
Find a rational number between \[-\dfrac{4}{9}\] and\[\dfrac{6}{5}\].
Answer
586.5k+ views
Hint: In this given question, we have to find a rational number between two given numbers. Let us assume a number $N$ between two given numbers ($a$ and $b$).
As we know that between two rational numbers, there are infinite rational numbers, so one of them will be –
$N=\dfrac{a+b}{2}$ .
After getting $N$, we can calculate another number which lies between $N$ and $a$, or $N$ and $b$; and so on. By this method, we can calculate infinite rational numbers between $a$ and $b$.
Complete step by step answer:
Rational number: A number that can be represented as $\dfrac{p}{q}$, where both $p$ and $q$ are integers, and $q$ is not equal to zero. $\left( q\ne 0 \right)$
Example,$\dfrac{3}{7}$
$\dfrac{p}{q}=\dfrac{3}{7}$, where $p=3$ and $q=7$.
So, $\dfrac{3}{7}$ is a rational number.
Now, let us assume the given numbers as $a$ and $b$.
So, $a=-\dfrac{4}{9}$, $b=\dfrac{6}{5}$.
Let ${{N}_{1}},{{N}_{2}},{{N}_{3}}$ are rational numbers that lies between $a$ and $b$. So these can be represented on number line as below:
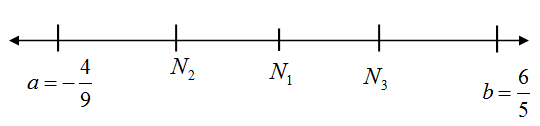
Now let ${{N}_{1}}$ is the first rational number between $a$ and $b$.
$N=\dfrac{a+b}{2}$
$a=-\dfrac{4}{9}$ , $b=\dfrac{6}{5}$
$\Rightarrow {{N}_{1}}=\dfrac{-\dfrac{4}{9}+\dfrac{6}{5}}{2}$
$\Rightarrow {{N}_{1}}=\dfrac{1}{2}\left( \dfrac{-20+54}{45} \right)$
$\Rightarrow {{N}_{1}}=\dfrac{1}{2}\left( \dfrac{34}{45} \right)$
$\Rightarrow {{N}_{1}}=\dfrac{17}{45}$
Now, let ${{N}_{2}}$ is the rational number between $a$ and ${{N}_{1}}$.
\[{{N}_{2}}=\dfrac{a+{{N}_{1}}}{2}\]
$a=-\dfrac{4}{9}$ , ${{N}_{1}}=\dfrac{17}{45}$
$\Rightarrow {{N}_{2}}=\dfrac{1}{2}\left( -\dfrac{4}{9}+\dfrac{17}{45} \right)$
$\Rightarrow {{N}_{2}}=\dfrac{1}{2}\left( \dfrac{-20+17}{45} \right)$
$\Rightarrow {{N}_{2}}=\dfrac{1}{2}\left( \dfrac{-3}{45} \right)$
$\Rightarrow {{N}_{2}}=\dfrac{-1}{30}$
Now let ${{N}_{3}}$ be the first rational number between ${{N}_{1}}$ and $b$.
\[{{N}_{3}}=\dfrac{{{N}_{1}}+b}{2}\]
$b=\dfrac{6}{5}$ , ${{N}_{1}}=\dfrac{17}{45}$
$\Rightarrow {{N}_{3}}=\dfrac{1}{2}\left( \dfrac{17}{45}+\dfrac{6}{5} \right)$
$\Rightarrow {{N}_{3}}=\dfrac{1}{2}\left( \dfrac{17+54}{45} \right)$
$\Rightarrow {{N}_{3}}=\dfrac{71}{2\times 45}$
$\Rightarrow {{N}_{3}}=\dfrac{71}{90}$
Hence, ${{N}_{1}}=\dfrac{17}{45}$ , ${{N}_{2}}=\dfrac{-1}{30}$ and ${{N}_{3}}=\dfrac{71}{90}$ are the three rational numbers between \[-\dfrac{4}{9}\] and \[\dfrac{6}{5}\].
Note: This question can be solved by another method. We have to get rational numbers between \[-\dfrac{4}{9}\] and\[\dfrac{6}{5}\]. Firstly, take LCM of denominators of both the numbers, and then by multiplying the suitable number, make the denominator equal for both numbers.
\[-\dfrac{4}{9}\] and \[\dfrac{6}{5}\]
LCM $\left( 9,5 \right)=45$
So,
$-\dfrac{4}{9}\times \dfrac{5}{5}$ and $\dfrac{6}{5}\times \dfrac{9}{9}$
\[~-\dfrac{20}{45}\] and $\dfrac{54}{45}$
Now when both denominators are equal, take any integer between numerators of both numbers. The rational number that you get will be between the given numbers.
\[~-\dfrac{20}{45}\] and $\dfrac{54}{45}$
So let’s take $-15,12$ and $36$.
Thus, $-\dfrac{15}{45},\dfrac{12}{45}$ and $\dfrac{36}{45}$are in between $-\dfrac{4}{9}$ and $\dfrac{6}{5}$.
Hence, $-\dfrac{1}{3},\dfrac{4}{15}$ and $\dfrac{4}{5}$ are in between $-\dfrac{4}{9}$ and $\dfrac{6}{5}$.
(ii) Students should take care of calculation in addition to rational numbers and then divide by $2$. Many students forget to divide by $2$.
As we know that between two rational numbers, there are infinite rational numbers, so one of them will be –
$N=\dfrac{a+b}{2}$ .
After getting $N$, we can calculate another number which lies between $N$ and $a$, or $N$ and $b$; and so on. By this method, we can calculate infinite rational numbers between $a$ and $b$.
Complete step by step answer:
Rational number: A number that can be represented as $\dfrac{p}{q}$, where both $p$ and $q$ are integers, and $q$ is not equal to zero. $\left( q\ne 0 \right)$
Example,$\dfrac{3}{7}$
$\dfrac{p}{q}=\dfrac{3}{7}$, where $p=3$ and $q=7$.
So, $\dfrac{3}{7}$ is a rational number.
Now, let us assume the given numbers as $a$ and $b$.
So, $a=-\dfrac{4}{9}$, $b=\dfrac{6}{5}$.
Let ${{N}_{1}},{{N}_{2}},{{N}_{3}}$ are rational numbers that lies between $a$ and $b$. So these can be represented on number line as below:

