
How do you find an equation of the parabola with vertex $\left( -2,1 \right)$ and directrix $x=1$?
Answer
558k+ views
Hint: We start solving the problem by drawing the figure representing the given information. We then make use of the facts that the axis of the parabola is perpendicular to the directrix of the parabola and passes through the vertex to find the axis of the parabola. We then find the intersection point of the axis and parabola. We then make the necessary calculations to get the focus of the parabola. We then make use of the fact that the distance between the point on parabola and its focus is equal to the distance between the point on parabola and its directrix to proceed through the problem. We then make the necessary calculations to get the required equation of a parabola.
Complete step by step answer:
According to the problem, we are asked to find the equation of the parabola with vertex $\left( -2,1 \right)$ and directrix $x=1$.
Let us draw the figure representing the given information.
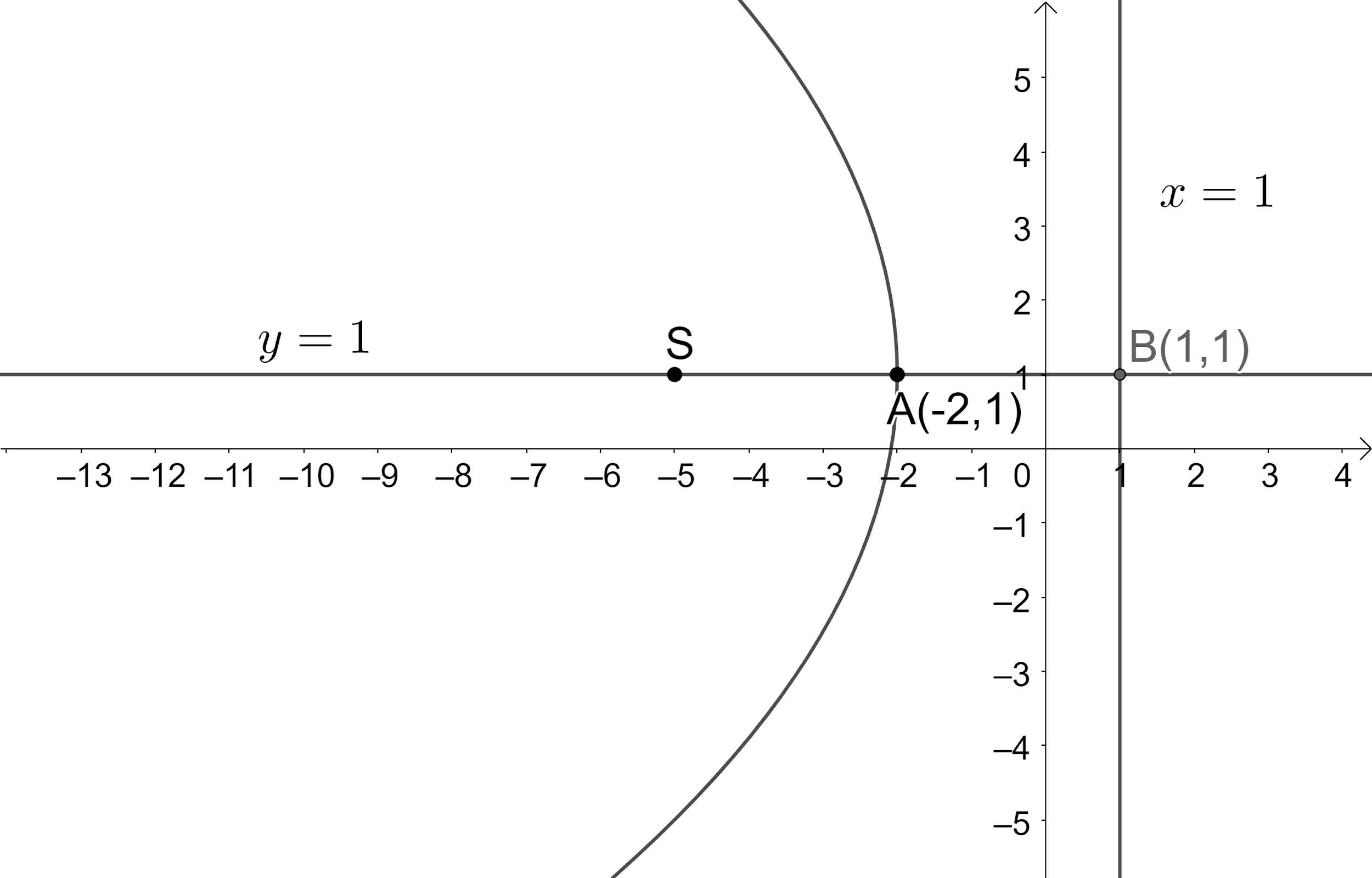
We know that the axis of the parabola is perpendicular to the directrix of the parabola and passes through the vertex.
We know that the general equation of the line perpendicular to $x=k$ is $y=p$. Let us assume the equation of the axis be $y=p$ ---(1).
But this axis is passing through $A\left( -2,1 \right)$.
So, we have $1=p$ ---(2).
Let us substitute equation (2) in equation (1).
So, the equation of the axis of the parabola is $y=1$.
We know that the point of intersection of the lines $x=a$ and $y=b$ is $\left( a,b \right)$. So, the point of intersection of the lines $x=1$ and $y=1$ is $B\left( 1,1 \right)$.
We know that vertex A is the midpoint of the focus S and B.
Let us assume $S\left( a,b \right)$ be the focus of parabola.
So, we have $\left( -2,1 \right)=\left( \dfrac{a+1}{2},\dfrac{b+1}{2} \right)$.
