
How do you find \[\cos \] if \[\sin = \left( {\dfrac{5}{{13}}} \right)\] ?
Answer
558.9k+ views
Hint: We are given the value of sine function and asked to find the value of cosine. To know the value of cosine we will need an equation to convert sine to cosine. For this you will need to recall a trigonometric identity of sine and cosine. Use this trigonometric identity to find the value of cosine.
Complete step-by-step answer:
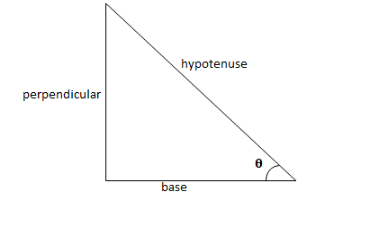
In case of a right angled triangle, we can write hypotenuse, base and perpendicular in terms of sine and cosine function as,
\[\sin \theta = \dfrac{{{\text{perpendicular}}}}{{{\text{hypotenuse}}}}\] and \[\cos \theta = \dfrac{{{\text{base}}}}{{{\text{hypotenuse}}}}\]
Given, \[\sin = \left( {\dfrac{5}{{13}}} \right)\]
We are asked to find the value of cosine function.
To find cosine we need an equation to convert sine function to cosine function.
From trigonometric identities, we have an equation,
\[{\sin ^2}\theta + {\cos ^2}\theta = 1\] (i)
Here, \[\sin \theta = \left( {\dfrac{5}{{13}}} \right)\]
Putting this value in equation (i) we get,
\[{\left( {\dfrac{5}{{13}}} \right)^2} + {\cos ^2}\theta = 1\]
\[ \Rightarrow {\cos ^2}\theta = 1 - {\left( {\dfrac{5}{{13}}} \right)^2}\]
\[ \Rightarrow {\cos ^2}\theta = 1 - \dfrac{{25}}{{169}}\]
\[ \Rightarrow {\cos ^2}\theta = \dfrac{{144}}{{169}}\]
\[ \Rightarrow \cos \theta = \pm \sqrt {\dfrac{{144}}{{169}}} \]
\[ \Rightarrow \cos \theta = \pm \dfrac{{12}}{{13}}\]
Therefore, the value of cosine is \[ \pm \dfrac{{12}}{{13}}\] .
So, the correct answer is “ \[ \pm \dfrac{{12}}{{13}}\] ”.
Note: There are three main functions in trigonometry, these are sine, cosine and tangent. There are three other trigonometric functions which can be written in terms of the main functions, these are cosecant which is inverse of sine, secant which is inverse of cosine and cotangent which is inverse of tangent. Also, while solving questions related to trigonometry, you should always remember the basic trigonometric identities. The trigonometric identity \[{\sin ^2}\theta + {\cos ^2}\theta = 1\] is also known as Pythagorean identity.
Complete step-by-step answer:

In case of a right angled triangle, we can write hypotenuse, base and perpendicular in terms of sine and cosine function as,
\[\sin \theta = \dfrac{{{\text{perpendicular}}}}{{{\text{hypotenuse}}}}\] and \[\cos \theta = \dfrac{{{\text{base}}}}{{{\text{hypotenuse}}}}\]
Given, \[\sin = \left( {\dfrac{5}{{13}}} \right)\]
We are asked to find the value of cosine function.
To find cosine we need an equation to convert sine function to cosine function.
From trigonometric identities, we have an equation,
\[{\sin ^2}\theta + {\cos ^2}\theta = 1\] (i)
Here, \[\sin \theta = \left( {\dfrac{5}{{13}}} \right)\]
Putting this value in equation (i) we get,
\[{\left( {\dfrac{5}{{13}}} \right)^2} + {\cos ^2}\theta = 1\]
\[ \Rightarrow {\cos ^2}\theta = 1 - {\left( {\dfrac{5}{{13}}} \right)^2}\]
\[ \Rightarrow {\cos ^2}\theta = 1 - \dfrac{{25}}{{169}}\]
\[ \Rightarrow {\cos ^2}\theta = \dfrac{{144}}{{169}}\]
\[ \Rightarrow \cos \theta = \pm \sqrt {\dfrac{{144}}{{169}}} \]
\[ \Rightarrow \cos \theta = \pm \dfrac{{12}}{{13}}\]
Therefore, the value of cosine is \[ \pm \dfrac{{12}}{{13}}\] .
So, the correct answer is “ \[ \pm \dfrac{{12}}{{13}}\] ”.
Note: There are three main functions in trigonometry, these are sine, cosine and tangent. There are three other trigonometric functions which can be written in terms of the main functions, these are cosecant which is inverse of sine, secant which is inverse of cosine and cotangent which is inverse of tangent. Also, while solving questions related to trigonometry, you should always remember the basic trigonometric identities. The trigonometric identity \[{\sin ^2}\theta + {\cos ^2}\theta = 1\] is also known as Pythagorean identity.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

10 examples of friction in our daily life




