
Find graphically, the maximum value of \[z = 2x + 5y\] , subject to constraints given below:
\[2x + 4y \leqslant 8\]
\[3x + y \leqslant 6\]
\[x + y \leqslant 4\]
\[x \geqslant 0,y \leqslant 0.6\]
Answer
534k+ views
Hint: To solve the above question, we have to carefully study the floor plan shown in the diagram of the sample house. A floor plan shows the layout of buildings seen from the top view. You have to read the room labels and identify the number of bedrooms and the number of bathrooms present in the plan to know what type of apartment it is.
Complete step by step solution:
In the first step, we will separate the \[y\] variables on one side. We get,
\[4y \leqslant 8 - 2x\]
\[y \leqslant 6 - 3x\]
\[y \leqslant 4 - x\]
\[x \geqslant 0,y \leqslant 0.6\]
Now, to maximize the value of\[z = 2x + 5y\] we will convert the inequalities into equations. Now we will be dealing with lines.
\[4y = 8 - 2x\] or \[2y = 4 - x\]
\[y = 6 - 3x\]
\[y = 4 - x\]
\[x = 0,y = 0.6\]
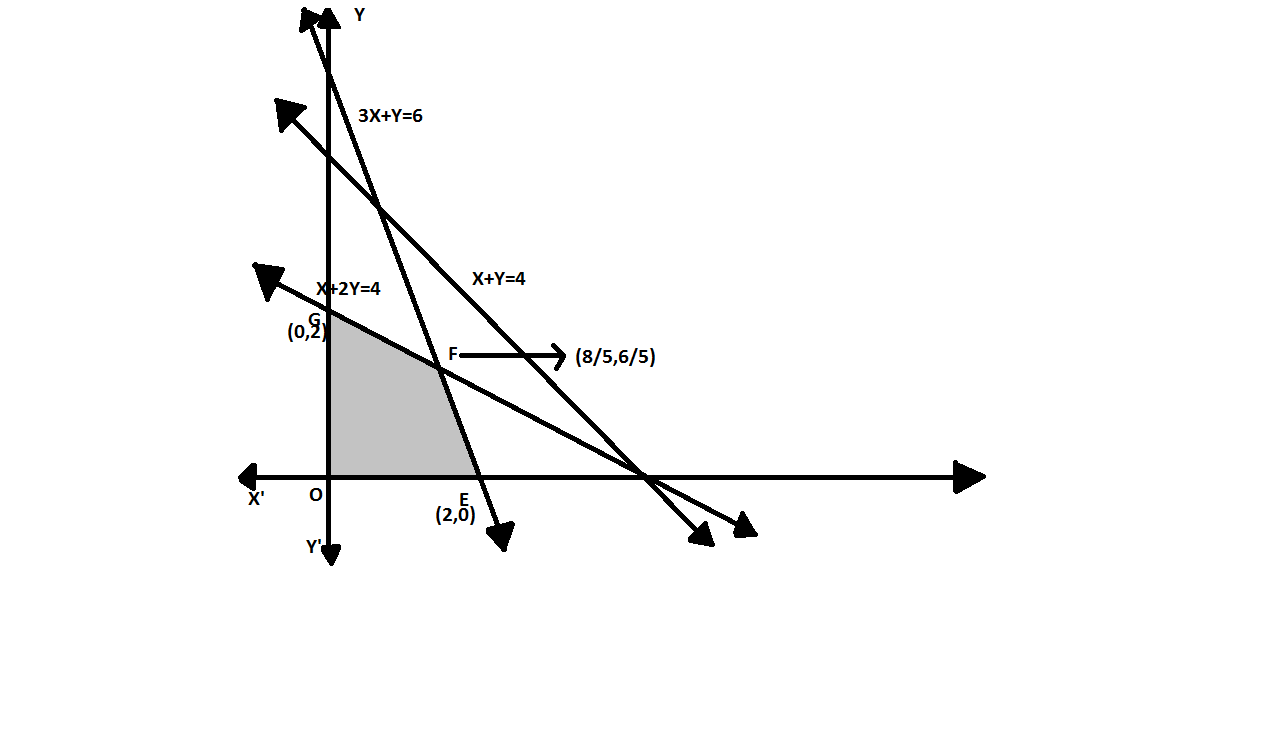
The first line, \[2y = 4 - x\] passes through the points \[\left( {4,0} \right),\left( {0,2} \right)\] .
The second line, \[y = 6 - 3x\] passes through the points \[\left( {2,0} \right),\left( {0,6} \right)\] .
