
Find all the zeroes of $2{{x}^{4}}-3{{x}^{3}}-3{{x}^{2}}+6x-2$, if you know that two of its zeroes are $\sqrt{2}$ and $-\sqrt{2}$?
Answer
570.9k+ views
Hint: We start solving the problem by recalling the fact that if ‘a’ is zero of the polynomial $f\left( x \right)$, then $x-a$ is the factor of $f\left( x \right)$. We then find the factors using the given zeros and then multiply them. We then perform long division by taking the obtained result of multiplication as a divisor and the given polynomial is divided to get the quotient. We then factorize the quotient and then equate the factors to zero to get all the zeroes of the given polynomial.
Complete step-by-step answer:
According to the problem, we are asked to find the zeros of the polynomial $2{{x}^{4}}-3{{x}^{3}}-3{{x}^{2}}+6x-2$ if two of the zeroes are $\sqrt{2}$ and $-\sqrt{2}$.
We know that if ‘a’ is zero of the polynomial $f\left( x \right)$, then $x-a$ is the factor of $f\left( x \right)$.
So, we get $x-\sqrt{2}$ and $x+\sqrt{2}$ are the factors of the polynomial $2{{x}^{4}}-3{{x}^{3}}-3{{x}^{2}}+6x-2$.
Let us find the multiplication of both the factors $x-\sqrt{2}$ and $x+\sqrt{2}$.
So, the product is $\left( x-\sqrt{2} \right)\times \left( x+\sqrt{2} \right)={{x}^{2}}-2$.
Let us divide $2{{x}^{4}}-3{{x}^{3}}-3{{x}^{2}}+6x-2$ with ${{x}^{2}}-2$ by using long division process as shown below:
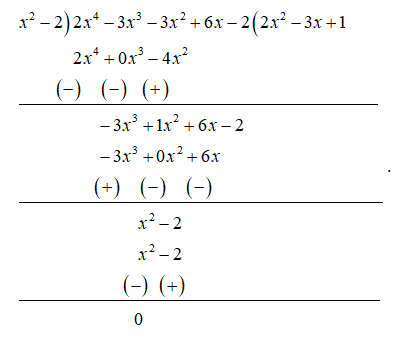
From the division algorithm, we know that dividend = $\left( \text{Divisor}\times \text{Quotient} \right)+\text{Remainder}$.
Here we have $2{{x}^{4}}-3{{x}^{3}}-3{{x}^{2}}+6x-2$ as dividend, ${{x}^{2}}-2$ as divisor, $2{{x}^{2}}-3x+1$ as quotient and 0 as the remainder.
So, we get $2{{x}^{4}}-3{{x}^{3}}-3{{x}^{2}}+6x-2=\left( {{x}^{2}}-2 \right)\times \left( 2{{x}^{2}}-3x+1 \right)$.
Now, let us factorize $2{{x}^{2}}-3x+1$ to get the remaining zeros of $2{{x}^{4}}-3{{x}^{3}}-3{{x}^{2}}+6x-2$.
So, we get $2{{x}^{2}}-3x+1=2{{x}^{2}}-2x-x+1$.
$\Rightarrow 2{{x}^{2}}-3x+1=2x\left( x-1 \right)-1\left( x-1 \right)$.
$\Rightarrow 2{{x}^{2}}-3x+1=\left( 2x-1 \right)\left( x-1 \right)$.
So, we have found $2{{x}^{4}}-3{{x}^{3}}-3{{x}^{2}}+6x-2=\left( x-\sqrt{2} \right)\times \left( x+\sqrt{2} \right)\times \left( x-1 \right)\times \left( 2x-1 \right)$.
We know that zeroes are found when the given polynomial is equated to zero.
So, we get $\left( x-\sqrt{2} \right)\times \left( x+\sqrt{2} \right)\times \left( x-1 \right)\times \left( 2x-1 \right)=0$.
\[\Rightarrow x-\sqrt{2}=0\], $x+\sqrt{2}=0$, $x-1=0$, $2x-1=0$.
\[\Rightarrow x=\sqrt{2}\], $x=-\sqrt{2}$, $x=1$, $2x=1$.
\[\Rightarrow x=\sqrt{2}\], $x=-\sqrt{2}$, $x=1$, $x=\dfrac{1}{2}$.
∴ We have found the zeroes of the polynomial $2{{x}^{4}}-3{{x}^{3}}-3{{x}^{2}}+6x-2$ as $\sqrt{2}$, $-\sqrt{2}$, 1, $\dfrac{1}{2}$.
