
Find the area of a rhombus having each side equal to \[13\] cm and one of whose diagonals is \[24\] cm.
Answer
584.4k+ views
Hint: To solve this question, we will start with finding second diagonal by using Pythagoras theorem, as we have been given only one diagonal, and we need both the diagonals of rhombus to find the area of rhombus. After getting both values of diagonals, we will use the formula of the area of the rhombus and get our required answer.
Complete step-by-step answer:
We have been given a rhombus having each side equal to \[13\] cm and one of whose diagonals is \[24\] cm. We need to find the area of rhombus.
So, each side of the given rhombus $ = 13cm$
And, one of the diagonals of the given rhombus $ = 24cm$
Let the other diagonal of the given rhombus be \[{d_2}.\]
Now, let us construct a figure of rhombus to get a better idea of it.
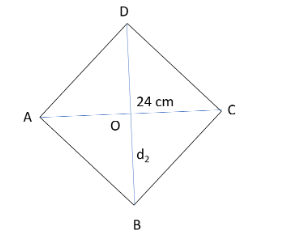
We know that, diagonals of rhombus bisect each other at \[90^\circ .\]
So, in \[\Delta AOD,\] on applying Pythagoras theorem, we get.
\[A{D^2}\; = O{D^2} + \;A{O^2}\]
where, AO $ = $ $\dfrac{1}{2}(24) = 12$\[cm,\] AD $ = $ \[13{\text{ }}cm\]
$
{(13)^2} = {(OD)^2} + {(12)^2} \\
169 = {(OD)^2} + 144 \\
{(OD)^2} = 169 - 144 \\
{(OD)^2} = 25 \\
OD = 5cm \\
$
We get OD \[ = {\text{ }}5{\text{ }}cm,\] So the other diagonal, \[{d_2} = {\text{ }}5 \times 2{\text{ }} = {\text{ }}10{\text{ }}cm\]
Now, we know that, Area of rhombus$ = \dfrac{1}{2} \times {d_1} \times {d_2}$
So, Area of rhombus $ = \dfrac{1}{2} \times 24 \times 10$
$
= 12 \times 10 \\
= 120cm \\
$
Thus, the area of a rhombus is 120 cm.
Note: In the solution, we have mentioned Pythagoras theorem, it is a theorem which gives the relation between sides of a right-angled triangle. The formula of Pythagoras theorem mentioned formula,
\[{\left( {Hypotenuse} \right)^2}{\text{ }} = {\text{ }}{\left( {Base} \right)^2}{\text{ }} + {\text{ }}{\left( {Perpendicular} \right)^2}\]
So, from the we have taken, AD \[ = \] Hypotenuse
AO \[ = \] Base (AO is half of diagonal AC)
OD \[ = \] Perpendicular (OD is half of diagonal BD).
Complete step-by-step answer:
We have been given a rhombus having each side equal to \[13\] cm and one of whose diagonals is \[24\] cm. We need to find the area of rhombus.
So, each side of the given rhombus $ = 13cm$
And, one of the diagonals of the given rhombus $ = 24cm$
Let the other diagonal of the given rhombus be \[{d_2}.\]
Now, let us construct a figure of rhombus to get a better idea of it.

We know that, diagonals of rhombus bisect each other at \[90^\circ .\]
So, in \[\Delta AOD,\] on applying Pythagoras theorem, we get.
\[A{D^2}\; = O{D^2} + \;A{O^2}\]
where, AO $ = $ $\dfrac{1}{2}(24) = 12$\[cm,\] AD $ = $ \[13{\text{ }}cm\]
$
{(13)^2} = {(OD)^2} + {(12)^2} \\
169 = {(OD)^2} + 144 \\
{(OD)^2} = 169 - 144 \\
{(OD)^2} = 25 \\
OD = 5cm \\
$
We get OD \[ = {\text{ }}5{\text{ }}cm,\] So the other diagonal, \[{d_2} = {\text{ }}5 \times 2{\text{ }} = {\text{ }}10{\text{ }}cm\]
Now, we know that, Area of rhombus$ = \dfrac{1}{2} \times {d_1} \times {d_2}$
So, Area of rhombus $ = \dfrac{1}{2} \times 24 \times 10$
$
= 12 \times 10 \\
= 120cm \\
$
Thus, the area of a rhombus is 120 cm.
Note: In the solution, we have mentioned Pythagoras theorem, it is a theorem which gives the relation between sides of a right-angled triangle. The formula of Pythagoras theorem mentioned formula,
\[{\left( {Hypotenuse} \right)^2}{\text{ }} = {\text{ }}{\left( {Base} \right)^2}{\text{ }} + {\text{ }}{\left( {Perpendicular} \right)^2}\]
So, from the we have taken, AD \[ = \] Hypotenuse
AO \[ = \] Base (AO is half of diagonal AC)
OD \[ = \] Perpendicular (OD is half of diagonal BD).
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 9 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 9 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Trending doubts
Difference Between Plant Cell and Animal Cell

Fill the blanks with the suitable prepositions 1 The class 9 english CBSE

Who is eligible for RTE class 9 social science CBSE

Which places in India experience sunrise first and class 9 social science CBSE

What is pollution? How many types of pollution? Define it

Name 10 Living and Non living things class 9 biology CBSE