Now let ${{N}_{1}}$ is the first rational number between $a$ and $b$.
$N=\dfrac{a+b}{2}$
$a=-\dfrac{4}{9}$ , $b=\dfrac{6}{5}$
$\Rightarrow {{N}_{1}}=\dfrac{-\dfrac{4}{9}+\dfrac{6}{5}}{2}$
$\Rightarrow {{N}_{1}}=\dfrac{1}{2}\left( \dfrac{-20+54}{45} \right)$
$\Rightarrow {{N}_{1}}=\dfrac{1}{2}\left( \dfrac{34}{45} \right)$
$\Rightarrow {{N}_{1}}=\dfrac{17}{45}$
Now, let ${{N}_{2}}$ is the rational number between $a$ and ${{N}_{1}}$.
\[{{N}_{2}}=\dfrac{a+{{N}_{1}}}{2}\]
$a=-\dfrac{4}{9}$ , ${{N}_{1}}=\dfrac{17}{45}$
$\Rightarrow {{N}_{2}}=\dfrac{1}{2}\left( -\dfrac{4}{9}+\dfrac{17}{45} \right)$
$\Rightarrow {{N}_{2}}=\dfrac{1}{2}\left( \dfrac{-20+17}{45} \right)$
$\Rightarrow {{N}_{2}}=\dfrac{1}{2}\left( \dfrac{-3}{45} \right)$
$\Rightarrow {{N}_{2}}=\dfrac{-1}{30}$
Now let ${{N}_{3}}$ be the first rational number between ${{N}_{1}}$ and $b$.
\[{{N}_{3}}=\dfrac{{{N}_{1}}+b}{2}\]
$b=\dfrac{6}{5}$ , ${{N}_{1}}=\dfrac{17}{45}$
$\Rightarrow {{N}_{3}}=\dfrac{1}{2}\left( \dfrac{17}{45}+\dfrac{6}{5} \right)$
$\Rightarrow {{N}_{3}}=\dfrac{1}{2}\left( \dfrac{17+54}{45} \right)$
$\Rightarrow {{N}_{3}}=\dfrac{71}{2\times 45}$
$\Rightarrow {{N}_{3}}=\dfrac{71}{90}$
Hence, ${{N}_{1}}=\dfrac{17}{45}$ , ${{N}_{2}}=\dfrac{-1}{30}$ and ${{N}_{3}}=\dfrac{71}{90}$ are the three rational numbers between \[-\dfrac{4}{9}\] and \[\dfrac{6}{5}\].
Note: This question can be solved by another method. We have to get rational numbers between \[-\dfrac{4}{9}\] and\[\dfrac{6}{5}\]. Firstly, take LCM of denominators of both the numbers, and then by multiplying the suitable number, make the denominator equal for both numbers.
\[-\dfrac{4}{9}\] and \[\dfrac{6}{5}\]
LCM $\left( 9,5 \right)=45$
So,
$-\dfrac{4}{9}\times \dfrac{5}{5}$ and $\dfrac{6}{5}\times \dfrac{9}{9}$
\[~-\dfrac{20}{45}\] and $\dfrac{54}{45}$
Now when both denominators are equal, take any integer between numerators of both numbers. The rational number that you get will be between the given numbers.
\[~-\dfrac{20}{45}\] and $\dfrac{54}{45}$
So let’s take $-15,12$ and $36$.
Thus, $-\dfrac{15}{45},\dfrac{12}{45}$ and $\dfrac{36}{45}$are in between $-\dfrac{4}{9}$ and $\dfrac{6}{5}$.
Hence, $-\dfrac{1}{3},\dfrac{4}{15}$ and $\dfrac{4}{5}$ are in between $-\dfrac{4}{9}$ and $\dfrac{6}{5}$.
(ii) Students should take care of calculation in addition to rational numbers and then divide by $2$. Many students forget to divide by $2$.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 9 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 9 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Trending doubts
Difference Between Plant Cell and Animal Cell

Fill the blanks with the suitable prepositions 1 The class 9 english CBSE

Who is eligible for RTE class 9 social science CBSE

Which places in India experience sunrise first and class 9 social science CBSE

What is pollution? How many types of pollution? Define it

Name 10 Living and Non living things class 9 biology CBSE




