
Find out the area (in square units) of the region bounded by the parabola, $\,y={{x}^{2}}+2$ and the lines \[y=x+1,\,x=0,\,x=3\]:
A. $\dfrac{15}{4}$
B. $\dfrac{15}{2}$
C. $\dfrac{21}{2}$
D. $\dfrac{17}{4}$
Answer
591.3k+ views
Hint: In order to find the area between the curves we have to do integration between the limits given in the question. For this question we will start by identifying the limits as [0,3] and then integrate the curves (parabola and line) by the basic power rule. After that we will put the upper limit and lower limit to find the area.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Let us draw the graph of the parabola and the lines given in the question, It will look like the following:
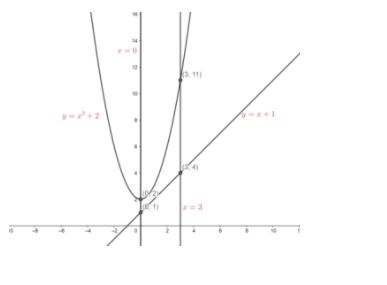
Now we have to find the area bound between these graphs and as we can see the lines x=0 and x=3, these lines shows the limit between which we have to find the area.
So we have to find the area between the curves $\,y={{x}^{2}}+2$ and $y=x+1$ on the interval [0,3]:
Now by the definition of area between the curves we know that:
The area between curves is the area between a curve $f\left( x \right)$ and $g\left( x \right)$ on an interval $\left[ a,b \right]$ is given by
$A=\int_{a}^{b}{|}f\left( x \right)-g\left( x \right)|dx$
Therefore, we will apply this definition to our question:
We have $f\left( x \right)={{x}^{2}}+2$ and $g\left( x \right)=x+1$ and we have the interval obtained as $\left[ 0,3 \right]$:
Therefore, Area between the curves become: $\int\limits_{0}^{3}{\left| \left( {{x}^{2}}+2 \right)-\left( x+1 \right) \right|}dx$
We will solve this integral to obtain our integral for this we will apply the basic property of ontegral that is:
$\int{\left( f\left( x \right)-g\left( x \right) \right)dx=}\int{f\left( x \right)dx-\int{g\left( x \right)dx}}$
Therefore,
\[\int\limits_{0}^{3}{\left| \left( {{x}^{2}}+2 \right)-\left( x+1 \right) \right|}dx=\int\limits_{0}^{3}{\left| \left( {{x}^{2}}+2 \right) \right|}dx-\int\limits_{0}^{3}{\left| \left( x+1 \right) \right|}dx\]
We will apply the power rule for integration to solve the given integration:
$\int{{{x}^{n}}dx=\dfrac{{{x}^{n+1}}}{n+1}+C}$
On applying this we will get the following:
\[\int\limits_{0}^{3}{\left| \left( {{x}^{2}}+2 \right) \right|}dx-\int\limits_{0}^{3}{\left| \left( x+1 \right) \right|}dx={{\left| \left| \dfrac{{{x}^{3}}}{3}+2x \right|-\left| \dfrac{{{x}^{2}}}{2}+x \right| \right|}^{3}}_{0}\]
We will now put the upper limit and lower limit in the above equation we will have:
\[\begin{align}
& {{\left| \left| \dfrac{{{x}^{3}}}{3}+2x \right|-\left| \dfrac{{{x}^{2}}}{2}+x \right| \right|}^{3}}_{0} \\
& \Rightarrow \left| \left( \dfrac{{{3}^{3}}}{3}+2\left( 3 \right) \right)-\left( \dfrac{{{0}^{3}}}{3}+2\left( 0 \right) \right) \right|-\left| \left( \dfrac{{{3}^{2}}}{2}+3 \right)-\left( \dfrac{{{0}^{2}}}{2}+0 \right) \right| \\
& \Rightarrow 15-\left( \dfrac{15}{2} \right) \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{15}{2} \\
\end{align}\]
Therefore, The area is $\dfrac{15}{2}$ .
So, the correct answer is “Option b”.
Note: Students can get confused while applying the upper limit and the lower limit, first apply the upper limit into the equation and then followed by a negative sign apply the lower limit. Since here our lower limit is 0, calculation is easy but it can get tedious if the limit is something other than 0.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Let us draw the graph of the parabola and the lines given in the question, It will look like the following:

