
Fill the blanks in the following equation
\[~~~A-\text{ }(B\cup C\cup D)\text{ }=\text{ }\left( A-B \right)\cap \ldots .\cap \ldots ..\]
Answer
576.9k+ views
Hint: As we know that the Venn diagram for four sets is so complicated we are going to check what the answer will be when we take it as two and three sets and then we can get the answer for four sets. Check first for 2 sets and then check for three sets using the Venn diagram.
Complete step by step answer:
So let us first take two sets i.e. A and B ;
Which implies the question will be A-B and this is equal to A-B which is the same.
Now coming to the next three sets i.e. A, B, C ;
Which implies the question will be \[A-\text{ }(B\cup C)\text{ }=\text{ }\left( A-B \right)\cap \ldots .\]
Now we will find what the value of the question is.. using a Venn diagram for 3 sets.
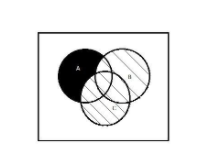
The above diagram is a Venn diagram of 3 sets A, B, C.
We know that the part with lines is \[(B\cup C)\] which implies the shaded part(that is the region that is painted with dark black color ) will be \[A-\text{ }(B\cup C)\]
It can be clearly told that the shaded part will also be equal to intersection of (A-C) and (A-B)
which implies \[A-\text{ }(B\cup C)\text{ }=\text{ }\left( A-B \right)\cap \left( A-C \right)\]
From this iteration we can easily say that for four sets \[A-\text{ }(B\cup C\cup \text{ }D)\text{ }=\text{ }\left( A-B \right)\cap \left( A-C \right)\cap \left( A-D \right)\]
So the terms that are to be filled in the question are \[\left( A-C \right)\text{ }and\text{ }\left( A-D \right).\]
Note:
While solving questions involving intersection and union of sets it is always better to solve it using a venn diagram representing the sets. Questions of this kind can also be solved using direct usage of laws of sets but it might make the problem lengthier to solve. $A-\left( B\cap C \right)$ represents the space that excludes intersection of B and C from A.
Complete step by step answer:
So let us first take two sets i.e. A and B ;
Which implies the question will be A-B and this is equal to A-B which is the same.
Now coming to the next three sets i.e. A, B, C ;
Which implies the question will be \[A-\text{ }(B\cup C)\text{ }=\text{ }\left( A-B \right)\cap \ldots .\]
Now we will find what the value of the question is.. using a Venn diagram for 3 sets.

The above diagram is a Venn diagram of 3 sets A, B, C.
We know that the part with lines is \[(B\cup C)\] which implies the shaded part(that is the region that is painted with dark black color ) will be \[A-\text{ }(B\cup C)\]
It can be clearly told that the shaded part will also be equal to intersection of (A-C) and (A-B)
which implies \[A-\text{ }(B\cup C)\text{ }=\text{ }\left( A-B \right)\cap \left( A-C \right)\]
From this iteration we can easily say that for four sets \[A-\text{ }(B\cup C\cup \text{ }D)\text{ }=\text{ }\left( A-B \right)\cap \left( A-C \right)\cap \left( A-D \right)\]
So the terms that are to be filled in the question are \[\left( A-C \right)\text{ }and\text{ }\left( A-D \right).\]
Note:
While solving questions involving intersection and union of sets it is always better to solve it using a venn diagram representing the sets. Questions of this kind can also be solved using direct usage of laws of sets but it might make the problem lengthier to solve. $A-\left( B\cap C \right)$ represents the space that excludes intersection of B and C from A.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




