
How do you find $ \sin \theta $ , when the value of $ \cos \theta $ is $ \dfrac{3}{5} $ ?
Answer
570.9k+ views
Hint:
We start solving the problem by squaring both sides of the equation $ \cos \theta =\dfrac{3}{5} $ . We then make use of the fact that $ {{\cos }^{2}}\theta =1-{{\sin }^{2}}\theta $ to proceed through the problem. We then make the necessary calculations and apply square root on both sides of the resultant equation. We then make use of the result $ \sqrt{\dfrac{a}{b}}=\dfrac{\sqrt{a}}{\sqrt{b}} $ and make the necessary calculations to get the required value(s) of $ \sin \theta $ .
Complete step by step answer:
According to the problem, we are asked to find the value of $ \sin \theta $ , and the value of $ \cos \theta $ is given as $ \dfrac{3}{5} $ .
So, we have $ \cos \theta =\dfrac{3}{5} $ ---(1).
Let us square on both sides in equation (1).
$ \Rightarrow {{\cos }^{2}}\theta =\dfrac{9}{25} $ ---(2).
We know that $ {{\cos }^{2}}\theta =1-{{\sin }^{2}}\theta $ . Let us use this result in equation (2).
$ \Rightarrow 1-{{\sin }^{2}}\theta =\dfrac{9}{25} $ .
\[\Rightarrow {{\sin }^{2}}\theta =1-\dfrac{9}{25}\].
\[\Rightarrow {{\sin }^{2}}\theta =\dfrac{25-9}{25}\].
\[\Rightarrow {{\sin }^{2}}\theta =\dfrac{16}{25}\] ---(3).
Let us apply the square root on both sides of the equation (3).
\[\Rightarrow \sqrt{{{\sin }^{2}}\theta }=\sqrt{\dfrac{16}{25}}\] ---(4).
We know that $ \sqrt{\dfrac{a}{b}}=\dfrac{\sqrt{a}}{\sqrt{b}} $ . Let us use this result in equation (4).
\[\Rightarrow \sin \theta =\dfrac{\sqrt{16}}{\sqrt{25}}\].
\[\Rightarrow \sin \theta =\dfrac{\pm 4}{5}\].
So, we have found the value(s) of $ \sin \theta $ as $ \pm \dfrac{4}{5} $ .
Note:
Here we have two values for $ \sin \theta $ as we know that cosine function is the position in both the first and fourth quadrant of the quadrant systems. We can also solve this problem as shown below:
We know that cosine of an angle in a right-angle triangle is defined as the ratio of the adjacent side to its hypotenuse.
So, let us draw the figure to represent this.
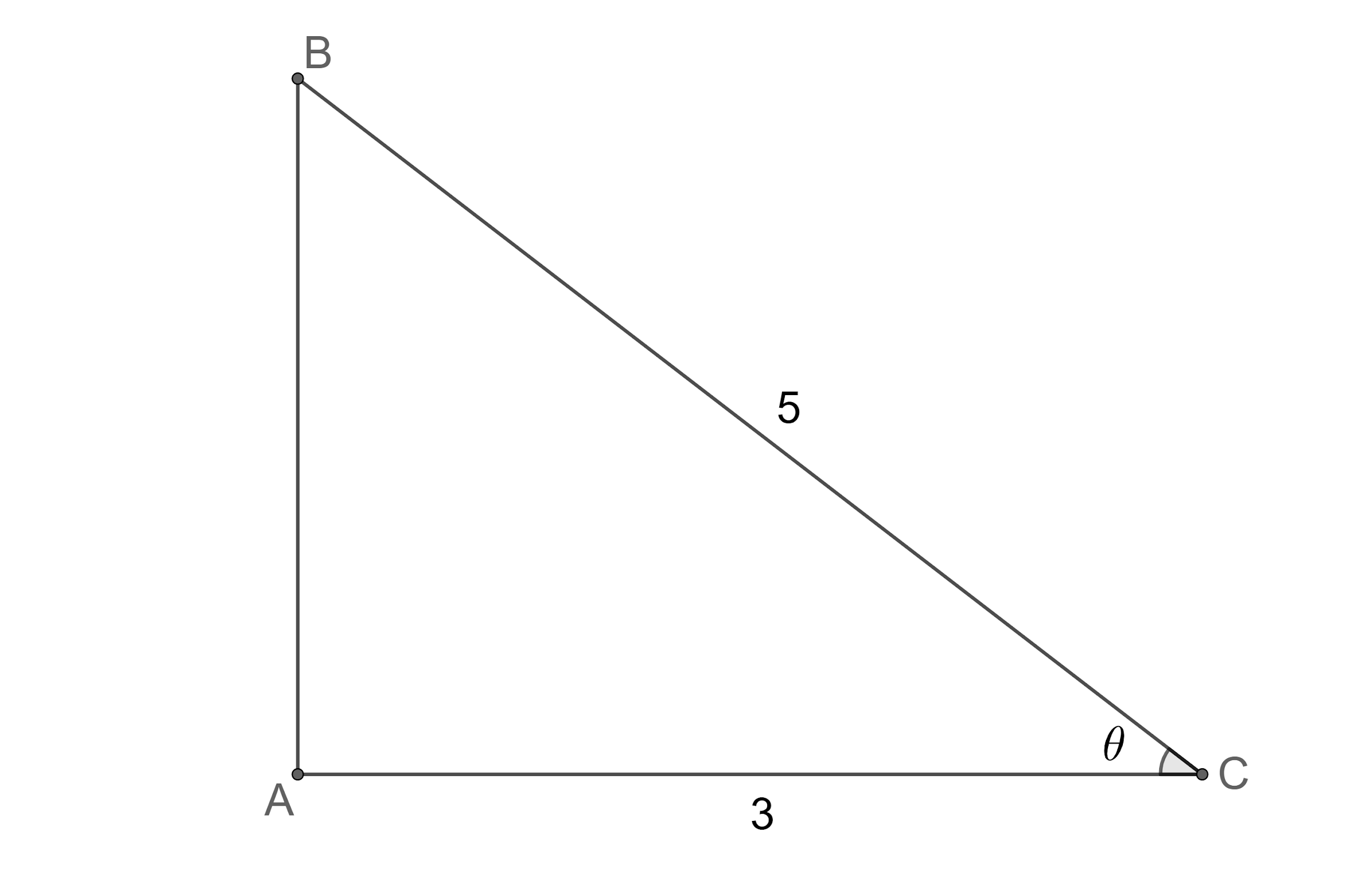
From Pythagoras theorem, we know that the square of the hypotenuse is equal to the sum of squares of the other two sides in the right-angle triangle.
So, we get $ A{{B}^{2}}+A{{C}^{2}}=B{{C}^{2}} $ .
$ \Rightarrow A{{B}^{2}}+{{3}^{2}}={{5}^{2}} $ .
$ \Rightarrow A{{B}^{2}}+9=25 $ .
$ \Rightarrow A{{B}^{2}}=16 $ .
$ \Rightarrow AB=4 $ .
We know that sine of an angle in a right-angle triangle is defined as the ratio of the opposite side to its hypotenuse.
So, we get $ \sin \theta =\dfrac{AB}{AC}=\dfrac{4}{5} $ .
