},\dfrac{5\pi }{4},\dfrac{8\pi }{4},...$
Note that all these lines are parallel to y axis.
Note: Now note that to find the asymptote of the function of the form $\dfrac{f\left( x \right)}{g\left( x \right)}$ first we check the condition $g\left( x \right)=0$ Now this will given us vertical asymptote which are parallel to y axis. Similarly the value $y=\underset{x\to \infty }{\mathop{\lim }}\,\dfrac{f\left( x \right)}{g\left( x \right)}$ will given us horizontal asymptote which are parallel to x axis.
Note that the given function has no horizontal asymptote.
Complete step by step solution:
Now let us first understand the concept of asymptote.
The asymptote is a line to which the curve gets very close to but does not touch.
Hence if the line represents value 3 then the curve approaches 3 bet never reaches the value.
Now to find asymptote and check the values on which the function is not defined and the end points behavior on function.
Hence we can get the asymptote x = a and y = $\underset{x\to \infty }{\mathop{\lim }}\,f\left( x \right)$
Now let us understand this with an example.
Consider the expression $\dfrac{1}{x-1}$
Here we know that the function is not defined on x = 1 and the $\underset{x\to \infty }{\mathop{\lim }}\,f\left( x \right)\to 0$
Hence x = 1 and y = 0 are asymptote of the equation.
Now if we draw the graph of expression we get,

Hence we get an asymptote on y = 0 and x = 1
Now let us consider the given equation $y=\csc \left( 4x+\pi \right)$
Now we know that $\csc \theta =\dfrac{1}{\sin \theta }$ .
Hence we can write the equation as $y=\dfrac{1}{\sin \left( 4x+\pi \right)}$
Now the function is not defined when the value of $\sin \left( 4x+\pi \right)$ is 0.
Now we know that $\sin x=0$ for $x=n\pi $
Hence $\sin \left( 4x+\pi \right)=0$ when $4x+\pi =n\pi $
Now rearranging the terms we get, $4x=\left( 3n-1 \right)\pi $
Hence we have the denominator is 0 form $x=\dfrac{\left( 3n-1 \right)\pi }{4}$
Hence we have a asymptote $x=\dfrac{2\pi }{4},\dfrac{5\pi }{4},\dfrac{8\pi }{4},...$
Note that all these lines are parallel to y axis.
Note: Now note that to find the asymptote of the function of the form $\dfrac{f\left( x \right)}{g\left( x \right)}$ first we check the condition $g\left( x \right)=0$ Now this will given us vertical asymptote which are parallel to y axis. Similarly the value $y=\underset{x\to \infty }{\mathop{\lim }}\,\dfrac{f\left( x \right)}{g\left( x \right)}$ will given us horizontal asymptote which are parallel to x axis.
Note that the given function has no horizontal asymptote.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

10 examples of friction in our daily life




