
Find the angle measure of \[x\] in the following figures:

Answer
567.6k+ views
Hint: Here, we need to find the value of \[x\] in the given figures. We will use the angle sum property of a quadrilateral to find the value of \[x\] in first figures. Then we will use the properties of linear pair angles to find the angle in the third figure. We will then use the angle sum property of a pentagon to find the value of \[x\] in the fourth figure.
Complete step-by-step answer:
(a)
The sum of all the interior angles of a quadrilateral is equal to \[360^\circ \].
Therefore, we get
\[50^\circ + 130^\circ + 120^\circ + x = 360^\circ \]
This is a linear equation in terms of \[x\]. We will solve this equation to find the value of \[x\].
Adding the terms of the equation, we get
\[ \Rightarrow 300^\circ + x = 360^\circ \]
Subtracting \[300^\circ \] from both sides of the equation, we get
\[ \Rightarrow 300^\circ + x - 300^\circ = 360^\circ - 300^\circ \]
Thus, we get
\[ \Rightarrow x = 60^\circ \]
Therefore, we get the value of \[x\] as \[60^\circ \].
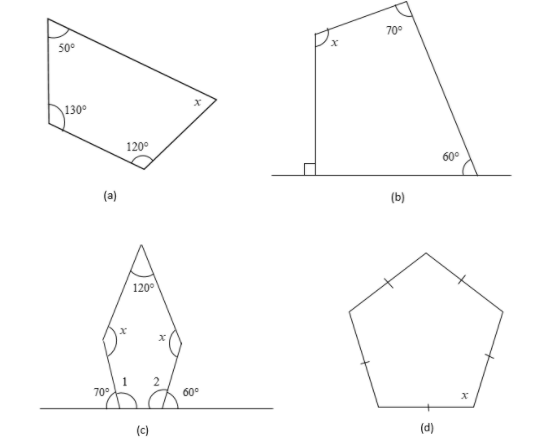
(b)
First, we will mark another angle in the figure.
The sum of all the angles lying on a line is equal to \[180^\circ \]. These angles are said to form a linear pair.
From the figure, we can observe that the right angle and angle 1 form a linear pair.
Therefore, we get
\[90^\circ + \angle 1 = 180^\circ \]
Subtracting \[90^\circ \] from both sides of the equation, we get
\[\begin{array}{l} \Rightarrow 90^\circ + \angle 1 - 90^\circ = 180^\circ - 90^\circ \\ \Rightarrow \angle 1 = 90^\circ \end{array}\]
The sum of all the interior angles of a quadrilateral is equal to \[360^\circ \].
Therefore, we get
\[70^\circ + 60^\circ + \angle 1 + x = 360^\circ \]
This is a linear equation in terms of \[x\]. We will solve this equation to find the value of \[x\].
Substituting \[\angle 1 = 90^\circ \] in the equation, we get
\[ \Rightarrow 70^\circ + 60^\circ + 90^\circ + x = 360^\circ \]
Adding the terms of the equation, we get
\[ \Rightarrow 220^\circ + x = 360^\circ \]
Subtracting \[220^\circ \] from both sides of the equation, we get
\[ \Rightarrow 220^\circ + x - 220^\circ = 360^\circ - 220^\circ \]
Thus, we get
\[ \Rightarrow x = 140^\circ \]
Therefore, we get the value of \[x\] as \[140^\circ \].
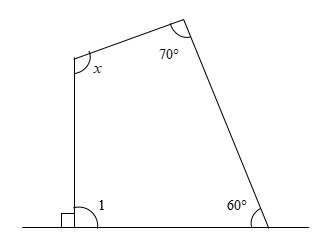
(c)
First, we will mark two angles in the figure.
The sum of all the angles lying on a line is equal to \[180^\circ \]. These angles are said to form a linear pair.
From the figure, we can observe that the angle measuring \[70^\circ \] and angle 1 form a linear pair.
Therefore, we get
\[70^\circ + \angle 1 = 180^\circ \]
Subtracting \[70^\circ \] from both sides of the equation, we get
\[\begin{array}{l} \Rightarrow 70^\circ + \angle 1 - 70^\circ = 180^\circ - 70^\circ \\ \Rightarrow \angle 1 = 110^\circ \end{array}\]
From the figure, we can observe that the angle measuring \[60^\circ \] and angle 2 form a linear pair.
Therefore, we get
\[60^\circ + \angle 2 = 180^\circ \]
Subtracting \[60^\circ \] from both sides of the equation, we get
\[\begin{array}{l} \Rightarrow 60^\circ + \angle 2 - 60^\circ = 180^\circ - 60^\circ \\ \Rightarrow \angle 2 = 120^\circ \end{array}\]
The sum of all the interior angles of a pentagon is equal to \[540^\circ \].
Therefore, we get
\[120^\circ + x + x + \angle 1 + \angle 2 = 540^\circ \]
This is a linear equation in terms of \[x\]. We will solve this equation to find the value of \[x\].
Substituting \[\angle 1 = 110^\circ \] and \[\angle 2 = 120^\circ \] in the equation, we get
\[ \Rightarrow 120^\circ + x + x + 110^\circ + 120^\circ = 540^\circ \]
Adding the terms of the equation, we get
\[ \Rightarrow 350^\circ + 2x = 540^\circ \]
Subtracting \[350^\circ \] from both sides of the equation, we get
\[\begin{array}{l} \Rightarrow 2x = 540^\circ - 350^\circ \\ \Rightarrow 2x = 190^\circ \end{array}\]
Dividing both sides of the equation by 2, we get
\[ \Rightarrow x = 95^\circ \]
Therefore, we get the value of \[x\] as \[95^\circ \].
(d)
It is shown that all sides of the pentagon are equal.
Therefore, the given pentagon is a regular pentagon.
We know that all the sides and interior angles of a regular polygon are equal.
Therefore, we get the measure of the five interior angles as \[x\].
The sum of all the interior angles of a pentagon is equal to \[540^\circ \].
Therefore, we get
\[x + x + x + x + x = 540^\circ \]
This is a linear equation in terms of \[x\]. We will solve this equation to find the value of \[x\].
Adding the terms of the equation, we get
\[ \Rightarrow 5x = 540^\circ \]
Dividing both sides of the equation by 5, we get
\[ \Rightarrow x = 108^\circ \]
Therefore, we get the value of \[x\] as \[108^\circ \].
Note: We have formed linear equations in one variable in terms of \[x\] in the solution. A linear equation in one variable is an equation that can be written in the form \[ax + b = 0\], where \[a\] is not equal to 0, and \[a\] and \[b\] are real numbers. For example, \[x - 100 = 0\] and \[100P - 566 = 0\] are linear equations in one variable \[x\] and \[P\] respectively. A linear equation in one variable has only one solution.
We used the term ‘regular polygon’ in the solution. A polygon is a closed figure made using straight lines as sides. A regular polygon is a polygon whose interior angles and sides are equal. For example: a square is a regular polygon having 4 sides, a pentagon is a regular polygon having 5 sides, a hexagon is a regular polygon having 6 sides, etc.
Complete step-by-step answer:
(a)
The sum of all the interior angles of a quadrilateral is equal to \[360^\circ \].
Therefore, we get
\[50^\circ + 130^\circ + 120^\circ + x = 360^\circ \]
This is a linear equation in terms of \[x\]. We will solve this equation to find the value of \[x\].
Adding the terms of the equation, we get
\[ \Rightarrow 300^\circ + x = 360^\circ \]
Subtracting \[300^\circ \] from both sides of the equation, we get
\[ \Rightarrow 300^\circ + x - 300^\circ = 360^\circ - 300^\circ \]
Thus, we get
\[ \Rightarrow x = 60^\circ \]
Therefore, we get the value of \[x\] as \[60^\circ \].
(b)
First, we will mark another angle in the figure.

