
Find ‘A’ and ‘B’ in the given reaction sequence.
$ C{H_3} - C \equiv CH\xrightarrow[{{\text{liq}}{\text{. N}}{{\text{H}}_3}}]{{{\text{Na}}}}(A)\xrightarrow{{{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_3}{\text{Cl}}}}(B) $
Answer
509.1k+ views
Hint : When an alkyne reacts with sodium in liquid ammonia, it reduces to give a trans alkene. The reduction of alkynes with sodium in liquid ammonia is complementary i.e., opposite to the catalytic hydrogenation of alkynes in which cis alkene is obtained as a product. The intermediate involved in this reduction reaction is radical anion.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
For the given reaction sequence, the structure of compound A in the given reaction will be as follows:
$ C{H_3} - C \equiv CH\xrightarrow[{{\text{liq}}{\text{. N}}{{\text{H}}_3}}]{{{\text{2Na}}}}C{H_3} - CH = C{H_2} + 2NaN{H_2} $
The mechanism for the reaction is given as follows:
Step-1: Sodium metal transfers an electron to the alkyne and formation of a radical-anion takes place. The reaction proceeds as follows:
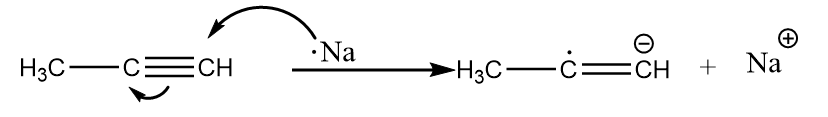
Step-2: The radical anion formed in the previous step attacks the ammonia molecule and removes the proton to undergo acid-base reaction. The reaction proceeds as follows:
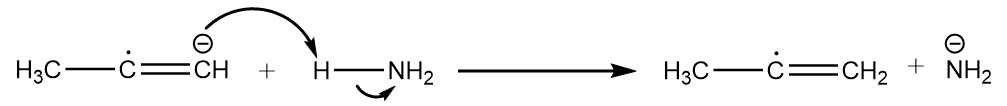
Step-3: Now, the second atom of sodium shares its electrons to the radical and formation of carbanion takes place. The reaction proceeds as follows:
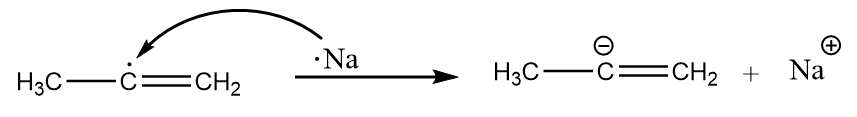
Step-4: The carbanion removes the proton from ammonia to give respective alkene. The reaction takes place as follows:
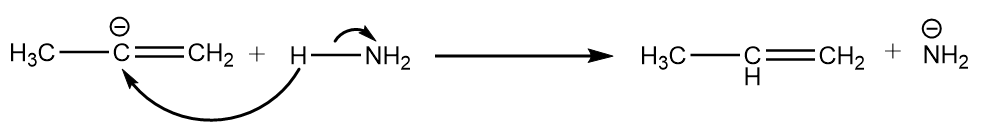
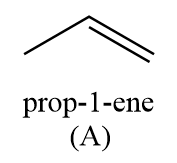
Hence, the compound ‘A’ formed is prop-1-ene.
On further reaction of A with chloromethane, the structure of B formed will be as follows:
$ C{H_3} - CH = C{H_2}\xrightarrow{{{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_3}{\text{Cl}}}}C{H_3} - CH = CH - C{H_3} $
The mechanism for the reaction is as follows:
Step-1: $ NaN{H_2} $ acts as a base and extracts acidic hydrogen from prop-1-ene and forms an intermediate along with the removal of ammonia. The reaction takes place as follows:
$ C{H_3} - CH = C{H_2} + NaN{H_2} \to C{H_3} - CH = CHNa + N{H_3} $
Step-2: The intermediate formed in the previous step reacts with chloromethane and formation of but-2-ene takes place along with the removal of sodium chloride. The reaction takes place as follows:
$ C{H_3} - CH = CHNa + C{H_3}Cl \to C{H_3} - CH = CH - C{H_3} + NaCl $
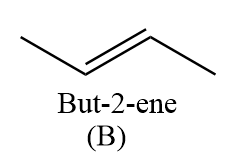
Hence, the compound ‘B’ formed is but-2-ene.
Thus, we can conclude that in the given reaction sequence, the structure of ‘A’ and ‘B’ are as follows:
Note :
Remember that ordinary alkene does not react with solvated electrons or does not form a stable radical anion, so the reaction stops at the trans alkene stage i.e., no further reduction takes place after formation of the respective alkene.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
For the given reaction sequence, the structure of compound A in the given reaction will be as follows:
$ C{H_3} - C \equiv CH\xrightarrow[{{\text{liq}}{\text{. N}}{{\text{H}}_3}}]{{{\text{2Na}}}}C{H_3} - CH = C{H_2} + 2NaN{H_2} $
The mechanism for the reaction is given as follows:
Step-1: Sodium metal transfers an electron to the alkyne and formation of a radical-anion takes place. The reaction proceeds as follows:

Step-2: The radical anion formed in the previous step attacks the ammonia molecule and removes the proton to undergo acid-base reaction. The reaction proceeds as follows:
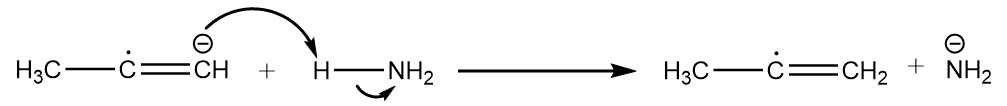
Step-3: Now, the second atom of sodium shares its electrons to the radical and formation of carbanion takes place. The reaction proceeds as follows:

Step-4: The carbanion removes the proton from ammonia to give respective alkene. The reaction takes place as follows:

Hence, the compound ‘A’ formed is prop-1-ene.
On further reaction of A with chloromethane, the structure of B formed will be as follows:
$ C{H_3} - CH = C{H_2}\xrightarrow{{{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_3}{\text{Cl}}}}C{H_3} - CH = CH - C{H_3} $
The mechanism for the reaction is as follows:
Step-1: $ NaN{H_2} $ acts as a base and extracts acidic hydrogen from prop-1-ene and forms an intermediate along with the removal of ammonia. The reaction takes place as follows:
$ C{H_3} - CH = C{H_2} + NaN{H_2} \to C{H_3} - CH = CHNa + N{H_3} $
Step-2: The intermediate formed in the previous step reacts with chloromethane and formation of but-2-ene takes place along with the removal of sodium chloride. The reaction takes place as follows:
$ C{H_3} - CH = CHNa + C{H_3}Cl \to C{H_3} - CH = CH - C{H_3} + NaCl $
Hence, the compound ‘B’ formed is but-2-ene.
Thus, we can conclude that in the given reaction sequence, the structure of ‘A’ and ‘B’ are as follows:


Note :
Remember that ordinary alkene does not react with solvated electrons or does not form a stable radical anion, so the reaction stops at the trans alkene stage i.e., no further reduction takes place after formation of the respective alkene.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