Note: We can solve the problem by performing trial and error method for the given polynomial. We can also solve this problem as shown below:
We are given the polynomial $2{{x}^{4}}-3{{x}^{3}}-3{{x}^{2}}+6x-2$ and two of the zeroes are $\sqrt{2}$ and $-\sqrt{2}$. Let us assume the remaining two zeroes are ‘p’ and ‘q’.
We know that the sum of the zeroes of the polynomial $a{{x}^{4}}+b{{x}^{3}}+c{{x}^{2}}+dx+e$ is $\dfrac{-b}{a}$ and product of the zeroes of the polynomial $a{{x}^{4}}+b{{x}^{3}}+c{{x}^{2}}+dx+e$ is $\dfrac{e}{a}$.
So, we get $\sqrt{2}-\sqrt{2}+p+q=\dfrac{-\left( -3 \right)}{2}$,
$\Rightarrow p+q=\dfrac{3}{2}$.
$\Rightarrow q=\dfrac{3}{2}-p$ ---(1).
Now, we have $\left( \sqrt{2} \right)\times \left( -\sqrt{2} \right)\times p\times q=\dfrac{-2}{2}$.
$\Rightarrow -2pq=-1$.
$\Rightarrow pq=\dfrac{1}{2}$ ---(2).
Let us substitute equation (1) in equation (2).
$\Rightarrow p\left( \dfrac{3}{2}-p \right)=\dfrac{1}{2}$.
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{3}{2}p-{{p}^{2}}=\dfrac{1}{2}$.
$\Rightarrow {{p}^{2}}-\dfrac{3}{2}p+\dfrac{1}{2}=0$.
$\Rightarrow {{p}^{2}}-\dfrac{1}{2}p-p+\dfrac{1}{2}=0$.
$\Rightarrow p\left( p-\dfrac{1}{2} \right)-1\left( p-\dfrac{1}{2} \right)=0$.
$\Rightarrow \left( p-1 \right)\left( p-\dfrac{1}{2} \right)=0$.
$\Rightarrow p-1=0$ or $p-\dfrac{1}{2}=0$.
$\Rightarrow p=1$ or $p=\dfrac{1}{2}$.
Let us substitute these values in equation (2) to get the values of ‘q’.
If $p=1$, then $1\times q=\dfrac{1}{2}\Leftrightarrow q=\dfrac{1}{2}$.
If $p=\dfrac{1}{2}$, then $\dfrac{1}{2}\times q=\dfrac{1}{2}\Leftrightarrow q=1$.
Complete step-by-step answer:
According to the problem, we are asked to find the zeros of the polynomial $2{{x}^{4}}-3{{x}^{3}}-3{{x}^{2}}+6x-2$ if two of the zeroes are $\sqrt{2}$ and $-\sqrt{2}$.
We know that if ‘a’ is zero of the polynomial $f\left( x \right)$, then $x-a$ is the factor of $f\left( x \right)$.
So, we get $x-\sqrt{2}$ and $x+\sqrt{2}$ are the factors of the polynomial $2{{x}^{4}}-3{{x}^{3}}-3{{x}^{2}}+6x-2$.
Let us find the multiplication of both the factors $x-\sqrt{2}$ and $x+\sqrt{2}$.
So, the product is $\left( x-\sqrt{2} \right)\times \left( x+\sqrt{2} \right)={{x}^{2}}-2$.
Let us divide $2{{x}^{4}}-3{{x}^{3}}-3{{x}^{2}}+6x-2$ with ${{x}^{2}}-2$ by using long division process as shown below:
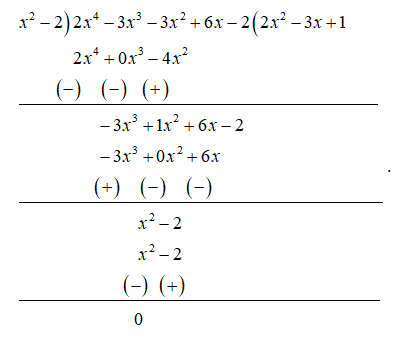
From the division algorithm, we know that dividend = $\left( \text{Divisor}\times \text{Quotient} \right)+\text{Remainder}$.
Here we have $2{{x}^{4}}-3{{x}^{3}}-3{{x}^{2}}+6x-2$ as dividend, ${{x}^{2}}-2$ as divisor, $2{{x}^{2}}-3x+1$ as quotient and 0 as the remainder.
