
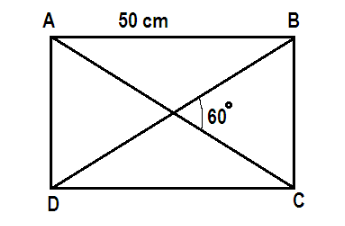
Find the area of the rectangle shown below in the figure:
A. \[\dfrac{{2500}}{{\sqrt 2 }}\]
B. 2500
C. \[\dfrac{{2500}}{{\sqrt 3 }}\]
D. 1250
E. 5000

Answer
570k+ views
Hint: In a rectangle we know that diagonals are equal and bisect each other. In the given problem we have to find the area of the triangle but only one side is given as 50 cm and diagonals are bisecting each other at 60 to get the area we need the other side of the rectangle.
Complete step-by-step answer:
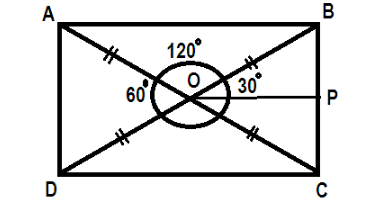
As we know that area of rectangle is:
$ L \times B $ ( where L is the length and B is the breadth of the rectangle)
Also we know that diagonals are bisecting each other. Let us give the intersection point as O. From O draw a line OP which will bisect at P. Hence P is the middle point to side BC and therefore diagonals bisect each other. They will form a triangle BOC which is an equilateral triangle.
Now we will consider triangle BOP in which BP is perpendicular and OP as base.
We know that
$
\Rightarrow \dfrac{P}{B} = \dfrac{{BP}}{{OP}} = \tan {30^ \circ } \\
\therefore \tan {30^ \circ } = \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 3 }} \\
\Rightarrow \dfrac{{BP}}{{OP}} = \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 3 }} \\
$
By cross multiplication we get
$
\Rightarrow BP\sqrt 3 = OP \\
\therefore OP = 25\;cm \\
\Rightarrow BP = \dfrac{{OP}}{{\sqrt 3 }} = \dfrac{{25}}{{\sqrt 3 }}\;cm \;
$
Since P is the mid point to the side BC therefore
$
\Rightarrow BC = 2 \times BP \\
\Rightarrow BC = 2 \times \dfrac{{25}}{{\sqrt 3 }} = \dfrac{{50}}{{\sqrt 3 }}\;cm \\
$
Now the area of the rectangle ABCD= length × breadth
$
\Rightarrow AB \times BC \\
= 50 \times \dfrac{{50}}{{\sqrt 3 }} = \dfrac{{2500}}{{\sqrt 3 }}\;cm \\
$
So, the correct answer is “Option C”.
Note: Rectangle is a quadrilateral whose opposite sides are equal and all the angles are 90°. Diagonal of the rectangle cuts the rectangle into two similar and equal right angle triangles. Its diagonals bisect each other at different angles where one is acute and the other is obtuse.
Complete step-by-step answer:

As we know that area of rectangle is:
$ L \times B $ ( where L is the length and B is the breadth of the rectangle)
Also we know that diagonals are bisecting each other. Let us give the intersection point as O. From O draw a line OP which will bisect at P. Hence P is the middle point to side BC and therefore diagonals bisect each other. They will form a triangle BOC which is an equilateral triangle.
Now we will consider triangle BOP in which BP is perpendicular and OP as base.
We know that
$
\Rightarrow \dfrac{P}{B} = \dfrac{{BP}}{{OP}} = \tan {30^ \circ } \\
\therefore \tan {30^ \circ } = \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 3 }} \\
\Rightarrow \dfrac{{BP}}{{OP}} = \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 3 }} \\
$
By cross multiplication we get
$
\Rightarrow BP\sqrt 3 = OP \\
\therefore OP = 25\;cm \\
\Rightarrow BP = \dfrac{{OP}}{{\sqrt 3 }} = \dfrac{{25}}{{\sqrt 3 }}\;cm \;
$
Since P is the mid point to the side BC therefore
$
\Rightarrow BC = 2 \times BP \\
\Rightarrow BC = 2 \times \dfrac{{25}}{{\sqrt 3 }} = \dfrac{{50}}{{\sqrt 3 }}\;cm \\
$
Now the area of the rectangle ABCD= length × breadth
$
\Rightarrow AB \times BC \\
= 50 \times \dfrac{{50}}{{\sqrt 3 }} = \dfrac{{2500}}{{\sqrt 3 }}\;cm \\
$
So, the correct answer is “Option C”.
Note: Rectangle is a quadrilateral whose opposite sides are equal and all the angles are 90°. Diagonal of the rectangle cuts the rectangle into two similar and equal right angle triangles. Its diagonals bisect each other at different angles where one is acute and the other is obtuse.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




