
Find the area of a quadrilateral ABCD in which $ AD = 24cm $ , $ \angle BAD = {90^ \circ } $ and BCD form an equilateral triangle whose each side is equal to $ 26cm $ . (take $ \sqrt 3 = 1.73 $ )
Answer
533.1k+ views
Hint: solve this problem we should know about:
Quadrilateral: the polygon having four sides.
Equilateral triangle: The triangle having all sides is equal.
Area of the equilateral triangle can be calculated by $ \dfrac{{\sqrt 3 {a^2}}}{4} $ where $ a $ is the side of the triangle.
Right-angle triangle: the triangle in which one side is perpendicular to the other side.
Area of triangle \[ = \dfrac{1}{2} \times base \times height\]
Complete step by step solution:
Lets first try to draw the diagram as per given in question:
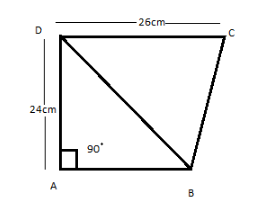
As given in the question $ \Delta BCD $ is an equilateral triangle. And from given data we can conclude that $ \Delta DAB $ is a right angled triangle.
Here, we have to calculate the area of quadrilateral ABCD.
We can find it by separating it in two triangles $ \Delta BCD $ and $ \Delta DAB $ .
The area of $ \Delta BCD $ will be calculated by the area of the equilateral triangle $ \dfrac{{\sqrt 3 {a^2}}}{4} $ .
Here, $ a $ is length of side of triangle $ = 26cm $
So, keeping it in the area formula. We get,
$ \dfrac{{\sqrt 3 {a^2}}}{4} = \dfrac{{\sqrt 3 {{\left( {26} \right)}^2}}}{4} $
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{\sqrt 3 {a^2}}}{4} = \dfrac{{1.73 \times 676}}{4} $
Solving it,
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{\sqrt 3 {a^2}}}{4} = 292.37 $
Area of equilateral triangle $ \Delta BCD $ will be $ = 292.37 $
Area of triangle $ \Delta DAB $ $ = base \times height $
The right triangle height is equal to the perpendicular side.
So, we have to calculate the length of AB.
By using Pythagora's theorem. We can say that,
$ A{D^2} + A{B^2} = D{B^2} $
Keeping value in it,
$ {24^2} + A{B^2} = {26^2} $
Solving it,
$ \Rightarrow 576 + A{B^2} = 676 $
Transfer numerical on one side.
$ \Rightarrow A{B^2} = 676 - 576 $
$ \Rightarrow A{B^2} = 100 $
By take under root on both side,
$ \Rightarrow AB = \sqrt {100} = 10cm $
Area of $ \Delta DAB = \dfrac{1}{2} \times 24 \times 10 = 120c{m^2} $
Area of quadrilateral ABCD $ = Area\,of\,\Delta BCD + Area\,of\,\Delta DAB $
By keeping values from above,
Area of quadrilateral ABCD $ = 292.37c{m^2} + 120c{m^2} = 412.37c{m^2} $ .
Hence the area of the given figure is $ 412.37c{m^2} $ .
So, the correct answer is “ $ 412.37c{m^2} $”.
Note: ythagoras theorem: In a right angled triangle the square of hypotenuse is always equal to the sum of squares of the other two sides.
In mathematically, $ A{B^2} + B{C^2} = A{D^2} $
Area of triangle with three sides (Heron’s Formula) $ A = \sqrt {s(s - a)(s - b)(s - c)} $ .
Here s is a semi-perimeter of the triangle $ = \dfrac{{\left( {a + b + c} \right)}}{2} $ .
Quadrilateral: the polygon having four sides.
Equilateral triangle: The triangle having all sides is equal.
Area of the equilateral triangle can be calculated by $ \dfrac{{\sqrt 3 {a^2}}}{4} $ where $ a $ is the side of the triangle.
Right-angle triangle: the triangle in which one side is perpendicular to the other side.
Area of triangle \[ = \dfrac{1}{2} \times base \times height\]
Complete step by step solution:
Lets first try to draw the diagram as per given in question:

As given in the question $ \Delta BCD $ is an equilateral triangle. And from given data we can conclude that $ \Delta DAB $ is a right angled triangle.
Here, we have to calculate the area of quadrilateral ABCD.
We can find it by separating it in two triangles $ \Delta BCD $ and $ \Delta DAB $ .
The area of $ \Delta BCD $ will be calculated by the area of the equilateral triangle $ \dfrac{{\sqrt 3 {a^2}}}{4} $ .
Here, $ a $ is length of side of triangle $ = 26cm $
So, keeping it in the area formula. We get,
$ \dfrac{{\sqrt 3 {a^2}}}{4} = \dfrac{{\sqrt 3 {{\left( {26} \right)}^2}}}{4} $
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{\sqrt 3 {a^2}}}{4} = \dfrac{{1.73 \times 676}}{4} $
Solving it,
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{\sqrt 3 {a^2}}}{4} = 292.37 $
Area of equilateral triangle $ \Delta BCD $ will be $ = 292.37 $
Area of triangle $ \Delta DAB $ $ = base \times height $
The right triangle height is equal to the perpendicular side.
So, we have to calculate the length of AB.
By using Pythagora's theorem. We can say that,
$ A{D^2} + A{B^2} = D{B^2} $
Keeping value in it,
$ {24^2} + A{B^2} = {26^2} $
Solving it,
$ \Rightarrow 576 + A{B^2} = 676 $
Transfer numerical on one side.
$ \Rightarrow A{B^2} = 676 - 576 $
$ \Rightarrow A{B^2} = 100 $
By take under root on both side,
$ \Rightarrow AB = \sqrt {100} = 10cm $
Area of $ \Delta DAB = \dfrac{1}{2} \times 24 \times 10 = 120c{m^2} $
Area of quadrilateral ABCD $ = Area\,of\,\Delta BCD + Area\,of\,\Delta DAB $
By keeping values from above,
Area of quadrilateral ABCD $ = 292.37c{m^2} + 120c{m^2} = 412.37c{m^2} $ .
Hence the area of the given figure is $ 412.37c{m^2} $ .
So, the correct answer is “ $ 412.37c{m^2} $”.
Note: ythagoras theorem: In a right angled triangle the square of hypotenuse is always equal to the sum of squares of the other two sides.
In mathematically, $ A{B^2} + B{C^2} = A{D^2} $

Area of triangle with three sides (Heron’s Formula) $ A = \sqrt {s(s - a)(s - b)(s - c)} $ .
Here s is a semi-perimeter of the triangle $ = \dfrac{{\left( {a + b + c} \right)}}{2} $ .
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 9 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 9 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Trending doubts
Difference Between Plant Cell and Animal Cell

Fill the blanks with the suitable prepositions 1 The class 9 english CBSE

Who is eligible for RTE class 9 social science CBSE

Which places in India experience sunrise first and class 9 social science CBSE

What is pollution? How many types of pollution? Define it

Name 10 Living and Non living things class 9 biology CBSE