The sum of all the angles lying on a line is equal to \[180^\circ \]. These angles are said to form a linear pair.
From the figure, we can observe that the right angle and angle 1 form a linear pair.
Therefore, we get
\[90^\circ + \angle 1 = 180^\circ \]
Subtracting \[90^\circ \] from both sides of the equation, we get
\[\begin{array}{l} \Rightarrow 90^\circ + \angle 1 - 90^\circ = 180^\circ - 90^\circ \\ \Rightarrow \angle 1 = 90^\circ \end{array}\]
The sum of all the interior angles of a quadrilateral is equal to \[360^\circ \].
Therefore, we get
\[70^\circ + 60^\circ + \angle 1 + x = 360^\circ \]
This is a linear equation in terms of \[x\]. We will solve this equation to find the value of \[x\].
Substituting \[\angle 1 = 90^\circ \] in the equation, we get
\[ \Rightarrow 70^\circ + 60^\circ + 90^\circ + x = 360^\circ \]
Adding the terms of the equation, we get
\[ \Rightarrow 220^\circ + x = 360^\circ \]
Subtracting \[220^\circ \] from both sides of the equation, we get
\[ \Rightarrow 220^\circ + x - 220^\circ = 360^\circ - 220^\circ \]
Thus, we get
\[ \Rightarrow x = 140^\circ \]
Therefore, we get the value of \[x\] as \[140^\circ \].
(c)
First, we will mark two angles in the figure.

