
Figure shows a part of an electric circuit. The potentials at the points a, b and c are 30V, 12V and 2V respectively. Find the currents through the three resistors.
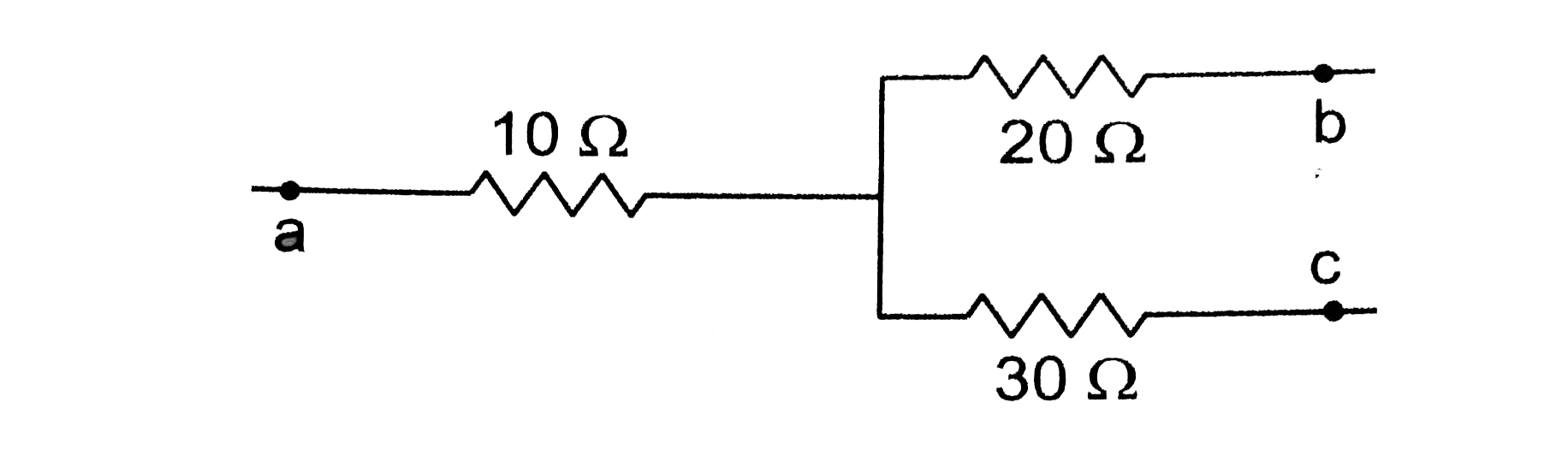
Answer
502.2k+ views
Hint :To answer this question, we first need to understand what an electric circuit is. A channel for transmitting electric current is known as an electric circuit. An electric circuit consists of a device, such as a battery or a generator, that provides energy to the charged particles that make up the current; equipment that uses current, such as lamps, electric motors, or computers; and the connecting wires or transmission lines.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
KVL- Kirchhoff's circuit rules are two equalities in the lumped element model of electrical circuits that deal with current and potential difference. Gustav Kirchhoff, a German physicist, was the first to describe them in 1845. This broadened Georg Ohm's work and came before James Clerk Maxwell's.
KCL- Kirchhoff's circuit rules are two equalities in the lumped element model of electrical circuits that deal with current and potential difference. Gustav Kirchhoff, a German physicist, was the first to describe them in 1845. This broadened Georg Ohm's work and came before James Clerk Maxwell's.
