
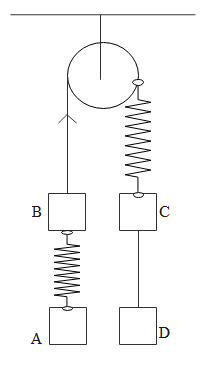
Find out which block will have zero acceleration just after cutting
A. spring between AB
B. string between BC
C. spring between BC
D. string between CD
Initially entire system is in equilibrium

Answer
585.3k+ views
Hint: Since it is given that the entire system is in equilibrium the first thing we should do is to balance the forces on every given block. When we balance all the forces we get net force on them as zero and when we cut any string or spring we can find which block has zero acceleration
Complete step by step answer:
First if we consider block D then the tension acting to the string which is attached to D will be equal to its mass in order to be in equilibrium. So tension in the CD string ${{\text{T}}_{{\text{CD}}}}$ will be mg. on the block C both weight and tension acts so tension in spring BC will be 2mg. Same will be the tension in string BC ${{\text{T}}_{{\text{BC}}}}$ will be 2mg. Coming to block A weight will be balanced by the spring force between BA so spring force will be mg. so ${{\text{T}}_{{\text{AB}}}}$ will be mg.
Now if we cut spring between A and B for block B 2mg(weight + previous spring force) acts downward and 2mg tension acts upward so acceleration on B will be zero
If we cut the string between BC then on block C 2mg tension acts upward and 2mg force acts downward so block C will have zero acceleration
If we cut spring between BC and consider the block D as tension mg acting upward and weight mg acting downward hence D will have zero acceleration
If we cut string between CD then block A will be having mg force acting downward and mg tension acting upward hence block A will have zero acceleration
So when
A. Spring between AB is cut – block B will have zero acceleration (${a_B} = 0$)
B. String between BC is cut – block C will have zero acceleration (${a_C} = 0$)
C. Spring between BC is cut – block D will have zero acceleration (${a_D} = 0$)
D. String between CD is cut – block A will have zero acceleration (${a_A} = 0$)
Note:
When the string is cut then immediately tension becomes zero but when spring is cut then the restoring force which it was exerting previously on a block still remains the same and it will come into action after we cut the spring. In this way string and spring are quite different.
Complete step by step answer:

First if we consider block D then the tension acting to the string which is attached to D will be equal to its mass in order to be in equilibrium. So tension in the CD string ${{\text{T}}_{{\text{CD}}}}$ will be mg. on the block C both weight and tension acts so tension in spring BC will be 2mg. Same will be the tension in string BC ${{\text{T}}_{{\text{BC}}}}$ will be 2mg. Coming to block A weight will be balanced by the spring force between BA so spring force will be mg. so ${{\text{T}}_{{\text{AB}}}}$ will be mg.
Now if we cut spring between A and B for block B 2mg(weight + previous spring force) acts downward and 2mg tension acts upward so acceleration on B will be zero
If we cut the string between BC then on block C 2mg tension acts upward and 2mg force acts downward so block C will have zero acceleration
If we cut spring between BC and consider the block D as tension mg acting upward and weight mg acting downward hence D will have zero acceleration
If we cut string between CD then block A will be having mg force acting downward and mg tension acting upward hence block A will have zero acceleration
So when
A. Spring between AB is cut – block B will have zero acceleration (${a_B} = 0$)
B. String between BC is cut – block C will have zero acceleration (${a_C} = 0$)
C. Spring between BC is cut – block D will have zero acceleration (${a_D} = 0$)
D. String between CD is cut – block A will have zero acceleration (${a_A} = 0$)
Note:
When the string is cut then immediately tension becomes zero but when spring is cut then the restoring force which it was exerting previously on a block still remains the same and it will come into action after we cut the spring. In this way string and spring are quite different.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