So, we get $2{{x}^{4}}-3{{x}^{3}}-3{{x}^{2}}+6x-2=\left( {{x}^{2}}-2 \right)\times \left( 2{{x}^{2}}-3x+1 \right)$.
Now, let us factorize $2{{x}^{2}}-3x+1$ to get the remaining zeros of $2{{x}^{4}}-3{{x}^{3}}-3{{x}^{2}}+6x-2$.
So, we get $2{{x}^{2}}-3x+1=2{{x}^{2}}-2x-x+1$.
$\Rightarrow 2{{x}^{2}}-3x+1=2x\left( x-1 \right)-1\left( x-1 \right)$.
$\Rightarrow 2{{x}^{2}}-3x+1=\left( 2x-1 \right)\left( x-1 \right)$.
So, we have found $2{{x}^{4}}-3{{x}^{3}}-3{{x}^{2}}+6x-2=\left( x-\sqrt{2} \right)\times \left( x+\sqrt{2} \right)\times \left( x-1 \right)\times \left( 2x-1 \right)$.
We know that zeroes are found when the given polynomial is equated to zero.
So, we get $\left( x-\sqrt{2} \right)\times \left( x+\sqrt{2} \right)\times \left( x-1 \right)\times \left( 2x-1 \right)=0$.
\[\Rightarrow x-\sqrt{2}=0\], $x+\sqrt{2}=0$, $x-1=0$, $2x-1=0$.
\[\Rightarrow x=\sqrt{2}\], $x=-\sqrt{2}$, $x=1$, $2x=1$.
\[\Rightarrow x=\sqrt{2}\], $x=-\sqrt{2}$, $x=1$, $x=\dfrac{1}{2}$.
∴ We have found the zeroes of the polynomial $2{{x}^{4}}-3{{x}^{3}}-3{{x}^{2}}+6x-2$ as $\sqrt{2}$, $-\sqrt{2}$, 1, $\dfrac{1}{2}$.
Note: We can solve the problem by performing trial and error method for the given polynomial. We can also solve this problem as shown below:
We are given the polynomial $2{{x}^{4}}-3{{x}^{3}}-3{{x}^{2}}+6x-2$ and two of the zeroes are $\sqrt{2}$ and $-\sqrt{2}$. Let us assume the remaining two zeroes are ‘p’ and ‘q’.
We know that the sum of the zeroes of the polynomial $a{{x}^{4}}+b{{x}^{3}}+c{{x}^{2}}+dx+e$ is $\dfrac{-b}{a}$ and product of the zeroes of the polynomial $a{{x}^{4}}+b{{x}^{3}}+c{{x}^{2}}+dx+e$ is $\dfrac{e}{a}$.
So, we get $\sqrt{2}-\sqrt{2}+p+q=\dfrac{-\left( -3 \right)}{2}$,
$\Rightarrow p+q=\dfrac{3}{2}$.
$\Rightarrow q=\dfrac{3}{2}-p$ ---(1).
Now, we have $\left( \sqrt{2} \right)\times \left( -\sqrt{2} \right)\times p\times q=\dfrac{-2}{2}$.
$\Rightarrow -2pq=-1$.
$\Rightarrow pq=\dfrac{1}{2}$ ---(2).
Let us substitute equation (1) in equation (2).
$\Rightarrow p\left( \dfrac{3}{2}-p \right)=\dfrac{1}{2}$.
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{3}{2}p-{{p}^{2}}=\dfrac{1}{2}$.
$\Rightarrow {{p}^{2}}-\dfrac{3}{2}p+\dfrac{1}{2}=0$.
$\Rightarrow {{p}^{2}}-\dfrac{1}{2}p-p+\dfrac{1}{2}=0$.
$\Rightarrow p\left( p-\dfrac{1}{2} \right)-1\left( p-\dfrac{1}{2} \right)=0$.
$\Rightarrow \left( p-1 \right)\left( p-\dfrac{1}{2} \right)=0$.
$\Rightarrow p-1=0$ or $p-\dfrac{1}{2}=0$.
$\Rightarrow p=1$ or $p=\dfrac{1}{2}$.
Let us substitute these values in equation (2) to get the values of ‘q’.
If $p=1$, then $1\times q=\dfrac{1}{2}\Leftrightarrow q=\dfrac{1}{2}$.
If $p=\dfrac{1}{2}$, then $\dfrac{1}{2}\times q=\dfrac{1}{2}\Leftrightarrow q=1$.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

A moving boat is observed from the top of a 150 m high class 10 maths CBSE




