
Find the area of the triangle \[ABC\] with \[A\left( {1, - 4} \right)\] and midpoints of sides through \[A\] being \[\left( {2, - 1} \right)\] and \[\left( {0, - 1} \right)\]
Answer
554.4k+ views
Hint:
Here, we are required to find the area of a triangle \[ABC\]. We will use the midpoint formula, and find the other two vertices of the given triangle. Then we will substitute the values in the formula of the area of the triangle and after solving it, we will get the required answer.
Formula Used:
We will use the following formulas:
1) Area of triangle \[ = \dfrac{1}{2}\left[ {{x_1}\left( {{y_2} - {y_3}} \right) + {x_2}\left( {{y_3} - {y_1}} \right) + {x_3}\left( {{y_1} - {y_2}} \right)} \right]\]
2) Midpoint formula: Coordinates of midpoint \[D = \left( {\dfrac{{{A_1} + {A_2}}}{2},\dfrac{{{B_1} + {B_2}}}{2}} \right)\] where, \[\left( {{A_1},{B_1}} \right)\]and \[\left( {{A_2},{B_2}} \right)\] are the coordinates of the points \[A\]and \[B\] respectively.
Complete step by step solution:
We will draw a figure showing all the given points and conditions.
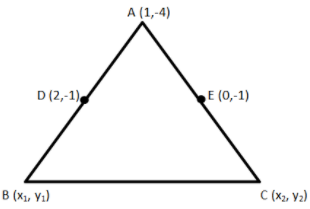
Now, since point \[D\left( {2, - 1} \right)\] is the midpoint of the side \[AB\].
Hence, substituting \[\left( {{A_1},{B_1}} \right) = \left( {1, - 4} \right)\] and \[\left( {{A_2},{B_2}} \right) = \left( {{x_1},{y_1}} \right)\] in the formula \[D = \left( {\dfrac{{{A_1} + {A_2}}}{2},\dfrac{{{B_1} + {B_2}}}{2}} \right)\], we get
Coordinates of point \[D = \left( {\dfrac{{1 + {x_1}}}{2},\dfrac{{ - 4 + {y_1}}}{2}} \right)\]
\[ \Rightarrow \left( {2, - 1} \right) = \left( {\dfrac{{1 + {x_1}}}{2},\dfrac{{ - 4 + {y_1}}}{2}} \right)\]
Now, comparing \[x\]and \[y\]coordinates, we get
\[ \Rightarrow 2 = \dfrac{{1 + {x_1}}}{2}\] and \[ - 1 = \dfrac{{ - 4 + {y_1}}}{2}\]
\[ \Rightarrow {x_1} = 3\] and \[{y_1} = 2\]
Hence, point \[B = \left( {3,2} \right)\].
Similarly, point \[E\left( {0, - 1} \right)\] is the midpoint of the side \[AC\].
Hence, by midpoint formula Coordinates of point \[E = \left( {\dfrac{{{A_1} + {A_2}}}{2},\dfrac{{{B_1} + {B_2}}}{2}} \right)\].
Hence, substituting \[\left( {{A_1},{B_1}} \right) = \left( {1, - 4} \right)\] and \[\left( {{A_2},{B_2}} \right) = \left( {{x_2},{y_2}} \right)\] in the above equation, we get,
Coordinates of point \[E = \left( {\dfrac{{1 + {x_2}}}{2},\dfrac{{ - 4 + {y_2}}}{2}} \right)\]
\[ \Rightarrow \left( {0, - 1} \right) = \left( {\dfrac{{1 + {x_2}}}{2},\dfrac{{ - 4 + {y_2}}}{2}} \right)\]
Now, comparing \[x\] and \[y\] coordinates,
\[ \Rightarrow 0 = \dfrac{{1 + {x_2}}}{2}\] and \[ - 1 = \dfrac{{ - 4 + {y_2}}}{2}\]
\[ \Rightarrow {x_2} = - 1\] and \[{y_2} = 2\]
Hence, point \[C = \left( { - 1,2} \right)\].
