
How do you find the area of a triangle whose vertices are \[A(2,4)\], \[B( - 2,0)\] and \[C(4, - 2)\].
Answer
491.4k+ views
Hint: We use the concepts of geometry, triangle and matrices to solve this problem. A triangle is a polygon (a closed figure) of three sides. A matrix is a group of elements arranged in different numbers of rows and columns. It is represented as \[{A_{m \times n}}\] where \[m\] is the number of rows and \[n\] is the number of columns.
Complete step by step solution:
The triangle formed by points \[A(2,4)\], \[B( - 2,0)\] and \[C(4, - 2)\] is given below.
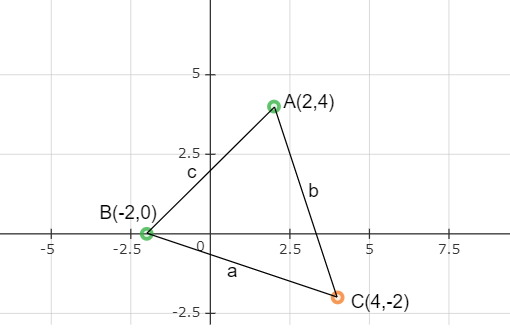
The side opposite to point ‘A’ is \[a\] units.
The side opposite to point ‘B’ is \[b\] units.
The side opposite to point ‘C’ is \[c\] units.
Area of a triangle with vertices \[\left( {{x_1},{y_1}} \right)\], \[\left( {{x_2},{y_2}} \right)\] and \[\left( {{x_3},{y_3}} \right)\] is given by half times the determinant of matrix ‘A’, where \[A = \left( {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}}
{{x_1}}&{{y_1}}&1 \\
{{x_2}}&{{y_2}}&1 \\
{{x_3}}&{{y_3}}&1
\end{array}} \right)\]
So, mathematically, \[Area = \dfrac{1}{2}|A|\] square units.
So, area of this triangle is
\[Area = \dfrac{1}{2}\left| {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}}
{{x_1}}&{{y_1}}&1 \\
{{x_2}}&{{y_2}}&1 \\
{{x_3}}&{{y_3}}&1
\end{array}} \right| = \left| {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}}
2&4&1 \\
{ - 2}&0&1 \\
4&{ - 2}&1
\end{array}} \right|\]
We all know that, determinant of a matrix \[\left( {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}}
{{a_{11}}}&{{a_{12}}}&{{a_{13}}} \\
{{a_{21}}}&{{a_{22}}}&{{a_{23}}} \\
{{a_{31}}}&{{a_{32}}}&{{a_{33}}}
\end{array}} \right)\] is equal to
\[\det = {a_{11}}({a_{22}}{a_{33}} - {a_{32}}{a_{23}}) - {a_{12}}({a_{21}}{a_{33}} - {a_{31}}{a_{23}}) + {a_{13}}({a_{21}}{a_{32}} - {a_{31}}{a_{22}})\]
So, we get,
\[Area = \dfrac{1}{2}.\left( {2((0)1 - ( - 2)1) - 4(( - 2)1 - (4)1) + 1(( - 2)( - 2) - (4).0)} \right)\]
\[ \Rightarrow Area = \dfrac{1}{2}.\left( {2(0 + 2) - 4( - 2 - 4) + 1(4 - 0)} \right)\]
On further simplification, we get finally,
\[ \Rightarrow Area = \dfrac{1}{2}.\left( {4 + 24 + 4} \right) = \dfrac{1}{2}\left( {32} \right) = 16\]
Therefore, we can conclude that, the area of a triangle with vertices \[A(2,4)\], \[B( - 2,0)\] and \[C(4, - 2)\] is equal to 16 square units.
Note:
We can also find the area of a triangle in another way. Let the lengths of sides of a triangle be \[a,b,c\].
Then area is given by \[area = \sqrt {s(s - a)(s - b)(s - c)} \], where \[s = \dfrac{{a + b + c}}{2}\].