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{a+1}{2}=-2$, $\dfrac{b+1}{2}=1$.
$\Rightarrow a+1=-4$, $b+1=2$.
$\Rightarrow a=-5$, $b=1$.
So, we have found the focus of the parabola as $S\left( -5,1 \right)$.
Let us assume $P\left( x,y \right)$ be the point on the parabola. We know that the distance between the point on parabola and its focus is equal to the distance between the point on parabola and its directrix.
So, we have $\sqrt{{{\left( x+5 \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( y-1 \right)}^{2}}}=\dfrac{\left| x-1 \right|}{\sqrt{{{1}^{2}}}}$.
$\Rightarrow \sqrt{{{x}^{2}}+10x+25+{{y}^{2}}-2y+1}=\dfrac{\left| x-1 \right|}{1}$.
$\Rightarrow \sqrt{{{x}^{2}}+10x+{{y}^{2}}-2y+26}=\left| x-1 \right|$.
$\Rightarrow {{x}^{2}}+10x+{{y}^{2}}-2y+26={{\left( x-1 \right)}^{2}}$.
$\Rightarrow {{x}^{2}}+10x+{{y}^{2}}-2y+26={{x}^{2}}-2x+1$.
$\Rightarrow 12x+{{y}^{2}}-2y+25=0$.
$\Rightarrow {{y}^{2}}-2y+1=-12x-24$.
$\Rightarrow {{\left( y-1 \right)}^{2}}=-12\left( x+2 \right)$.
$\therefore $ We have found the equation of the parabola as ${{\left( y-1 \right)}^{2}}=-12\left( x+2 \right)$.
Note:
We can see that the given problem contains a huge amount of calculation, so we need to perform each step carefully to avoid confusion and calculation mistakes. We can also solve the given problem by first finding the distance between the vertex and directrix as ‘a’ and then making use of the fact that the equation of the parabola with vertex $\left( h,k \right)$ in the second quadrant and directrix parallel to the y-axis and present in the first and fourth quadrant is ${{\left( y-k \right)}^{2}}=-4a\left( x-h \right)$. Similarly, we can expect problems to find the equation of the parabola with vertex $\left( 1,2 \right)$ and directrix $x+1$.
Complete step by step answer:
According to the problem, we are asked to find the equation of the parabola with vertex $\left( -2,1 \right)$ and directrix $x=1$.
Let us draw the figure representing the given information.

We know that the axis of the parabola is perpendicular to the directrix of the parabola and passes through the vertex.
We know that the general equation of the line perpendicular to $x=k$ is $y=p$. Let us assume the equation of the axis be $y=p$ ---(1).
But this axis is passing through $A\left( -2,1 \right)$.
So, we have $1=p$ ---(2).
Let us substitute equation (2) in equation (1).
So, the equation of the axis of the parabola is $y=1$.
We know that the point of intersection of the lines $x=a$ and $y=b$ is $\left( a,b \right)$. So, the point of intersection of the lines $x=1$ and $y=1$ is $B\left( 1,1 \right)$.
We know that vertex A is the midpoint of the focus S and B.
Let us assume $S\left( a,b \right)$ be the focus of parabola.
So, we have $\left( -2,1 \right)=\left( \dfrac{a+1}{2},\dfrac{b+1}{2} \right)$.
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{a+1}{2}=-2$, $\dfrac{b+1}{2}=1$.
$\Rightarrow a+1=-4$, $b+1=2$.
$\Rightarrow a=-5$, $b=1$.
So, we have found the focus of the parabola as $S\left( -5,1 \right)$.
Let us assume $P\left( x,y \right)$ be the point on the parabola. We know that the distance between the point on parabola and its focus is equal to the distance between the point on parabola and its directrix.
So, we have $\sqrt{{{\left( x+5 \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( y-1 \right)}^{2}}}=\dfrac{\left| x-1 \right|}{\sqrt{{{1}^{2}}}}$.
$\Rightarrow \sqrt{{{x}^{2}}+10x+25+{{y}^{2}}-2y+1}=\dfrac{\left| x-1 \right|}{1}$.
$\Rightarrow \sqrt{{{x}^{2}}+10x+{{y}^{2}}-2y+26}=\left| x-1 \right|$.
$\Rightarrow {{x}^{2}}+10x+{{y}^{2}}-2y+26={{\left( x-1 \right)}^{2}}$.
$\Rightarrow {{x}^{2}}+10x+{{y}^{2}}-2y+26={{x}^{2}}-2x+1$.
$\Rightarrow 12x+{{y}^{2}}-2y+25=0$.
$\Rightarrow {{y}^{2}}-2y+1=-12x-24$.
$\Rightarrow {{\left( y-1 \right)}^{2}}=-12\left( x+2 \right)$.
$\therefore $ We have found the equation of the parabola as ${{\left( y-1 \right)}^{2}}=-12\left( x+2 \right)$.
Note:
We can see that the given problem contains a huge amount of calculation, so we need to perform each step carefully to avoid confusion and calculation mistakes. We can also solve the given problem by first finding the distance between the vertex and directrix as ‘a’ and then making use of the fact that the equation of the parabola with vertex $\left( h,k \right)$ in the second quadrant and directrix parallel to the y-axis and present in the first and fourth quadrant is ${{\left( y-k \right)}^{2}}=-4a\left( x-h \right)$. Similarly, we can expect problems to find the equation of the parabola with vertex $\left( 1,2 \right)$ and directrix $x+1$.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

The draft of the Preamble of the Indian Constitution class 10 social science CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who gave "Inqilab Zindabad" slogan?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?