Now, substituting \[\left( {{x_1},{y_1}} \right) = \left( {1, - 4} \right)\], \[\left( {{x_2},{y_2}} \right) = \left( {3,2} \right)\] and \[\left( {{x_3},{y_3}} \right) = \left( { - 1,2} \right)\] in the formula area of triangle\[ = \dfrac{1}{2}\left[ {{x_1}\left( {{y_2} - {y_3}} \right) + {x_2}\left( {{y_3} - {y_1}} \right) + {x_3}\left( {{y_1} - {y_2}} \right)} \right]\], we get,
Area of triangle \[ABC\]\[ = \dfrac{1}{2}\left[ {1\left( {2 - 2} \right) + 3\left( {2 + 4} \right) - 1\left( { - 4 - 2} \right)} \right]\]
Subtracting the terms in the bracket, we get
\[ \Rightarrow \] Area of triangle \[ABC\]\[ = \dfrac{1}{2}\left[ {3\left( 6 \right) - 1\left( { - 6} \right)} \right]\]
Multiplying the terms, we get
\[ \Rightarrow \] Area of triangle \[ABC\]\[ = \dfrac{1}{2}\left[ {18 + 6} \right]\]
Simplifying the expression, we get
\[ \Rightarrow \] Area of triangle \[ABC\]\[ = \dfrac{{24}}{2} = 12\]
Therefore, the area of the triangle \[ABC = 12\] square units.
Hence, the area of the triangle \[ABC\] with \[A\left( {1, - 4} \right)\] and midpoints of sides through \[A\] being \[\left( {2, - 1} \right)\] and \[\left( {0, - 1} \right)\] is 12 square units.
Note:
A triangle is a two dimensional geometric shape which has three sides. There are different types of triangle such as equilateral triangle, right-angled triangle, isosceles triangle etc. Here, we have not used the general formula of area of triangle i.e. \[A = \dfrac{1}{2} \times {\rm{base}} \times {\rm{height}}\] because the coordinate of the midpoint of sides is given. So, we have to find the coordinate of the vertices and then substitute these values area of triangle\[ = \dfrac{1}{2}\left[ {{x_1}\left( {{y_2} - {y_3}} \right) + {x_2}\left( {{y_3} - {y_1}} \right) + {x_3}\left( {{y_1} - {y_2}} \right)} \right]\] to get the required area. We might make a mistake by using the coordinate of midpoint as the coordinate of vertices and substituting it in the formula. This will give use the wrong answer.
Here, we are required to find the area of a triangle \[ABC\]. We will use the midpoint formula, and find the other two vertices of the given triangle. Then we will substitute the values in the formula of the area of the triangle and after solving it, we will get the required answer.
Formula Used:
We will use the following formulas:
1) Area of triangle \[ = \dfrac{1}{2}\left[ {{x_1}\left( {{y_2} - {y_3}} \right) + {x_2}\left( {{y_3} - {y_1}} \right) + {x_3}\left( {{y_1} - {y_2}} \right)} \right]\]
2) Midpoint formula: Coordinates of midpoint \[D = \left( {\dfrac{{{A_1} + {A_2}}}{2},\dfrac{{{B_1} + {B_2}}}{2}} \right)\] where, \[\left( {{A_1},{B_1}} \right)\]and \[\left( {{A_2},{B_2}} \right)\] are the coordinates of the points \[A\]and \[B\] respectively.
Complete step by step solution:
We will draw a figure showing all the given points and conditions.

