
Find out the number of monochlorinated products (including stereoisomers) which are possible in the given reaction.
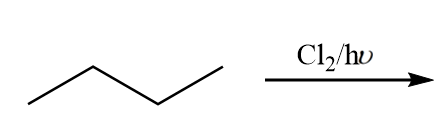
(A) $2$
(B) $3$
(C) $4$
(D) $5$

Answer
514.2k+ views
Hint :The two or more compounds which have the same molecular formula but differ in the arrangement of atoms in the space are known as stereoisomers. The most necessary condition for a compound to show stereoisomerism is that the compound should have at least one chiral carbon i.e., at least one carbon atom which is connected to four different groups.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
The reactant given in the question is n-butane and the attack of chlorine is possible at two positions in the carbon chain. The reactions possible are as follows:
Reaction-1: The attack of chlorine atom at first carbon:
When chlorine attacks the first carbon atom of n-butane in the presence of light, then the formation of 1-chlorobutane takes place along with the removal of $HCl$. The reaction proceeds as follows:
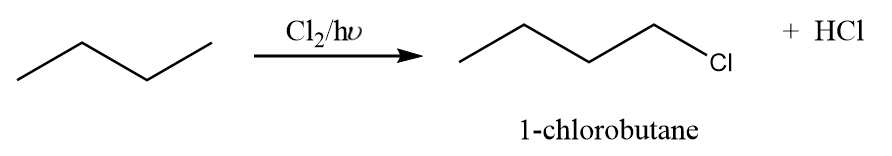
Reaction-2: The attack of chlorine atom at second carbon:
When chlorine attacks the second carbon atom of n-butane in the presence of light, then the formation of 2-chlorobutane takes place along with the removal of $HCl$. The reaction proceeds as follows:
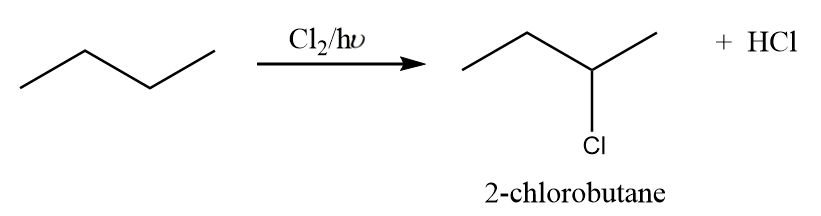
But the compound formed in the reaction i.e., 2-chlorobutane consist of a chiral carbon and thus, it will exist in its two absolute configurations which are as follows:
R-configuration: when chlorine atoms attack above the plane. The compound will be as follows:
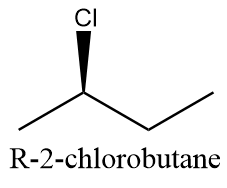
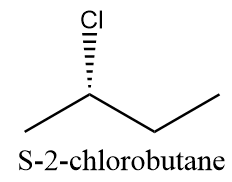
S-configuration: when chlorine atoms attack the chain from below the plane. The compound will be as follows:
Hence, three monochlorinated products (including stereoisomers) are possible for the given reaction.
So, option (B) is the correct answer.
Note :
It is important to note that n-butane is the symmetrical alkene, so the attack of chlorine on third and fourth carbon will form products identical to that of the first and second atom. Therefore, the attack on carbon third and fourth is not taken into consideration for the given reaction.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
The reactant given in the question is n-butane and the attack of chlorine is possible at two positions in the carbon chain. The reactions possible are as follows:
Reaction-1: The attack of chlorine atom at first carbon:
When chlorine attacks the first carbon atom of n-butane in the presence of light, then the formation of 1-chlorobutane takes place along with the removal of $HCl$. The reaction proceeds as follows:

Reaction-2: The attack of chlorine atom at second carbon:
When chlorine attacks the second carbon atom of n-butane in the presence of light, then the formation of 2-chlorobutane takes place along with the removal of $HCl$. The reaction proceeds as follows:

But the compound formed in the reaction i.e., 2-chlorobutane consist of a chiral carbon and thus, it will exist in its two absolute configurations which are as follows:
R-configuration: when chlorine atoms attack above the plane. The compound will be as follows:

S-configuration: when chlorine atoms attack the chain from below the plane. The compound will be as follows:

Hence, three monochlorinated products (including stereoisomers) are possible for the given reaction.
So, option (B) is the correct answer.
Note :
It is important to note that n-butane is the symmetrical alkene, so the attack of chlorine on third and fourth carbon will form products identical to that of the first and second atom. Therefore, the attack on carbon third and fourth is not taken into consideration for the given reaction.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




