
Find the area of the given figure:
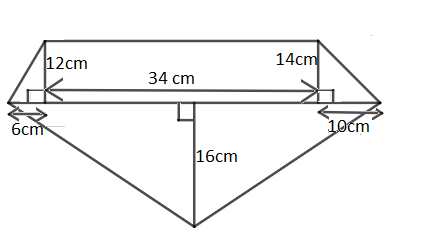

Answer
611.7k+ views
Hint: The given diagram is a composure of small-small two-dimensional mathematical objects. Find the two-dimensional mathematical objects which are put together to form the huge figure. BY adding the areas of the all the figures which we found will be the total area of the given figure. For reference we are giving a case of square with side “s”, area of rectangle with length “l” breadth “b” and area of triangle with height “h”, base length “a”.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Area of square = ${{s}^{2}}$
Area of rectangle = lb
Area of triangle = $\dfrac{1}{2}ah$
Given figure in the question for which area is to be found is:
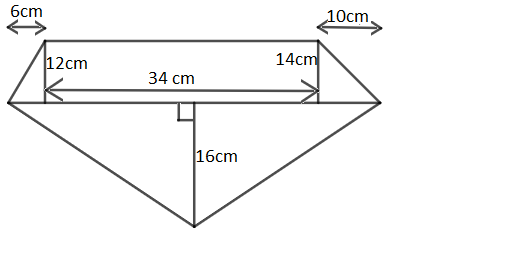
This can be broken into parts:
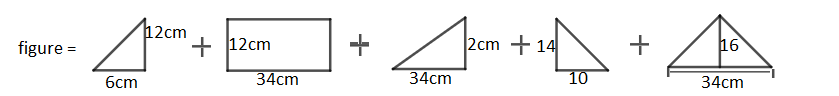
Case 1: On left most you can see a triangle with height 12 cm.
By basic knowledge of geometry, area of triangle with height h and base length $a=\dfrac{1}{2}ah$
Here in our case h = 12 cm, a = 6 cm
By substituting the above values in area formula, we get
$area=\dfrac{1}{2}\times 12\times 6=36c{{m}^{2}}$
Case 2: Drop a perpendicular from 12 cm to 14 cm line now in between a rectangle of 34 cm x 12 cm and a triangle of height 2 cm. Now take the rectangle
By basic knowledge of geometry, area of rectangle with length l and breadth b = lb
Here in our case l = 34 cm, b = 12 cm
So, area = 34 x 12 = 408 $c{{m}^{2}}$
Case 3: After the breakage we get a triangle of height 2 cm.
By basic knowledge of geometry, area of triangle with height ‘h’ and base length ‘a’ = $\dfrac{1}{2}ah$
Here in our case, a = 34 cm, h = 2 cm
$\begin{align}
& area=\dfrac{1}{2}\times 34\times 2 \\
& area=34c{{m}^{2}} \\
\end{align}$
Case 4: On right most you can see a triangle with height 14 cm
In our case h = 14 cm, a = 10 cm
$area=\dfrac{1}{2}\times 14\times 10=70c{{m}^{2}}$
Case 5: On bottom you can see a triangle with height 16 cm.
In our case h = 16 cm, a = 34 + 10 + 6 = 50 cm
$area=\dfrac{1}{2}\times 16\times 50=400c{{m}^{2}}$
Total area = Sum of all cases.
Total area = Case 1 + Case 2 + Case 3 + Case 4 + Case 5
= $\left( 36+408+34+70+400 \right)c{{m}^{2}}=948c{{m}^{2}}$
Hence $948c{{m}^{2}}$ is the total area of the given figure.
Note: Don’t consider the middle figure as a rectangle because opposite sides are 12, 14. So, convert it to rectangle + triangle. Don’t confuse here.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Area of square = ${{s}^{2}}$
Area of rectangle = lb
Area of triangle = $\dfrac{1}{2}ah$
Given figure in the question for which area is to be found is:

This can be broken into parts:

Case 1: On left most you can see a triangle with height 12 cm.
By basic knowledge of geometry, area of triangle with height h and base length $a=\dfrac{1}{2}ah$
Here in our case h = 12 cm, a = 6 cm
By substituting the above values in area formula, we get
$area=\dfrac{1}{2}\times 12\times 6=36c{{m}^{2}}$
Case 2: Drop a perpendicular from 12 cm to 14 cm line now in between a rectangle of 34 cm x 12 cm and a triangle of height 2 cm. Now take the rectangle
By basic knowledge of geometry, area of rectangle with length l and breadth b = lb
Here in our case l = 34 cm, b = 12 cm
So, area = 34 x 12 = 408 $c{{m}^{2}}$
Case 3: After the breakage we get a triangle of height 2 cm.
By basic knowledge of geometry, area of triangle with height ‘h’ and base length ‘a’ = $\dfrac{1}{2}ah$
Here in our case, a = 34 cm, h = 2 cm
$\begin{align}
& area=\dfrac{1}{2}\times 34\times 2 \\
& area=34c{{m}^{2}} \\
\end{align}$
Case 4: On right most you can see a triangle with height 14 cm
In our case h = 14 cm, a = 10 cm
$area=\dfrac{1}{2}\times 14\times 10=70c{{m}^{2}}$
Case 5: On bottom you can see a triangle with height 16 cm.
In our case h = 16 cm, a = 34 + 10 + 6 = 50 cm
$area=\dfrac{1}{2}\times 16\times 50=400c{{m}^{2}}$
Total area = Sum of all cases.
Total area = Case 1 + Case 2 + Case 3 + Case 4 + Case 5
= $\left( 36+408+34+70+400 \right)c{{m}^{2}}=948c{{m}^{2}}$
Hence $948c{{m}^{2}}$ is the total area of the given figure.
Note: Don’t consider the middle figure as a rectangle because opposite sides are 12, 14. So, convert it to rectangle + triangle. Don’t confuse here.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

A moving boat is observed from the top of a 150 m high class 10 maths CBSE