Now, since point \[D\left( {2, - 1} \right)\] is the midpoint of the side \[AB\].
Hence, substituting \[\left( {{A_1},{B_1}} \right) = \left( {1, - 4} \right)\] and \[\left( {{A_2},{B_2}} \right) = \left( {{x_1},{y_1}} \right)\] in the formula \[D = \left( {\dfrac{{{A_1} + {A_2}}}{2},\dfrac{{{B_1} + {B_2}}}{2}} \right)\], we get
Coordinates of point \[D = \left( {\dfrac{{1 + {x_1}}}{2},\dfrac{{ - 4 + {y_1}}}{2}} \right)\]
\[ \Rightarrow \left( {2, - 1} \right) = \left( {\dfrac{{1 + {x_1}}}{2},\dfrac{{ - 4 + {y_1}}}{2}} \right)\]
Now, comparing \[x\]and \[y\]coordinates, we get
\[ \Rightarrow 2 = \dfrac{{1 + {x_1}}}{2}\] and \[ - 1 = \dfrac{{ - 4 + {y_1}}}{2}\]
\[ \Rightarrow {x_1} = 3\] and \[{y_1} = 2\]
Hence, point \[B = \left( {3,2} \right)\].
Similarly, point \[E\left( {0, - 1} \right)\] is the midpoint of the side \[AC\].
Hence, by midpoint formula Coordinates of point \[E = \left( {\dfrac{{{A_1} + {A_2}}}{2},\dfrac{{{B_1} + {B_2}}}{2}} \right)\].
Hence, substituting \[\left( {{A_1},{B_1}} \right) = \left( {1, - 4} \right)\] and \[\left( {{A_2},{B_2}} \right) = \left( {{x_2},{y_2}} \right)\] in the above equation, we get,
Coordinates of point \[E = \left( {\dfrac{{1 + {x_2}}}{2},\dfrac{{ - 4 + {y_2}}}{2}} \right)\]
\[ \Rightarrow \left( {0, - 1} \right) = \left( {\dfrac{{1 + {x_2}}}{2},\dfrac{{ - 4 + {y_2}}}{2}} \right)\]
Now, comparing \[x\] and \[y\] coordinates,
\[ \Rightarrow 0 = \dfrac{{1 + {x_2}}}{2}\] and \[ - 1 = \dfrac{{ - 4 + {y_2}}}{2}\]
\[ \Rightarrow {x_2} = - 1\] and \[{y_2} = 2\]
Hence, point \[C = \left( { - 1,2} \right)\].
Now, substituting \[\left( {{x_1},{y_1}} \right) = \left( {1, - 4} \right)\], \[\left( {{x_2},{y_2}} \right) = \left( {3,2} \right)\] and \[\left( {{x_3},{y_3}} \right) = \left( { - 1,2} \right)\] in the formula area of triangle\[ = \dfrac{1}{2}\left[ {{x_1}\left( {{y_2} - {y_3}} \right) + {x_2}\left( {{y_3} - {y_1}} \right) + {x_3}\left( {{y_1} - {y_2}} \right)} \right]\], we get,
Area of triangle \[ABC\]\[ = \dfrac{1}{2}\left[ {1\left( {2 - 2} \right) + 3\left( {2 + 4} \right) - 1\left( { - 4 - 2} \right)} \right]\]
Subtracting the terms in the bracket, we get
\[ \Rightarrow \] Area of triangle \[ABC\]\[ = \dfrac{1}{2}\left[ {3\left( 6 \right) - 1\left( { - 6} \right)} \right]\]
Multiplying the terms, we get
\[ \Rightarrow \] Area of triangle \[ABC\]\[ = \dfrac{1}{2}\left[ {18 + 6} \right]\]
Simplifying the expression, we get
\[ \Rightarrow \] Area of triangle \[ABC\]\[ = \dfrac{{24}}{2} = 12\]
Therefore, the area of the triangle \[ABC = 12\] square units.
Hence, the area of the triangle \[ABC\] with \[A\left( {1, - 4} \right)\] and midpoints of sides through \[A\] being \[\left( {2, - 1} \right)\] and \[\left( {0, - 1} \right)\] is 12 square units.
Note:
A triangle is a two dimensional geometric shape which has three sides. There are different types of triangle such as equilateral triangle, right-angled triangle, isosceles triangle etc. Here, we have not used the general formula of area of triangle i.e. \[A = \dfrac{1}{2} \times {\rm{base}} \times {\rm{height}}\] because the coordinate of the midpoint of sides is given. So, we have to find the coordinate of the vertices and then substitute these values area of triangle\[ = \dfrac{1}{2}\left[ {{x_1}\left( {{y_2} - {y_3}} \right) + {x_2}\left( {{y_3} - {y_1}} \right) + {x_3}\left( {{y_1} - {y_2}} \right)} \right]\] to get the required area. We might make a mistake by using the coordinate of midpoint as the coordinate of vertices and substituting it in the formula. This will give use the wrong answer.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 9 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 9 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Trending doubts
Find the mode and median of the data 13 16 12 14 1-class-9-maths-CBSE

What were the main changes brought about by the Bolsheviks class 9 social science CBSE

What is the theme or message of the poem The road not class 9 english CBSE

What are the major achievements of the UNO class 9 social science CBSE

Explain the importance of pH in everyday life class 9 chemistry CBSE

Differentiate between parenchyma collenchyma and sclerenchyma class 9 biology CBSE




