
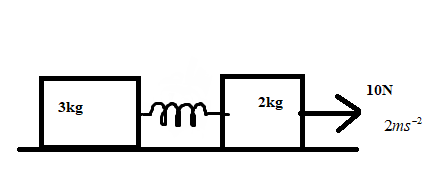
Find the acceleration of $3\;kg$ mass when acceleration of $2\;kg$ mass is $2\;ms^{-1}$ as shown in figure.

Answer
543.9k+ views
Hint: Here, since the two blocks are attached by a spring, the spring also experiences a tension, which affects the net force on the system of blocks. Using this knowledge we can solve the following question.
Formula used:
$F=ma$
Complete answer:
Consider the given set-up, where two blocks of different weights are connected by a spring. Thus the net force on the system is the vector sum of the extra force, tension on the spring and the forces acting on the blocks.
Now, consider the$2\;kg$ block alone, clearly the force action on the $2\;kg$ block is given as
$A-T=F_{2}$ where $T$ is the tension on the spring , $A=10N$ is the applied force and $F_{2}=ma$ is the force on the $m=2\;kg$ block due to an acceleration $a=2m/s^{2}$.
Though, we are trying to find the sum of force action on the individual blocks, since the tension acts in the opposite direction to the applied force we are subtracting the two.
$\implies 10-T=2\times 2$
$\implies 10-4=T$
$\implies T=6N$
Similarly, now consider the $3\;kg$ block alone, then clearly, only $T$ acts on this block, hence we have $T=F_{3}$ where $F_{3}=ma$ is the force on the $m=3\;kg$ block due to an acceleration $a$
Then we have, $T=3\times a$
$\implies a=\dfrac{6}{3}$
$\therefore a=2m/s^{2}$
Thus the $3\;kg$ block moves with an acceleration of $2m/s^{2}$.
Note:
We know the force and tension are vectors, that is they have both magnitude and direction. Hence when we try to add or subtract two or more vectors, we must also consider the direction of the vector along with their magnitude as done in the above question. From Newton's second law of motion we know that the force exerted by a moving object is given as this is used in the above sum extensively.
Formula used:
$F=ma$
Complete answer:
Consider the given set-up, where two blocks of different weights are connected by a spring. Thus the net force on the system is the vector sum of the extra force, tension on the spring and the forces acting on the blocks.
Now, consider the$2\;kg$ block alone, clearly the force action on the $2\;kg$ block is given as
$A-T=F_{2}$ where $T$ is the tension on the spring , $A=10N$ is the applied force and $F_{2}=ma$ is the force on the $m=2\;kg$ block due to an acceleration $a=2m/s^{2}$.
Though, we are trying to find the sum of force action on the individual blocks, since the tension acts in the opposite direction to the applied force we are subtracting the two.
$\implies 10-T=2\times 2$
$\implies 10-4=T$
$\implies T=6N$
Similarly, now consider the $3\;kg$ block alone, then clearly, only $T$ acts on this block, hence we have $T=F_{3}$ where $F_{3}=ma$ is the force on the $m=3\;kg$ block due to an acceleration $a$
Then we have, $T=3\times a$
$\implies a=\dfrac{6}{3}$
$\therefore a=2m/s^{2}$
Thus the $3\;kg$ block moves with an acceleration of $2m/s^{2}$.
Note:
We know the force and tension are vectors, that is they have both magnitude and direction. Hence when we try to add or subtract two or more vectors, we must also consider the direction of the vector along with their magnitude as done in the above question. From Newton's second law of motion we know that the force exerted by a moving object is given as this is used in the above sum extensively.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