The third line, \[y = 4 - x\] passes through the points \[\left( {4,0} \right),\left( {0,4} \right)\] .
We can plot the points on the graph and shade the region determined by these inequalities.
Now, we have to solve \[2y = 4 - x\] and \[y = 6 - 3x\] simultaneously, to get a point \[\left( {\dfrac{8}{5},\dfrac{6}{5}} \right)\] .
On plotting these points, we observe the region \[OEFG\] , \[O\left( {0,0} \right)\] , \[E\left( {2,0} \right)\] , \[F\left( {\dfrac{8}{5},\dfrac{6}{5}} \right)\] and \[G\left( {0,2} \right)\] . One of these points contains the optimal solution.
Now we have to calculate the maximum value of \[z = 2x + 5y\] ,
At \[O\left( {0,0} \right)\], \[z = 2\left( 0 \right) + 5\left( 0 \right)\]
\[ = 0\] .
At \[E\left( {2,0} \right)\] , \[z = 2\left( 2 \right) + 5\left( 0 \right)\]
\[ = 4\] .
At \[F\left( {\dfrac{8}{5},\dfrac{6}{5}} \right)\] , \[z = 2\left( {\dfrac{8}{5}} \right) + 5\left( {\dfrac{6}{5}} \right)\]
\[ = \dfrac{{46}}{5}\] .
And at \[G\left( {0,2} \right)\] , \[z = 2\left( 0 \right) + 5\left( 2 \right)\]
\[ = 10\] .
From the above values, we can derive that the maximum value of \[z = 2x + 5y\] is \[10\] .
Hence the maximum value of \[z = 2x + 5y\] is at point \[G\left( {0,2} \right)\] .
Note: To solve the above question, we have to follow certain steps which are required to graph solutions of inequality. First, the \[y\] variables in each inequality are separated on one side and after that the sign of inequality is changed into equality. After performing these steps, you can now graph a line.
Complete step by step solution:
In the first step, we will separate the \[y\] variables on one side. We get,
\[4y \leqslant 8 - 2x\]
\[y \leqslant 6 - 3x\]
\[y \leqslant 4 - x\]
\[x \geqslant 0,y \leqslant 0.6\]
Now, to maximize the value of\[z = 2x + 5y\] we will convert the inequalities into equations. Now we will be dealing with lines.
\[4y = 8 - 2x\] or \[2y = 4 - x\]
\[y = 6 - 3x\]
\[y = 4 - x\]
\[x = 0,y = 0.6\]
The first line, \[2y = 4 - x\] passes through the points \[\left( {4,0} \right),\left( {0,2} \right)\] .
The second line, \[y = 6 - 3x\] passes through the points \[\left( {2,0} \right),\left( {0,6} \right)\] .
The third line, \[y = 4 - x\] passes through the points \[\left( {4,0} \right),\left( {0,4} \right)\] .
We can plot the points on the graph and shade the region determined by these inequalities.
Now, we have to solve \[2y = 4 - x\] and \[y = 6 - 3x\] simultaneously, to get a point \[\left( {\dfrac{8}{5},\dfrac{6}{5}} \right)\] .
On plotting these points, we observe the region \[OEFG\] , \[O\left( {0,0} \right)\] , \[E\left( {2,0} \right)\] , \[F\left( {\dfrac{8}{5},\dfrac{6}{5}} \right)\] and \[G\left( {0,2} \right)\] . One of these points contains the optimal solution.
Now we have to calculate the maximum value of \[z = 2x + 5y\] ,
At \[O\left( {0,0} \right)\], \[z = 2\left( 0 \right) + 5\left( 0 \right)\]
\[ = 0\] .
At \[E\left( {2,0} \right)\] , \[z = 2\left( 2 \right) + 5\left( 0 \right)\]
\[ = 4\] .
At \[F\left( {\dfrac{8}{5},\dfrac{6}{5}} \right)\] , \[z = 2\left( {\dfrac{8}{5}} \right) + 5\left( {\dfrac{6}{5}} \right)\]
\[ = \dfrac{{46}}{5}\] .
And at \[G\left( {0,2} \right)\] , \[z = 2\left( 0 \right) + 5\left( 2 \right)\]
\[ = 10\] .
From the above values, we can derive that the maximum value of \[z = 2x + 5y\] is \[10\] .
Hence the maximum value of \[z = 2x + 5y\] is at point \[G\left( {0,2} \right)\] .

Note: To solve the above question, we have to follow certain steps which are required to graph solutions of inequality. First, the \[y\] variables in each inequality are separated on one side and after that the sign of inequality is changed into equality. After performing these steps, you can now graph a line.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




