
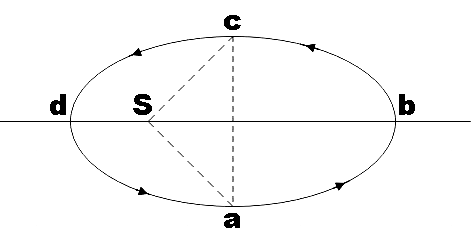
Figure shows elliptical path $abcd$ of a planet around the sun such that the area of triangle $csa$ is $\dfrac{1}{4}$ the area of the ellipse (see figure). With db as the semi-major axis, and ca as the semi minor axis, if ${{t}_{1}}$ is the time taken for planet to go over path $abc$ and ${{t}_{2}}$ for path taken over $cda$, then,
A. ${{t}_{1}}=4{{t}_{2}}$
B.${{t}_{1}}=2{{t}_{2}}$
C.${{t}_{1}}=3{{t}_{2}}$
D.${{t}_{1}}={{t}_{2}}$

Answer
571.8k+ views
Hint: As a first step you could recall Kepler’s second law of planetary motion. Now you could find the area swept by the planet for traveling from $a$ to c through b and the area swept by the planet when it moves from c to a through d. Then by applying the law, you will get the required relation between the time periods.
Complete step by step answer:
Figure shows elliptical path $abcd$ of a planet around the sun such that the area of triangle $csa$ is $\dfrac{1}{4}$ the area of the ellipse (see figure). With db as the semi-major axis, and ca as the semi minor axis, if ${{t}_{1}}$ is the time taken for planet to go over path $abc$ and ${{t}_{2}}$ for path taken over $cda$, then,
In the question, we are given an elliptical path $abcd$ of some planet around the sun such that the area of the triangle $csa$ marked in the given figure is one-fourth the whole area of the ellipse. We are asked to find the time taken to cover $cda$ in terms of time taken to cover the path $abc$.
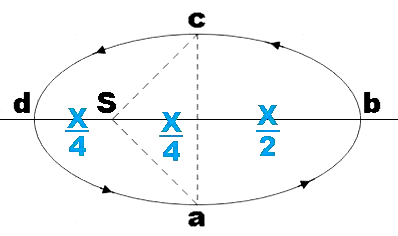
Let the total area of the ellipse be X, then the area of the triangle marked in the given figure will be, $\dfrac{x}{4}$
We have a semi-ellipse $abc$, whose area will be $\dfrac{X}{2}$ and in the left half, the area excluding the triangle part will be, $\dfrac{X}{4}$
Now, let us recall Kepler’s second law. This law states that the imaginary line connecting a planet and the sun sweeps out equal areas in equal interval of time or simply, areal velocity of the planet around the sun is a constant, that is,
${{v}_{A}}=\dfrac{A}{t}=k$
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{{{A}_{1}}}{{{t}_{1}}}=\dfrac{{{A}_{2}}}{{{t}_{2}}}$ ………………………. (1)
From the figure, ${{A}_{1}}$ is the area swept by the planet traveling from $a$ to c through b and ${{A}_{2}}$ is the area swept by the planet when it moves from c to a through d.
${{A}_{2}}=\dfrac{X}{4}$ …………………………………… (2)
${{A}_{1}}=\dfrac{X}{2}+\dfrac{X}{4}=\dfrac{3X}{4}$ ………………………… (3)
Substituting (2) and (3) in (1), we get,
$\dfrac{\left( \dfrac{3X}{4} \right)}{{{t}_{1}}}=\dfrac{\left( \dfrac{X}{4} \right)}{{{t}_{2}}}$
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{3}{{{t}_{1}}}=\dfrac{1}{{{t}_{2}}}$
$\therefore {{t}_{1}}=3{{t}_{2}}$
Therefore, we found the required relation to be ${{t}_{1}}=3{{t}_{2}}$.
So, the correct answer is “Option C”.
Note: Other than the law used in solving this question, we have two other Kepler’s laws for planetary motion. The first law is called the law of elliptical orbit which states that every planet moves around in an elliptical orbit with the sun at one of its focus. Then the other law is called the law of harmonics which states that the square of the time period of a planet is directly proportional to the cube of its orbital radius.
Complete step by step answer:
Figure shows elliptical path $abcd$ of a planet around the sun such that the area of triangle $csa$ is $\dfrac{1}{4}$ the area of the ellipse (see figure). With db as the semi-major axis, and ca as the semi minor axis, if ${{t}_{1}}$ is the time taken for planet to go over path $abc$ and ${{t}_{2}}$ for path taken over $cda$, then,
In the question, we are given an elliptical path $abcd$ of some planet around the sun such that the area of the triangle $csa$ marked in the given figure is one-fourth the whole area of the ellipse. We are asked to find the time taken to cover $cda$ in terms of time taken to cover the path $abc$.
Let the total area of the ellipse be X, then the area of the triangle marked in the given figure will be, $\dfrac{x}{4}$
We have a semi-ellipse $abc$, whose area will be $\dfrac{X}{2}$ and in the left half, the area excluding the triangle part will be, $\dfrac{X}{4}$

Now, let us recall Kepler’s second law. This law states that the imaginary line connecting a planet and the sun sweeps out equal areas in equal interval of time or simply, areal velocity of the planet around the sun is a constant, that is,
${{v}_{A}}=\dfrac{A}{t}=k$
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{{{A}_{1}}}{{{t}_{1}}}=\dfrac{{{A}_{2}}}{{{t}_{2}}}$ ………………………. (1)
From the figure, ${{A}_{1}}$ is the area swept by the planet traveling from $a$ to c through b and ${{A}_{2}}$ is the area swept by the planet when it moves from c to a through d.
${{A}_{2}}=\dfrac{X}{4}$ …………………………………… (2)
${{A}_{1}}=\dfrac{X}{2}+\dfrac{X}{4}=\dfrac{3X}{4}$ ………………………… (3)
Substituting (2) and (3) in (1), we get,
$\dfrac{\left( \dfrac{3X}{4} \right)}{{{t}_{1}}}=\dfrac{\left( \dfrac{X}{4} \right)}{{{t}_{2}}}$
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{3}{{{t}_{1}}}=\dfrac{1}{{{t}_{2}}}$
$\therefore {{t}_{1}}=3{{t}_{2}}$
Therefore, we found the required relation to be ${{t}_{1}}=3{{t}_{2}}$.
So, the correct answer is “Option C”.
Note: Other than the law used in solving this question, we have two other Kepler’s laws for planetary motion. The first law is called the law of elliptical orbit which states that every planet moves around in an elliptical orbit with the sun at one of its focus. Then the other law is called the law of harmonics which states that the square of the time period of a planet is directly proportional to the cube of its orbital radius.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