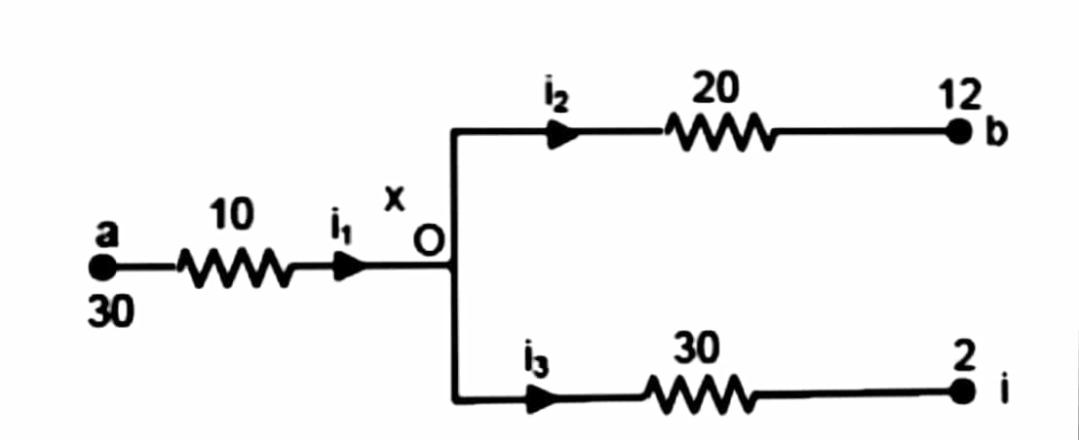
Let us assume that potential at O is V volts.
Applying ohm's law at each branch –
$ (30 - V) = 10{i_1} $
$ (V - 12) = 20{i_2} $
$ (V - 2) = 30{i_3} $
And by KCL we know that at point O
$ {i_1} = {i_2} + {i_3} $
Putting values
$ \dfrac{{30 - V}}{{10}} = \dfrac{{V - 12}}{{20}} + \dfrac{{V - 2}}{{30}} $
$ 30 - V = \dfrac{{V - 12}}{2} + \dfrac{{V - 2}}{3} $
$ 30 - V = \dfrac{{3V - 36 + 2V - 4}}{6} $
$ 180 - 6V = 5V - 40 $
$ 11V = 220 $
$ V = 20volts $
Putting values in current equations of each branch
So the final values of current are -
$ {i_1} = \dfrac{{30 - 20}}{{10}} = 1A \\
{i_2} = \dfrac{{20 - 12}}{{20}} = 0.4A \\
{i_3} = \dfrac{{20 - 2}}{{30}} = 0.6A $
Note :
Circuit analysis of more complex circuits is possible thanks to Kirchhoff's two laws. The technique is simple, despite the fact that the algebraic procedures are still somewhat complicated. These laws are widely used in the field of electrical engineering.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
KVL- Kirchhoff's circuit rules are two equalities in the lumped element model of electrical circuits that deal with current and potential difference. Gustav Kirchhoff, a German physicist, was the first to describe them in 1845. This broadened Georg Ohm's work and came before James Clerk Maxwell's.
KCL- Kirchhoff's circuit rules are two equalities in the lumped element model of electrical circuits that deal with current and potential difference. Gustav Kirchhoff, a German physicist, was the first to describe them in 1845. This broadened Georg Ohm's work and came before James Clerk Maxwell's.

Let us assume that potential at O is V volts.
Applying ohm's law at each branch –
$ (30 - V) = 10{i_1} $
$ (V - 12) = 20{i_2} $
$ (V - 2) = 30{i_3} $
And by KCL we know that at point O
$ {i_1} = {i_2} + {i_3} $
Putting values
$ \dfrac{{30 - V}}{{10}} = \dfrac{{V - 12}}{{20}} + \dfrac{{V - 2}}{{30}} $
$ 30 - V = \dfrac{{V - 12}}{2} + \dfrac{{V - 2}}{3} $
$ 30 - V = \dfrac{{3V - 36 + 2V - 4}}{6} $
$ 180 - 6V = 5V - 40 $
$ 11V = 220 $
$ V = 20volts $
Putting values in current equations of each branch
So the final values of current are -
$ {i_1} = \dfrac{{30 - 20}}{{10}} = 1A \\
{i_2} = \dfrac{{20 - 12}}{{20}} = 0.4A \\
{i_3} = \dfrac{{20 - 2}}{{30}} = 0.6A $
Note :
Circuit analysis of more complex circuits is possible thanks to Kirchhoff's two laws. The technique is simple, despite the fact that the algebraic procedures are still somewhat complicated. These laws are widely used in the field of electrical engineering.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