Now we have to find the area bound between these graphs and as we can see the lines x=0 and x=3, these lines shows the limit between which we have to find the area.
So we have to find the area between the curves $\,y={{x}^{2}}+2$ and $y=x+1$ on the interval [0,3]:
Now by the definition of area between the curves we know that:
The area between curves is the area between a curve $f\left( x \right)$ and $g\left( x \right)$ on an interval $\left[ a,b \right]$ is given by
$A=\int_{a}^{b}{|}f\left( x \right)-g\left( x \right)|dx$
Therefore, we will apply this definition to our question:
We have $f\left( x \right)={{x}^{2}}+2$ and $g\left( x \right)=x+1$ and we have the interval obtained as $\left[ 0,3 \right]$:
Therefore, Area between the curves become: $\int\limits_{0}^{3}{\left| \left( {{x}^{2}}+2 \right)-\left( x+1 \right) \right|}dx$
We will solve this integral to obtain our integral for this we will apply the basic property of ontegral that is:
$\int{\left( f\left( x \right)-g\left( x \right) \right)dx=}\int{f\left( x \right)dx-\int{g\left( x \right)dx}}$
Therefore,
\[\int\limits_{0}^{3}{\left| \left( {{x}^{2}}+2 \right)-\left( x+1 \right) \right|}dx=\int\limits_{0}^{3}{\left| \left( {{x}^{2}}+2 \right) \right|}dx-\int\limits_{0}^{3}{\left| \left( x+1 \right) \right|}dx\]
We will apply the power rule for integration to solve the given integration:
$\int{{{x}^{n}}dx=\dfrac{{{x}^{n+1}}}{n+1}+C}$
On applying this we will get the following:
\[\int\limits_{0}^{3}{\left| \left( {{x}^{2}}+2 \right) \right|}dx-\int\limits_{0}^{3}{\left| \left( x+1 \right) \right|}dx={{\left| \left| \dfrac{{{x}^{3}}}{3}+2x \right|-\left| \dfrac{{{x}^{2}}}{2}+x \right| \right|}^{3}}_{0}\]
We will now put the upper limit and lower limit in the above equation we will have:
\[\begin{align}
& {{\left| \left| \dfrac{{{x}^{3}}}{3}+2x \right|-\left| \dfrac{{{x}^{2}}}{2}+x \right| \right|}^{3}}_{0} \\
& \Rightarrow \left| \left( \dfrac{{{3}^{3}}}{3}+2\left( 3 \right) \right)-\left( \dfrac{{{0}^{3}}}{3}+2\left( 0 \right) \right) \right|-\left| \left( \dfrac{{{3}^{2}}}{2}+3 \right)-\left( \dfrac{{{0}^{2}}}{2}+0 \right) \right| \\
& \Rightarrow 15-\left( \dfrac{15}{2} \right) \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{15}{2} \\
\end{align}\]
Therefore, The area is $\dfrac{15}{2}$ .
So, the correct answer is “Option b”.
Note: Students can get confused while applying the upper limit and the lower limit, first apply the upper limit into the equation and then followed by a negative sign apply the lower limit. Since here our lower limit is 0, calculation is easy but it can get tedious if the limit is something other than 0.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 8 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 8 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 8 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Master Class 8 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 8 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 7 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Using empirical formula calculate the mode of the following class 1 statistics CBSE

What are the factors of 100 class 7 maths CBSE

Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What is BLO What is the full form of BLO class 8 social science CBSE

The value of 6 more than 7 is A 1 B 1 C 13 D 13 class 7 maths CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE




