
Find all rational numbers using a number line whose absolute value is $14$ .
Answer
585.3k+ views
Hint: Rational numbers are in the form$\dfrac{a}{b};b \ne 0$ . Any rational number can be reduced to an absolute value. Just take each value on line number as $b$ and find a rational number to that corresponding $b$ .
Complete step-by-step answer:
Step1: The process is to iterate through the number line and assume each entry as $b$ and find the required $a$ to make a rational number. As the denominator cannot be $0$ in a rational number hence we start with$1$ .
Suppose:
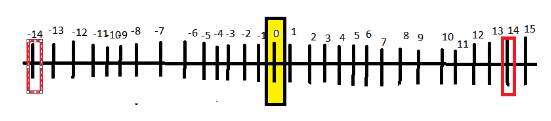
$\begin{align}
& b=1,a=14\times 1=14\text{ ; }\dfrac{14}{1} \\
& b=2,a=14\times 2=28;\text{ }\dfrac{28}{2} \\
& b=3,a=14\times 3=42;\text{ }\dfrac{42}{3} \\
\end{align}$
Similarly we can find all positive rational numbers.
To get a negative rational number we have to just put negative signs in both numerator and denominator.
$\dfrac{-14}{-1},\dfrac{-28}{-2},\dfrac{-42}{-3}$ And so on.
Additional Information: Absolute value of a rational number is nothing but the minimized or reduced value of a rational number. There may be infinite rational numbers with a single absolute value and hence we can just show some small set of numbers.
Note: Another method to solve this question is that we can find prime factors of absolute values and make rational numbers from that and to find all sets of rational numbers we have to just perform basic arithmetic operations on these rational numbers. One thing to be noted here is that the denominator of a rational number can never be zero because if the denominator becomes zero then the equation becomes undefined. Another thing we noted here is that there may be infinite possibility for a single absolute value but we will have equal numbers of negative and positive rational numbers. We can say that for each rational number for an absolute value we can have a corresponding negative rational number.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Step1: The process is to iterate through the number line and assume each entry as $b$ and find the required $a$ to make a rational number. As the denominator cannot be $0$ in a rational number hence we start with$1$ .
Suppose:

$\begin{align}
& b=1,a=14\times 1=14\text{ ; }\dfrac{14}{1} \\
& b=2,a=14\times 2=28;\text{ }\dfrac{28}{2} \\
& b=3,a=14\times 3=42;\text{ }\dfrac{42}{3} \\
\end{align}$
Similarly we can find all positive rational numbers.
To get a negative rational number we have to just put negative signs in both numerator and denominator.
$\dfrac{-14}{-1},\dfrac{-28}{-2},\dfrac{-42}{-3}$ And so on.
Additional Information: Absolute value of a rational number is nothing but the minimized or reduced value of a rational number. There may be infinite rational numbers with a single absolute value and hence we can just show some small set of numbers.
Note: Another method to solve this question is that we can find prime factors of absolute values and make rational numbers from that and to find all sets of rational numbers we have to just perform basic arithmetic operations on these rational numbers. One thing to be noted here is that the denominator of a rational number can never be zero because if the denominator becomes zero then the equation becomes undefined. Another thing we noted here is that there may be infinite possibility for a single absolute value but we will have equal numbers of negative and positive rational numbers. We can say that for each rational number for an absolute value we can have a corresponding negative rational number.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 8 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 8 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 8 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Master Class 8 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 8 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is BLO What is the full form of BLO class 8 social science CBSE

Citizens of India can vote at the age of A 18 years class 8 social science CBSE

Full form of STD, ISD and PCO

Advantages and disadvantages of science

Right to vote is a AFundamental Right BFundamental class 8 social science CBSE

What are the 12 elements of nature class 8 chemistry CBSE