Length of a line joining the points \[\left( {{x_1},{y_1}} \right)\] and \[\left( {{x_2},{y_2}} \right)\] is given by \[\sqrt {{{\left( {{x_2} - {x_1}} \right)}^2} + {{\left( {{y_2} - {y_1}} \right)}^2}} \].
Determinant of a matrix is defined as the sum of product of an element and its cofactor matrix in any row or a column.
Cofactor matrix is defined as \[{C_{ij}} = {( - 1)^{i + j}}|{M_{ij}}|\], where \[{M_{ij}}\] is a minor element.
A minor of an element is gained by removing the row and the column containing that element.
Complete step by step solution:
The triangle formed by points \[A(2,4)\], \[B( - 2,0)\] and \[C(4, - 2)\] is given below.

The side opposite to point ‘A’ is \[a\] units.
The side opposite to point ‘B’ is \[b\] units.
The side opposite to point ‘C’ is \[c\] units.
Area of a triangle with vertices \[\left( {{x_1},{y_1}} \right)\], \[\left( {{x_2},{y_2}} \right)\] and \[\left( {{x_3},{y_3}} \right)\] is given by half times the determinant of matrix ‘A’, where \[A = \left( {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}}
{{x_1}}&{{y_1}}&1 \\
{{x_2}}&{{y_2}}&1 \\
{{x_3}}&{{y_3}}&1
\end{array}} \right)\]
So, mathematically, \[Area = \dfrac{1}{2}|A|\] square units.
So, area of this triangle is
\[Area = \dfrac{1}{2}\left| {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}}
{{x_1}}&{{y_1}}&1 \\
{{x_2}}&{{y_2}}&1 \\
{{x_3}}&{{y_3}}&1
\end{array}} \right| = \left| {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}}
2&4&1 \\
{ - 2}&0&1 \\
4&{ - 2}&1
\end{array}} \right|\]
We all know that, determinant of a matrix \[\left( {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}}
{{a_{11}}}&{{a_{12}}}&{{a_{13}}} \\
{{a_{21}}}&{{a_{22}}}&{{a_{23}}} \\
{{a_{31}}}&{{a_{32}}}&{{a_{33}}}
\end{array}} \right)\] is equal to
\[\det = {a_{11}}({a_{22}}{a_{33}} - {a_{32}}{a_{23}}) - {a_{12}}({a_{21}}{a_{33}} - {a_{31}}{a_{23}}) + {a_{13}}({a_{21}}{a_{32}} - {a_{31}}{a_{22}})\]
So, we get,
\[Area = \dfrac{1}{2}.\left( {2((0)1 - ( - 2)1) - 4(( - 2)1 - (4)1) + 1(( - 2)( - 2) - (4).0)} \right)\]
\[ \Rightarrow Area = \dfrac{1}{2}.\left( {2(0 + 2) - 4( - 2 - 4) + 1(4 - 0)} \right)\]
On further simplification, we get finally,
\[ \Rightarrow Area = \dfrac{1}{2}.\left( {4 + 24 + 4} \right) = \dfrac{1}{2}\left( {32} \right) = 16\]
Therefore, we can conclude that, the area of a triangle with vertices \[A(2,4)\], \[B( - 2,0)\] and \[C(4, - 2)\] is equal to 16 square units.
Note:
We can also find the area of a triangle in another way. Let the lengths of sides of a triangle be \[a,b,c\].
Then area is given by \[area = \sqrt {s(s - a)(s - b)(s - c)} \], where \[s = \dfrac{{a + b + c}}{2}\].
Length of a line joining the points \[\left( {{x_1},{y_1}} \right)\] and \[\left( {{x_2},{y_2}} \right)\] is given by \[\sqrt {{{\left( {{x_2} - {x_1}} \right)}^2} + {{\left( {{y_2} - {y_1}} \right)}^2}} \].
Determinant of a matrix is defined as the sum of product of an element and its cofactor matrix in any row or a column.
Cofactor matrix is defined as \[{C_{ij}} = {( - 1)^{i + j}}|{M_{ij}}|\], where \[{M_{ij}}\] is a minor element.
A minor of an element is gained by removing the row and the column containing that element.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE

Give 10 examples of unisexual and bisexual flowers




