
Find by integration, the area bounded by the curve $y=2x-{{x}^{2}}$ and the x-axis.
Answer
606.9k+ views
Hint: Plot the curve on a graph. Use the fact that the area bounded by the curve y = f(x), the x-axis, and the ordinates x= a and x = b is given by $\int_{a}^{b}{\left| f\left( x \right) \right|dx}$. Argue that the required area is the area bounded by the curve $y=2x-{{x}^{2}}$, the x-axis and the ordinates x= 0 and x= 2.Hence prove that the required area is $\int_{0}^{2}{\left( 2x-{{x}^{2}} \right)dx}$. Integrate and hence find the required area.
Complete step-by-step answer:
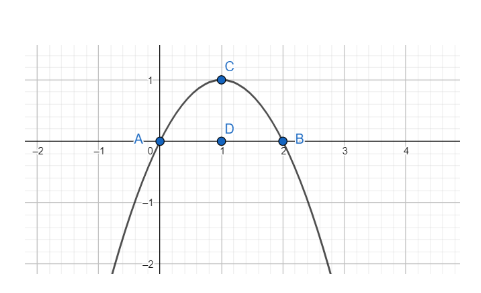
As is evident from the graph, the area bound the curve $y=2x-{{x}^{2}}$ is equal to the area ACBDA.
Finding the coordinates of A and B:
As is evident from the A and B are the roots of $f\left( x \right)=2x-{{x}^{2}}$
Hence, we have
$2x-{{x}^{2}}=0\Rightarrow x=0,2$
Hence, we have $A\equiv \left( 0,0 \right)$ and $B\equiv \left( 2,0 \right)$
Hence the area ACBDA is the area bounded by the curve $y=2x-{{x}^{2}}$, the x-axis and the ordinates x= 0 and x= 2.
We know that the area bounded by the curve y = f(x), the x-axis, and the ordinates x= a and x = b is given by $\int_{a}^{b}{\left| f\left( x \right) \right|dx}$
Hence, we have
Required area $=\int_{0}^{2}{\left| 2x-{{x}^{2}} \right|}dx$
Now, we have $2x-{{x}^{2}}=x\left( 2-x \right)$
In the interval (0,2), we have x and 2-x both are non-negative
Hence, we have $x\left( 2-x \right)\ge 0$
Hence, we have
$\left| x\left( 2-x \right) \right|=x\left( 2-x \right)$
Hence, we have
Required area $=\int_{0}^{2}{\left( 2x-{{x}^{2}} \right)dx}=\left. {{x}^{2}}-\dfrac{{{x}^{3}}}{3} \right|_{0}^{2}=\left( 4-\dfrac{8}{3} \right)=\dfrac{4}{3}$ square units.
Note: Alternative use the fact that the area bounded by the curve $y=C\left( x-a \right)\left( x-b \right)$ and the x-axis is given by $\dfrac{\left| C \right|{{\left( a-b \right)}^{3}}}{6}$
Here, we have $2x-{{x}^{2}}=-\left( x-0 \right)\left( x-2 \right)$
Hence a = 0, b = 2 and C =-1
Hence the required area is $\dfrac{\left| -1 \right|{{\left( 2-0 \right)}^{3}}}{6}=\dfrac{8}{6}=\dfrac{4}{3}$, which is the same as obtained above.
Complete step-by-step answer:

As is evident from the graph, the area bound the curve $y=2x-{{x}^{2}}$ is equal to the area ACBDA.
Finding the coordinates of A and B:
As is evident from the A and B are the roots of $f\left( x \right)=2x-{{x}^{2}}$
Hence, we have
$2x-{{x}^{2}}=0\Rightarrow x=0,2$
Hence, we have $A\equiv \left( 0,0 \right)$ and $B\equiv \left( 2,0 \right)$
Hence the area ACBDA is the area bounded by the curve $y=2x-{{x}^{2}}$, the x-axis and the ordinates x= 0 and x= 2.
We know that the area bounded by the curve y = f(x), the x-axis, and the ordinates x= a and x = b is given by $\int_{a}^{b}{\left| f\left( x \right) \right|dx}$
Hence, we have
Required area $=\int_{0}^{2}{\left| 2x-{{x}^{2}} \right|}dx$
Now, we have $2x-{{x}^{2}}=x\left( 2-x \right)$
In the interval (0,2), we have x and 2-x both are non-negative
Hence, we have $x\left( 2-x \right)\ge 0$
Hence, we have
$\left| x\left( 2-x \right) \right|=x\left( 2-x \right)$
Hence, we have
Required area $=\int_{0}^{2}{\left( 2x-{{x}^{2}} \right)dx}=\left. {{x}^{2}}-\dfrac{{{x}^{3}}}{3} \right|_{0}^{2}=\left( 4-\dfrac{8}{3} \right)=\dfrac{4}{3}$ square units.
Note: Alternative use the fact that the area bounded by the curve $y=C\left( x-a \right)\left( x-b \right)$ and the x-axis is given by $\dfrac{\left| C \right|{{\left( a-b \right)}^{3}}}{6}$
Here, we have $2x-{{x}^{2}}=-\left( x-0 \right)\left( x-2 \right)$
Hence a = 0, b = 2 and C =-1
Hence the required area is $\dfrac{\left| -1 \right|{{\left( 2-0 \right)}^{3}}}{6}=\dfrac{8}{6}=\dfrac{4}{3}$, which is the same as obtained above.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Chemistry: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 12 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Complete reduction of benzene diazonium chloride with class 12 chemistry CBSE

How can you identify optical isomers class 12 chemistry CBSE

Trending doubts
What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE

RNA and DNA are chiral molecules their chirality is class 12 chemistry CBSE

India is a sovereign socialist secular democratic republic class 12 social science CBSE

How many states of matter are there in total class 12 chemistry CBSE




