
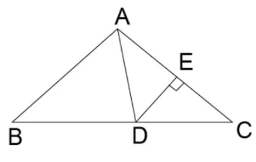
Find \[AD\] with the help of Apollonius theorem, where $ \Delta ABC $ is equilateral with side $ = 5cm $ .

Answer
533.1k+ views
Hint: To solve this problem we should know about the equilateral triangle and about the Apollonius theorem.
Equilateral triangle: The triangle having all sides are equal and all angles between the sides are equal.
Apollonius theorem: It states that the sum of the square of any two sides of any triangle equal twice the square on half the third side, together with twice the square on the median bisecting the third side.
Complete step by step solution:
As we have given in the question,
Here, $ AB = 5cm $ .
As it is an equilateral triangle. So all sides will be equal.
As by using Apollonius theorem. We can write it in mathematical form,
$ A{B^2} + A{C^2} = 2(A{D^2} + D{C^2}) $ ……………………… $ (1) $
As it is an equilateral triangle, $ AD $ bisect the base line $ BC $ .
So, $ DC = \dfrac{{BC}}{2} = \dfrac{5}{2} = 2.5cm $ .
Keeping values in $ (1) $ . We get,
$ \Rightarrow {5^2} + {5^2} = 2(A{D^2} + {2.5^2}) $
Further solving it. We get,
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{50}}{2} = A{D^2} + 6.25 $
Moving numerical term to one side,
$ \Rightarrow 25 - 6.25 = A{D^2} $
$ \Rightarrow 18.75 = A{D^2} $
By taking under-root on both side,
$ \Rightarrow \sqrt {18.75} = AD = 4.33 cm $
Hence, $ AD = 4.33cm $
So, the correct answer is “ $ AD = 4.33 cm $ ”.
Note: We can also solve this problem by simply using Pythagoras theorem. As it is an equilateral triangle the median will bisect the base line in the right angle. So, the equilateral triangle will change into a right-angle triangle and by using Pythagoras triangle we can easily calculate it.
Equilateral triangle: The triangle having all sides are equal and all angles between the sides are equal.
Apollonius theorem: It states that the sum of the square of any two sides of any triangle equal twice the square on half the third side, together with twice the square on the median bisecting the third side.
Complete step by step solution:
As we have given in the question,

Here, $ AB = 5cm $ .
As it is an equilateral triangle. So all sides will be equal.
As by using Apollonius theorem. We can write it in mathematical form,
$ A{B^2} + A{C^2} = 2(A{D^2} + D{C^2}) $ ……………………… $ (1) $
As it is an equilateral triangle, $ AD $ bisect the base line $ BC $ .
So, $ DC = \dfrac{{BC}}{2} = \dfrac{5}{2} = 2.5cm $ .
Keeping values in $ (1) $ . We get,
$ \Rightarrow {5^2} + {5^2} = 2(A{D^2} + {2.5^2}) $
Further solving it. We get,
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{50}}{2} = A{D^2} + 6.25 $
Moving numerical term to one side,
$ \Rightarrow 25 - 6.25 = A{D^2} $
$ \Rightarrow 18.75 = A{D^2} $
By taking under-root on both side,
$ \Rightarrow \sqrt {18.75} = AD = 4.33 cm $
Hence, $ AD = 4.33cm $
So, the correct answer is “ $ AD = 4.33 cm $ ”.
Note: We can also solve this problem by simply using Pythagoras theorem. As it is an equilateral triangle the median will bisect the base line in the right angle. So, the equilateral triangle will change into a right-angle triangle and by using Pythagoras triangle we can easily calculate it.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 8 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 8 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 8 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Master Class 8 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 8 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is BLO What is the full form of BLO class 8 social science CBSE

Citizens of India can vote at the age of A 18 years class 8 social science CBSE

Full form of STD, ISD and PCO

Advantages and disadvantages of science

Right to vote is a AFundamental Right BFundamental class 8 social science CBSE

What are the 12 elements of nature class 8 chemistry CBSE