We start solving the problem by squaring both sides of the equation $ \cos \theta =\dfrac{3}{5} $ . We then make use of the fact that $ {{\cos }^{2}}\theta =1-{{\sin }^{2}}\theta $ to proceed through the problem. We then make the necessary calculations and apply square root on both sides of the resultant equation. We then make use of the result $ \sqrt{\dfrac{a}{b}}=\dfrac{\sqrt{a}}{\sqrt{b}} $ and make the necessary calculations to get the required value(s) of $ \sin \theta $ .
Complete step by step answer:
According to the problem, we are asked to find the value of $ \sin \theta $ , and the value of $ \cos \theta $ is given as $ \dfrac{3}{5} $ .
So, we have $ \cos \theta =\dfrac{3}{5} $ ---(1).
Let us square on both sides in equation (1).
$ \Rightarrow {{\cos }^{2}}\theta =\dfrac{9}{25} $ ---(2).
We know that $ {{\cos }^{2}}\theta =1-{{\sin }^{2}}\theta $ . Let us use this result in equation (2).
$ \Rightarrow 1-{{\sin }^{2}}\theta =\dfrac{9}{25} $ .
\[\Rightarrow {{\sin }^{2}}\theta =1-\dfrac{9}{25}\].
\[\Rightarrow {{\sin }^{2}}\theta =\dfrac{25-9}{25}\].
\[\Rightarrow {{\sin }^{2}}\theta =\dfrac{16}{25}\] ---(3).
Let us apply the square root on both sides of the equation (3).
\[\Rightarrow \sqrt{{{\sin }^{2}}\theta }=\sqrt{\dfrac{16}{25}}\] ---(4).
We know that $ \sqrt{\dfrac{a}{b}}=\dfrac{\sqrt{a}}{\sqrt{b}} $ . Let us use this result in equation (4).
\[\Rightarrow \sin \theta =\dfrac{\sqrt{16}}{\sqrt{25}}\].
\[\Rightarrow \sin \theta =\dfrac{\pm 4}{5}\].
So, we have found the value(s) of $ \sin \theta $ as $ \pm \dfrac{4}{5} $ .
Note:
Here we have two values for $ \sin \theta $ as we know that cosine function is the position in both the first and fourth quadrant of the quadrant systems. We can also solve this problem as shown below:
We know that cosine of an angle in a right-angle triangle is defined as the ratio of the adjacent side to its hypotenuse.
So, let us draw the figure to represent this.

From Pythagoras theorem, we know that the square of the hypotenuse is equal to the sum of squares of the other two sides in the right-angle triangle.
So, we get $ A{{B}^{2}}+A{{C}^{2}}=B{{C}^{2}} $ .
$ \Rightarrow A{{B}^{2}}+{{3}^{2}}={{5}^{2}} $ .
$ \Rightarrow A{{B}^{2}}+9=25 $ .
$ \Rightarrow A{{B}^{2}}=16 $ .
$ \Rightarrow AB=4 $ .
We know that sine of an angle in a right-angle triangle is defined as the ratio of the opposite side to its hypotenuse.
So, we get $ \sin \theta =\dfrac{AB}{AC}=\dfrac{4}{5} $ .
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 10 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
A boat goes 24 km upstream and 28 km downstream in class 10 maths CBSE

State and explain Ohms law class 10 physics CBSE

Write a letter to the editor of a newspaper explaining class 10 english CBSE

Distinguish between soap and detergent class 10 chemistry CBSE

a Why did Mendel choose pea plants for his experiments class 10 biology CBSE

What is a "free hit" awarded for in limited-overs cricket?




