
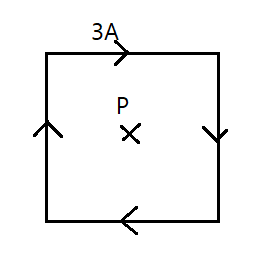
Find magnetic field at centre P if length of side of square loop is $20\;cm$
$\begin{align}
& A.12\sqrt{2}\times {{10}^{-6}}T \\
& B.12\times {{10}^{-6}}T \\
& C.6\times {{10}^{-6}}T \\
& D.6\sqrt{2}\times {{10}^{-6}}T \\
\end{align}$

Answer
567.9k+ views
Hint: We know that electricity and magnetism are interrelated. We know that a current carrying conductor can produce a magnetic field around itself. And similarly, a varying magnetic field induces a current in the wire which is kept in the near surrounding. Using the right hand thumb rule, we can find the direction of the magnetic field, when the direction of the current is given.
Formula:
$B=\dfrac{\mu_{0}i}{4\pi r}$
Complete answer:
We know that the magnetic field is an invisible force which is a vector that influences an electric charge and a few magnetic metals. Since it’s a vector clearly, it has both direction and magnitude. A magnet has two different poles, namely the North and the South Pole. Generally, the like poles attract, while the unlike poles repel. This is saying that, North Pole of one magnet repels from the north pole of another magnet, this is true for two South Pole also. However, if a North Pole of one magnet is brought near the south pole of another magnet, then they attract.
We also know that magnetic field $B$ for a straight wire is given as, $B=\dfrac{\mu_{0}i}{4\pi r}$
Clearly, from the right hand thumb rule, since the magnetic field inside the loop is directed into the paper, we can say that the net magnetic field at P is the sum total of all the magnetic fields due to the current carrying loop.
Then, we have, $B_{P}=4\times \dfrac{\mu_{0}i}{4\pi r}$
Here, given that $i=3A$ and $l=20cm$ then, $r=10cm$ where $r$ is the distance of the point from the wire. On substitution, we get,
$\implies B_{P}=\dfrac{4\mu_{0}\times 3}{4\pi\times 10\times 10^{-2}}$
$\implies B_{P}=12\times 10^{-7}\times 10^{1}$
$\therefore B_{P}=12\times 10^{6}T$
Thus, the correct answer is option is $B.12\times {{10}^{-6}}T$
Note:
We know that the magnetic field is a vector quality, and hence has both direction and magnitude. We can also say that, the direction of the magnetic field is given from the right hand thumb rule, provided, the direction of the current is known. And vice-versa.
Formula:
$B=\dfrac{\mu_{0}i}{4\pi r}$
Complete answer:
We know that the magnetic field is an invisible force which is a vector that influences an electric charge and a few magnetic metals. Since it’s a vector clearly, it has both direction and magnitude. A magnet has two different poles, namely the North and the South Pole. Generally, the like poles attract, while the unlike poles repel. This is saying that, North Pole of one magnet repels from the north pole of another magnet, this is true for two South Pole also. However, if a North Pole of one magnet is brought near the south pole of another magnet, then they attract.
We also know that magnetic field $B$ for a straight wire is given as, $B=\dfrac{\mu_{0}i}{4\pi r}$
Clearly, from the right hand thumb rule, since the magnetic field inside the loop is directed into the paper, we can say that the net magnetic field at P is the sum total of all the magnetic fields due to the current carrying loop.
Then, we have, $B_{P}=4\times \dfrac{\mu_{0}i}{4\pi r}$
Here, given that $i=3A$ and $l=20cm$ then, $r=10cm$ where $r$ is the distance of the point from the wire. On substitution, we get,
$\implies B_{P}=\dfrac{4\mu_{0}\times 3}{4\pi\times 10\times 10^{-2}}$
$\implies B_{P}=12\times 10^{-7}\times 10^{1}$
$\therefore B_{P}=12\times 10^{6}T$
Thus, the correct answer is option is $B.12\times {{10}^{-6}}T$
Note:
We know that the magnetic field is a vector quality, and hence has both direction and magnitude. We can also say that, the direction of the magnetic field is given from the right hand thumb rule, provided, the direction of the current is known. And vice-versa.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