The sum of all the angles lying on a line is equal to \[180^\circ \]. These angles are said to form a linear pair.
From the figure, we can observe that the angle measuring \[70^\circ \] and angle 1 form a linear pair.
Therefore, we get
\[70^\circ + \angle 1 = 180^\circ \]
Subtracting \[70^\circ \] from both sides of the equation, we get
\[\begin{array}{l} \Rightarrow 70^\circ + \angle 1 - 70^\circ = 180^\circ - 70^\circ \\ \Rightarrow \angle 1 = 110^\circ \end{array}\]
From the figure, we can observe that the angle measuring \[60^\circ \] and angle 2 form a linear pair.
Therefore, we get
\[60^\circ + \angle 2 = 180^\circ \]
Subtracting \[60^\circ \] from both sides of the equation, we get
\[\begin{array}{l} \Rightarrow 60^\circ + \angle 2 - 60^\circ = 180^\circ - 60^\circ \\ \Rightarrow \angle 2 = 120^\circ \end{array}\]
The sum of all the interior angles of a pentagon is equal to \[540^\circ \].
Therefore, we get
\[120^\circ + x + x + \angle 1 + \angle 2 = 540^\circ \]
This is a linear equation in terms of \[x\]. We will solve this equation to find the value of \[x\].
Substituting \[\angle 1 = 110^\circ \] and \[\angle 2 = 120^\circ \] in the equation, we get
\[ \Rightarrow 120^\circ + x + x + 110^\circ + 120^\circ = 540^\circ \]
Adding the terms of the equation, we get
\[ \Rightarrow 350^\circ + 2x = 540^\circ \]
Subtracting \[350^\circ \] from both sides of the equation, we get
\[\begin{array}{l} \Rightarrow 2x = 540^\circ - 350^\circ \\ \Rightarrow 2x = 190^\circ \end{array}\]
Dividing both sides of the equation by 2, we get
\[ \Rightarrow x = 95^\circ \]
Therefore, we get the value of \[x\] as \[95^\circ \].
(d)
It is shown that all sides of the pentagon are equal.
Therefore, the given pentagon is a regular pentagon.
We know that all the sides and interior angles of a regular polygon are equal.
Therefore, we get the measure of the five interior angles as \[x\].
The sum of all the interior angles of a pentagon is equal to \[540^\circ \].
Therefore, we get
\[x + x + x + x + x = 540^\circ \]
This is a linear equation in terms of \[x\]. We will solve this equation to find the value of \[x\].
Adding the terms of the equation, we get
\[ \Rightarrow 5x = 540^\circ \]
Dividing both sides of the equation by 5, we get
\[ \Rightarrow x = 108^\circ \]
Therefore, we get the value of \[x\] as \[108^\circ \].
Note: We have formed linear equations in one variable in terms of \[x\] in the solution. A linear equation in one variable is an equation that can be written in the form \[ax + b = 0\], where \[a\] is not equal to 0, and \[a\] and \[b\] are real numbers. For example, \[x - 100 = 0\] and \[100P - 566 = 0\] are linear equations in one variable \[x\] and \[P\] respectively. A linear equation in one variable has only one solution.
We used the term ‘regular polygon’ in the solution. A polygon is a closed figure made using straight lines as sides. A regular polygon is a polygon whose interior angles and sides are equal. For example: a square is a regular polygon having 4 sides, a pentagon is a regular polygon having 5 sides, a hexagon is a regular polygon having 6 sides, etc.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 9 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 9 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Trending doubts
Difference Between Plant Cell and Animal Cell

Fill the blanks with the suitable prepositions 1 The class 9 english CBSE

Who is eligible for RTE class 9 social science CBSE

Which places in India experience sunrise first and class 9 social science CBSE

What is pollution? How many types of pollution? Define it

Name 10 Living and Non living things class 9 biology CBSE




